Bulgaria facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of Bulgaria
|
|
|---|---|
![Location of Bulgaria (dark green)– on the European continent (green & dark grey)– in the European Union (green) — [Legend]](/images/thumb/e/e9/EU-Bulgaria.svg/250px-EU-Bulgaria.svg.png)
Location of Bulgaria (dark green)
– on the European continent (green & dark grey) |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Sofia 42°41′51″N 23°19′21″E / 42.69750°N 23.32250°E |
| Official languages | Bulgarian |
| Official script | Cyrillic |
| Ethnic groups
(2021 census)
|
|
| Religion
(2021 census)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic |
| Iliana Iotova | |
| Rosen Zhelyazkov | |
|
• Chairperson of the National Assembly
|
Natalia Kiselova |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Establishment history | |
| 681–1018 | |
| 1185–1396 | |
| 3 March 1878 | |
|
• Independence from the Ottoman Empire
|
5 October 1908 |
|
• Monarchy abolished
|
15 September 1946 |
| 15 November 1990 | |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
110,993.6 km2 (42,854.9 sq mi) (103rd) |
|
• Water (%)
|
2.16 |
| Population | |
|
• December 2024 estimate
|
6,437,360 (109th) |
|
• 2022 census
|
6,447,710 |
|
• Density
|
58/km2 (150.2/sq mi) (154th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2023) | ▼ 37.2 medium |
| HDI (2023) | very high · 55th |
| Currency | Euro (€) (EUR) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Calling code | +359 |
| ISO 3166 code | BG |
| Internet TLD |
|
Bulgaria, officially known as the Republic of Bulgaria, is a fascinating country in Southeast Europe. It sits on the eastern part of the Balkan Peninsula, south of the Danube River and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria shares borders with Greece, Turkey, Serbia, North Macedonia, and Romania. It covers about 110,994 square kilometers, making it the tenth largest country in the European Union. Sofia is Bulgaria's capital and largest city. Other important cities are Burgas, Plovdiv, and Varna.
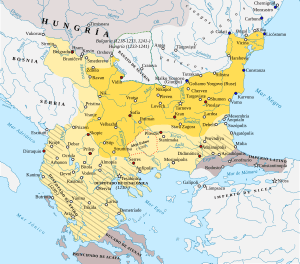
The land where Bulgaria is today has a very long history. One of the first groups of people lived there around 6,500 BC. Over many centuries, different ancient groups like the Thracians and Romans lived and fought in this area. Around the 6th century, the early Slavs settled here. Later, in the late 7th century, a group called the Bulgars, led by Asparuh, arrived. They created the First Bulgarian Empire in 681 AD. This empire became very powerful and helped create the Cyrillic script, which is still used today. After a long time, the Byzantine Empire conquered the First Bulgarian Empire. But in 1185, a new Second Bulgarian Empire was formed. It grew strong under leaders like Ivan Asen II. Eventually, this empire also faced challenges and fell under the rule of the Ottoman Empire in 1396, which lasted for almost 500 years.
In 1878, after a war, the third Bulgarian state was formed. It declared full independence from the Ottoman Empire in 1908. In the 20th century, Bulgaria was involved in both world wars. After World War II, in 1946, Bulgaria became a socialist state. This period ended in 1989, when the country began its journey to become a democracy.
Since 1991, Bulgaria has been a parliamentary republic with 28 regions called provinces. Its economy is strong and focuses on services, manufacturing, mining, and agriculture. Bulgaria is important for natural gas and oil pipelines because of its location near the Black Sea. Today, Bulgaria is a member of the European Union and NATO. It also belongs to the Schengen Area and the eurozone.
Contents
Exploring Bulgaria's Past
What's in a Name? The Origin of "Bulgaria"
The name Bulgaria comes from the Bulgars. They were a group of people who founded the First Bulgarian Empire. Historians believe their name might come from an old word meaning "to mix" or "to stir." This could refer to them being "disturbers" or a "mixed group" of people.
Ancient Times and Early Settlements

The earliest signs of human life in Bulgaria date back about 150,000 years. Around 6,500 BC, the Karanovo culture thrived here, known for its farming. The Varna culture (around 5,000 BC) was famous for creating the world's oldest golden jewelry. This treasure helps us understand ancient societies.
The Thracians were an important ancient group in the Balkans. They were skilled metalworkers. The Roman Empire took control of the region in 45 AD. Later, around the 6th century, Slavic tribes settled in these lands.
The First Bulgarian Empire: A Powerful Beginning
In 680 AD, the Bulgars, led by Khan Asparukh, arrived and formed the First Bulgarian Empire. This empire was officially recognized by the Byzantine Empire in 681 AD. It became a major power in the Balkans.
Under leaders like Krum and Boris I, Bulgaria grew stronger. Boris I made Eastern Orthodox Christianity the official religion in 864. The Cyrillic alphabet was developed in the capital, Preslav. This alphabet helped unite the Slavs and Bulgars. A "golden age" of culture and power began under Simeon the Great. The First Bulgarian Empire lasted until 1018, when the Byzantines conquered it.
The Second Bulgarian Empire: A New Era
After some time, a new Bulgarian state was formed in 1185 by nobles Ivan Asen I and Peter IV. This was the Second Bulgarian Empire, with its capital at Tarnovo. It reached its peak under Ivan Asen II (1218–1241), expanding its borders and seeing culture flourish.
However, after many conflicts, the empire weakened. By the 14th century, it broke into smaller parts. These smaller states were then conquered by the Ottoman Turks.
Ottoman Rule: A Long Period of Change
The Ottomans completed their conquest of Bulgarian lands by 1396. This began a period of nearly five centuries of Ottoman rule. During this time, Bulgarians faced new taxes and their culture was suppressed.
As the Ottoman Empire weakened, other European powers like Austria and Russia became interested in helping Bulgarian Christians. This led to several uprisings. The Russo-Turkish War of 1877–78 finally brought an end to Ottoman rule in Bulgaria.
The Third Bulgarian State: Modern Bulgaria
The Treaty of San Stefano in 1878 created an autonomous Bulgarian principality. However, other European powers changed these borders with the Treaty of Berlin. This created a smaller Principality of Bulgaria. Bulgaria declared full independence from the Ottoman Empire on 5 October 1908. This day is now a national holiday.
In the early 20th century, Bulgaria was involved in several conflicts, including two Balkan Wars and World War I. After World War I, Tsar Boris III ruled the country. Bulgaria joined the Axis powers in World War II but saved its Jewish population from concentration camps.
After World War II, in 1946, Bulgaria became a socialist state under Soviet influence. This period saw rapid industrial growth. In 1989, the Communist Party gave up its power, and Bulgaria began its transition to a democracy.
Since 1991, Bulgaria has adopted a democratic constitution. It joined NATO in 2004 and the European Union in 2007. Bulgaria continues to work on improving its economy and society.
Bulgaria's Geography and Natural Wonders
Landforms and Rivers
Bulgaria is a medium-sized country in Southeast Europe. Its land borders are about 1,808 kilometers long, and its Black Sea coastline is 354 kilometers long. Key features include the Danubian Plain, the Balkan Mountains, the Upper Thracian Plain, and the Rila-Rhodope mountain range.
The Balkan Mountains stretch across the middle of the country. In the southwest, the Rila and Pirin mountains are very high. Musala, at 2,925 meters, is the highest point in Bulgaria and the Balkans. Plains cover about one-third of the country. Most rivers are short, but the Iskar is the longest entirely within Bulgaria.
Climate: Seasons and Weather
Bulgaria has a varied climate due to its location between Mediterranean and continental air masses. Northern Bulgaria is generally cooler and wetter than the south. Temperatures can range from very cold (-38.3°C) to very hot (45.2°C).
The country experiences significant snowfall in winter. The Mediterranean influence brings hot, dry weather in late summer. Bulgaria has five main climate zones, from continental in the north to alpine in the high mountains.
Biodiversity and Conservation: Protecting Nature

Bulgaria has rich biodiversity, with many plant and animal species. It has three national parks, 11 nature parks, and 10 biosphere reserves. You can find 93 mammal species and 49% of Europe's butterfly species here.
Large mammals include deer, wild boar, golden jackals, and red foxes. Over 3,800 plant species grow in Bulgaria, with 170 found only here. Forests cover about 36% of the country's land. Bulgaria is working to protect its ecosystems and endangered species.
How Bulgaria is Governed
Understanding Bulgaria's Government

Bulgaria is a parliamentary democracy. This means people vote for representatives to make laws. The prime minister is the head of government and holds the most power. Citizens aged 18 and older can vote.
The government has three main parts: the legislative (makes laws), executive (carries out laws), and judicial (interprets laws). The president is the head of state and commander-in-chief of the armed forces. The president can suggest changes to laws, but the parliament can override this.
The National Assembly has 240 members, called deputies. They are elected for four-year terms. The National Assembly makes laws, approves the budget, and chooses the prime minister.
Legal System: Rules and Justice
Bulgaria uses a civil law legal system. The Ministry of Justice oversees the courts. The highest courts are the Supreme Administrative Court and the Supreme Court of Cassation. They ensure laws are applied correctly. The Supreme Judicial Council manages the system and appoints judges.
Law enforcement is handled by the Ministry of the Interior. The General Directorate of National Police (GDNP) works to prevent crime and keep public order. The Border Police Service and National Gendarmerie also help with security.
Administrative Divisions: How Bulgaria is Organized
Bulgaria is divided into 28 provinces, plus the capital city, Sofia City. Each province is named after its main city. These provinces are further divided into 265 municipalities. Mayors lead the municipalities and are elected for four-year terms.
Foreign Relations: Bulgaria's Place in the World

Bulgaria joined the United Nations in 1955. It is also a founding member of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE). Since the end of the Cold War, Bulgaria has focused on joining European and Atlantic organizations.
Bulgaria became a full member of the European Union on 1 January 2007. It also joined NATO in March 2004. Bulgaria has good relationships with many countries, including China, Vietnam, and Russia. After the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, Bulgaria provided assistance to Ukraine.
Military: Protecting the Nation
The Bulgarian Armed Forces protect Bulgaria. They include land forces, a navy, and an air force. There are about 36,950 active troops. The military is modernizing with new equipment that meets NATO standards. This includes F-16 fighter jets and new vehicles.
Bulgaria's Economy and Innovation
Economic Growth and Development
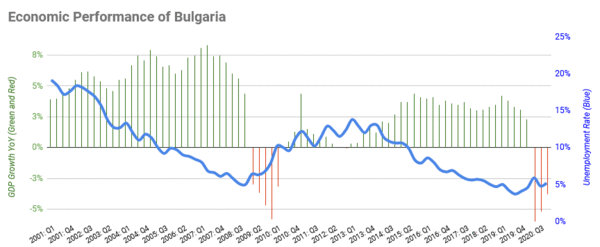
Bulgaria has an open market economy. The private sector makes up most of its economic activity. In the past, Bulgaria was mainly an agricultural country. By the 1980s, it had become an industrial economy.
After some economic challenges in the 1990s, the economy has largely recovered. Bulgaria has low corporate income tax rates, which helps businesses. The national currency is the lev, which is linked to the euro.
Industries and Tourism
Many Bulgarians work in agriculture, industry, and services. Key industries include metal and mineral extraction, chemicals, machine building, and food processing. Bulgaria is Europe's fifth-largest coal producer.
Bulgaria is also the world's largest producer of lavender and rose oil, which are used in perfumes. Tourism is a big part of the economy. Popular places to visit include Sofia, Plovdiv, Veliko Tarnovo, and coastal resorts like Sunny Beach.
Science and Technology: Reaching for the Stars
Bulgaria invests in research and development. The Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (BAS) receives much of the public funding. Research in chemistry, materials science, and physics is strong. Bulgaria also participates in Antarctic research.
The information and communication technologies (ICT) sector is growing. Bulgaria was known for its computing technology during the Soviet era. It is a leader in high performance computing in Southeast Europe.
Bulgaria has contributed to space exploration. It has launched scientific satellites and sent two cosmonauts into space. Bulgarian instruments have been used in missions to Mars and the Moon. In 2017, Bulgaria launched its first geostationary communications satellite, BulgariaSat-1.
Infrastructure: Connecting the Country
Telephone and internet services are widely available in Bulgaria. The country's location and energy sector make it an important energy hub in Europe. Thermal power plants, nuclear power, and renewable sources generate electricity.
Bulgaria has a good road network and railroads are important for freight. Sofia is the main airport, while Varna and Burgas are key seaports.
People and Culture of Bulgaria
Population and Ethnic Groups
Ethnic groups in Bulgaria (2021 census) Bulgarians (84.57%) Turks (8.40%) Romani (4.41%) Others (1.31%) Undeclared (1.31%)
In 2022, Bulgaria's population was about 6.4 million people. Most people (72.5%) live in cities. Sofia is the largest city, followed by Plovdiv, Varna, and Burgas.
Bulgarians are the main ethnic group, making up 84.6% of the population. There are also significant Turkish and Roma minorities. Bulgaria's population has been changing since 1989, with some people moving to other countries. The average age of the population is around 43 years.
Bulgaria scores high in gender equality. Women have equal political rights and high participation in the workforce.
Largest Cities in Bulgaria
|
Largest cities or towns in Bulgaria
2021 Census |
||
|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Pop. |
| 1 | Sofia | 1,190,256 |
| 2 | Plovdiv | 321,824 |
| 3 | Varna | 311,093 |
| 4 | Burgas | 188,242 |
| 5 | Ruse | 123,134 |
| 6 | Stara Zagora | 121,582 |
| 7 | Pleven | 90,209 |
| 8 | Sliven | 79,362 |
| 9 | Dobrich | 71,947 |
| 10 | Shumen | 67,300 |
Health and Well-being
Bulgaria's healthcare system faces challenges, including an aging population. Most deaths are due to cancer and heart conditions. Healthcare is available to everyone, but people often pay for some services themselves. The average life expectancy is 74.8 years.
Education: Learning and Growing
Public education in Bulgaria is free and required. It includes 12 grades, with primary school from grades one to eight and secondary school from nine to twelve. Higher education offers bachelor's and master's degrees. Sofia University is the highest-ranked university.
While educational standards were once very high, there have been efforts to improve student performance in reading, math, and science. Most Bulgarians (98.4%) can read and write.
Language: The Sound of Bulgaria
Bulgarian is the official language. It belongs to the Slavic group but has some unique grammar rules. For example, it uses a definite article at the end of words.
Religion: Faith and Traditions
Bulgaria is a secular state, meaning it has no official religion, but Eastern Orthodox Christianity is considered the traditional religion. About two-thirds of Bulgarians identify as Eastern Orthodox Christians. The Bulgarian Orthodox Church gained its independence in 927 AD.
Muslims are the second-largest religious group, making up about 10% of the population. Other religions include Roman Catholicism and Judaism. A growing number of Bulgarians do not identify with any religion.
Bulgarian Culture and Arts
Folk Traditions and Festivals
Bulgarian culture mixes old folk traditions with modern influences. Fire is an important element in folklore, used to ward off evil spirits. Rituals like kukeri (people dressed in costumes) and survakari are still practiced. Martenitsa is also a popular celebration.
Nestinarstvo, a fire-dance from ancient times, is recognized by UNESCO. Nine historical and natural sites in Bulgaria are UNESCO World Heritage Sites, including Pirin National Park and the Rila Monastery.
Literature and Visual Arts
Bulgarian literature flourished in the Middle Ages with the Preslav and Ohrid literary schools. They helped spread Christianity and the Cyrillic alphabet. Later, the Tarnovo Literary School produced high-quality manuscripts.
After a period of decline, Bulgarian literature and art revived in the 19th century. Ivan Vazov is a famous Bulgarian writer. In visual arts, Zahari Zograf was a pioneer. Modern artists like Christo are known worldwide.
Music and Media
Bulgarian folk music has a unique sound, blending different influences. It uses traditional instruments like the gadulka and gaida. A special feature is its "extended rhythmical time." The Bulgarian State Television Female Vocal Choir won a Grammy Award for their folk music.
Modern classical music began in the late 19th century. Singers like Ghena Dimitrova and Boris Christoff became world-famous. Bulgarian artists also excel in jazz and electropop.
Major media outlets include the Bulgarian National Radio and newspapers like Trud.
Cuisine and Drinks
Bulgarian cuisine is similar to other Balkan countries, with Turkish and Greek influences. Popular foods include yogurt, banitsa, and shopska salad. Bulgaria is known for its wine and Rakia, a traditional fruit brandy.
Sports and Achievements
Olympic Success and Top Athletes

Bulgaria first participated in the modern Olympic Games in 1896. Bulgarian athletes have won many medals, especially in weightlifting and wrestling. Coach Ivan Abadzhiev helped Bulgaria dominate weightlifting in the 1980s.
Stefka Kostadinova holds the world record in women's high jump. Grigor Dimitrov was the first Bulgarian tennis player to reach the top 3 in ATP rankings.
Football: Bulgaria's Favorite Sport
Football is the most popular sport. The Bulgaria national football team achieved 4th place at the 1994 FIFA World Cup. Hristo Stoichkov was a top player, winning the Ballon d'Or.
CSKA Sofia and Levski Sofia are the most successful football clubs in Bulgaria. Ludogorets is also a notable club, having quickly risen to play in the UEFA Champions League.
See also
 In Spanish: Bulgaria para niños
In Spanish: Bulgaria para niños
- Outline of Bulgaria
- Labour law in Bulgaria
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |