Turkey facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of Türkiye
Türkiye Cumhuriyeti (Turkish)
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Capital | Ankara 39°55′N 32°51′E / 39.917°N 32.850°E |
| Largest city | Istanbul 41°1′N 28°57′E / 41.017°N 28.950°E |
| Official languages | Turkish |
| Spoken languages |
|
| Ethnic groups
(2016)
|
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Unitary presidential republic |
| Recep Tayyip Erdoğan | |
| Cevdet Yılmaz | |
| Numan Kurtulmuş | |
| Legislature | Grand National Assembly |
| Establishment | |
| c. 1299 | |
| 19 May 1919 | |
|
• Government of the Grand National Assembly
|
23 April 1920 |
|
• Sultanate abolished
|
1 November 1922 |
| 24 July 1923 | |
|
• Republic declared
|
29 October 1923 |
|
• Current constitution
|
9 November 1982 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
783,562 km2 (302,535 sq mi) (36th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
2.03 |
| Population | |
|
• December 2023 estimate
|
|
|
• Density
|
111/km2 (287.5/sq mi) (83rd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2019) | medium |
| HDI (2022) | very high · 45th |
| Currency | Turkish lira (₺) (TRY) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (TRT) |
| Calling code | +90 |
| ISO 3166 code | TR |
| Internet TLD | .tr |
Turkey (in Turkish: Türkiye) is a country that connects two continents: Europe and Asia. It covers an area of about 780,000 square kilometers.
Turkey is a republic, which means its government is led by elected officials. The country has 81 provinces. The money used in Turkey is called the Turkish Lira. Ankara is the capital city, located in central Anatolia. The biggest city for culture and business is Istanbul, which is partly in Europe. Istanbul used to be called Constantinople. The modern country of Turkey was founded in 1923, after World War I and a fight for independence. Before that, it was the main part of the powerful Ottoman Empire.
Many ancient civilizations lived in the area that is now Turkey. These include the Hittites, the Roman Empire, and the Byzantine Empire. Many important events in the history of Christianity also happened here. Because Turkey is located on both continents, some people call it the "door" between Europe and Asia.
Turkey has a warm and varied climate. This allows many different food crops to grow. Farming, raising livestock, and forestry are important industries. Turkey grows enough food to feed its own people. Turkish factories make things like airplanes, electronics, cars, clothing, and textiles. These products are used at home and sold to other countries.
Turkey is a very popular place for tourists. It has hundreds of kilometers of beautiful beaches along the Aegean and Mediterranean coasts. There are also many important historical places to visit.
Contents
History of Turkey
People have lived in Anatolia (the Asian part of Turkey) for a very long time. It is one of the oldest inhabited places in the world, besides Africa.
Early Empires and Kingdoms
The first major empire in this area was the Hittites. They lived there from the 18th to the 13th century BC. The Hittites spoke an Indo-European language and had a developed culture in Central Anatolia. Their kingdom was later destroyed.
From 1950 BCE, Greeks and Assyrians lived in parts of southeastern Turkey. The Assyrians ruled this area until their empire was conquered in 612 BC. After that, Anatolia was home to many different kingdoms. These included the Achaemenid Empire, Hellenistic kingdoms, Roman Empire, Byzantine Empire, Seljuk Empire, and Mongol Empire.
The Ottoman Empire
In the 14th century, after the Mongol Empire fell, a leader named Osman started a new empire. It was named after him: the Ottoman Empire. This empire became one of the longest-lasting empires ever. It also spread across the Balkans in Europe. The Ottoman Empire was ruled by Islamic law, but other religions had certain minority rights.
Modern Turkey's Beginnings
The Ottoman Empire was one of the Central Powers in World War I. During the war, many Armenians living in the Ottoman Empire suffered greatly. After the war, the Ottoman Empire was defeated and broken up. However, Atatürk led the Turkish army to fight off foreign enemies, including the Greeks.
Mustafa Kemal Atatürk became the first President of Turkey. He made many big changes to make Turkey more modern. For example, he removed religious secondary schools. Some people did not like these changes because they felt they went against Islam.
For many years, Kurdish fighters (often called the "PKK") fought the Turkish government. They wanted more autonomy for the Kurds in southeastern Turkey. The Turkish government and most countries consider them terrorists.
Turkey has been working to become closer with Europe. It applied to join the EEC in 1987. It joined the European Union Customs Union in 1995 and started talks to join the European Union in 2005.
In 2014, Recep Tayyip Erdoğan became Turkey's first directly elected president. In 2017, a public vote changed the government system. The country moved from a parliamentary system to a presidential system. This meant the president gained more power, and the role of prime minister was removed.
How Turkey is Organized
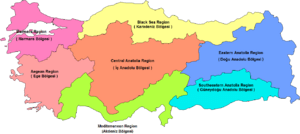
Turkey is divided into 81 provinces for administrative reasons. Each province is then split into smaller districts, making a total of 973 districts. For geographic and economic studies, Turkey is also divided into 7 regions and 21 smaller subregions.
Government and Politics
Turkey is a presidential republic with a multi-party system. This means many different political parties can exist. The government has three main parts:
- The legislative branch, which makes laws, is the Grand National Assembly of Turkey.
- The executive branch, which carries out laws, is led by the President of Turkey.
- The judicial branch, which interprets laws, includes the Constitutional Court, the Court of Cassation, and the Court of Jurisdictional Disputes.
The Parliament has 600 seats. These seats are given to provinces based on their population. Both the Parliament members and the president serve for five years, with elections happening on the same day. The president is chosen by a direct vote from the people. A president can serve for two terms. However, if the parliament calls for early elections during the second term, the president can run again. The Constitutional Court has 15 members. They are elected for a single 12-year term and must retire when they turn 65.
Geography of Turkey
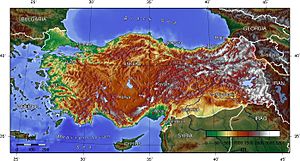
Turkey covers an area of 783,562 square kilometers (about 302,535 square miles). With the Turkish straits and Sea of Marmara in between, Turkey acts as a bridge between Western Asia and Southeastern Europe. Most of Turkey (97%) is on the Asian side, often called Anatolia. The European side, called Eastern Thrace, has about 10% of the population and covers 3% of the land.
Turkey is surrounded by seas on three sides: the Aegean Sea to the west, the Black Sea to the north, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Turkey shares borders with Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east. To the south, it borders Syria and Iraq. To the northwest, its European part borders Greece and Bulgaria.
Turkey is divided into "seven major regions": Marmara, Aegean, Central Anatolia, Black Sea, Eastern Anatolia, Southeastern Anatolia, and the Mediterranean. Generally, the inland Anatolian Plateau becomes more rugged as you go east. Mountain ranges include the Köroğlu and Pontic mountains in the north, and the Taurus Mountains in the south. The Lakes Region has some of Turkey's largest lakes, like Lake Beyşehir and Lake Eğirdir.
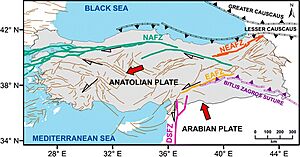
The eastern Anatolian plateau is a mountainous area where the Arabian and Eurasian tectonic plates meet. This area includes Mount Ararat, Turkey's highest point at 5,137 meters (16,854 feet), and Lake Van, the country's largest lake. Eastern Turkey is also where major rivers like the Euphrates, Tigris, and Aras begin. The Southeastern Anatolia Region includes the northern plains of Upper Mesopotamia.
Earthquakes happen often in Turkey. Most of the population lives in areas with different levels of earthquake risk. About 70% live in the highest or second-highest risk areas. The Anatolian plate is surrounded by major fault lines. The North Anatolian Fault zone is considered one of the most dangerous natural hazards. The 2023 Turkey–Syria earthquakes were the deadliest in recent Turkish history.
Biodiversity and Wildlife

Turkey is located where land, sea, and air routes meet three continents. This, along with its many different habitats, has created a huge variety of species and a rich ecosystem. Out of 36 global biodiversity hotspots, Turkey contains three: the Mediterranean, Irano-Anatolian, and Caucasus hotspots.
The forests of Turkey are home to the Turkey oak. A common tree is the orientalis (plane tree). The Turkish pine (Pinus brutia) is found mostly in Turkey and other eastern Mediterranean countries. Several wild types of tulip flowers are native to Anatolia. The tulip was first brought to Western Europe from the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century.
Turkey has 40 national parks, 189 nature parks, and many other protected areas. Examples include Gallipoli Peninsula Historical National Park and Mount Nemrut National Park. The Northern Anatolian conifer and deciduous forests cover most of the Pontic Mountains in northern Turkey. This region is home to animals like the Eurasian sparrowhawk, golden eagle, and Caucasian black grouse.
The Anatolian leopard is still found in very small numbers in northeastern and southeastern Turkey. Other wild cats in Turkey's forests include the Eurasian lynx, European wildcat, and caracal. The Caspian tiger, which is now extinct, lived in eastern Turkey until the mid-1900s. Famous domestic animals from Ankara include the Angora cat, Angora rabbit, and Angora goat. From Van Province, there is the Van cat. The national dog breeds are the Kangal, Malaklı, and Akbaş.
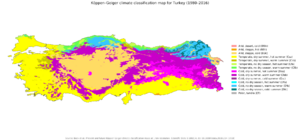
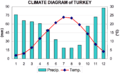
Climate of Turkey
The coastal areas of Turkey along the Aegean and Mediterranean Seas have a temperate Mediterranean climate. This means they have hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. The Black Sea coast has a temperate oceanic climate with warm, wet summers and cool, wet winters. This is the only region in Turkey that gets a lot of rain all year. The eastern Black Sea coast receives the most rain, averaging 2,200 mm (87 inches) annually.
The coastal areas along the Sea of Marmara have a mix of Mediterranean and oceanic climates. They have warm to hot, somewhat dry summers and cool, wet winters. Snow falls on the Marmara and Black Sea coasts almost every winter but usually melts quickly. Snow is rare on the Aegean coast and very rare on the Mediterranean coast.
Winters on the Anatolian plateau are very cold. Temperatures can drop to -30 to -40 degrees Celsius (-22 to -40 degrees Fahrenheit) in northeastern Anatolia. Snow can stay on the ground for at least 120 days a year, and all year on the highest mountains. In central Anatolia, temperatures can fall below -20 degrees Celsius (-4 degrees Fahrenheit). Mountains near the coast block the warm Mediterranean air from reaching inland. This gives the central Anatolian Plateau a continental climate with very different seasons.
Turkey is very sensitive to climate change due to its location and other factors. It aims to have net zero emissions by 2053. Achieving these climate goals will require big investments but will also bring economic benefits.
|
People of Turkey

In 2023, Turkey's population was over 85 million people. About 93% of the population lived in cities and towns. Most people (68.3%) are between 15 and 64 years old. Children aged 0–14 make up 21.4%, and those 65 or older are 10.2%. Between 1950 and 2020, Turkey's population grew from 20.9 million to 83.6 million. However, the population growth rate was very low in 2023. In 2023, the average number of children a woman had was 1.51, which is below the number needed to keep the population stable.
Ethnic Groups and Languages
Turkey is home to at least 47 different ethnic groups. According to the World Factbook, 70-75% of Turkey's citizens are ethnic Turks.
Kurds are the largest ethnic minority group. Their exact numbers are debated, but estimates range from 12% to 20% of the population. Kurds form a majority in several eastern provinces like Diyarbakır and Van. Many Kurds have also moved to major cities in central and western Turkey. Istanbul, for example, is estimated to have three million Kurds, making it the city with the largest Kurdish population in the world. Some people have more than one ethnic identity, like being both Turk and Kurd.
Non-Kurdish ethnic minorities make up 7–12% of the population.
The official language of Turkey is Turkish. It is the most widely spoken Turkic language in the world. About 85% to 90% of the population speak Turkish as their first language. Kurdish speakers are the largest language minority. Other minority languages include Arabic, Caucasian languages, and Gagauz. The language rights of officially recognized minorities like Armenian, Greek, and Hebrew are protected. There are also several endangered languages in Turkey.
Culture of Turkey
In the 19th century, people in the Ottoman Empire discussed what it meant to be Turkish. There were three main ideas: Turkism, Islamism, and Westernism. Turkish culture was also shaped by the ancient cultures of Anatolia. After the Republic was formed in 1923, Kemalism focused on Turkish culture. It tried to make "Islam a personal belief" and aimed for modernization. Today, Turkey has many local cultures. Things like music, folk dance, or different kinds of kebap can show what a local area is like. Turkey also has a national culture, with "national movie stars, rock bands, fashion trends, and soccer and basketball leagues."
Literature, Theatre, and Visual Arts
Turkish literature is more than a thousand years old. The Seljuk and Ottoman periods produced many literary works and poems. Turkic stories and poems from Central Asia were also passed down. The Book of Dede Korkut is an example of old oral stories. Dīwān Lughāt al-Turk, from the 11th century, has information about the Turkish language and poetry. Yunus Emre, influenced by Rumi, was an important writer of Anatolian Turkish poetry. Ottoman Divan poetry used fancy words and complex language. It included Sufi mysticism, romance, and formal styles.
In the 19th century, Ottoman literature was influenced by the West. New types of writing, like novels and journalism, appeared. Aşk-ı Memnu by Halid Ziya Uşaklıgil was the "first truly refined Turkish novel." Fatma Aliye Topuz was the first female Turkish novelist. After the Republic was declared in 1923, Atatürk made changes like the language reform and alphabet reform. Since then, Turkish literature has shown the social and economic conditions in Turkey with more variety. The "Village Novel" style appeared in the mid-1950s, talking about poverty. An example is Memed, My Hawk by Yaşar Kemal. Orhan Pamuk won the 2006 Nobel Prize in Literature.
Turkey has four main types of theatre: "folk theatre, popular theatre, court theater, and Western theater." Turkish folk theatre is thousands of years old and still exists in rural areas. Popular theatre includes plays with live actors, puppet and shadow plays, and storytelling. An example of shadow play is Karagöz and Hacivat. Court theatre was a more refined version of popular theatre. Western theatre started appearing in Turkey in the 19th century. After the Turkish Republic was formed, a state conservatory and the State Theatre Company were created.
Turkey's visual arts can be divided into "decorative" and "fine" arts. Fine arts, or güzel sanatlar, include sculpture and painting. Turkish artists in these fields have become known worldwide. Photography, fashion design, and graphic arts are other areas where Turkish artists are recognized. The first sale of modern Turkish art by Sotheby's London was in 2009. Istanbul Modern and the Istanbul Biennial are places to see contemporary Turkish art. Turkey has also seen a return of traditional arts. This includes Ottoman-era arts like ceramics and carpets. Textile and carpet design, glass and ceramics, calligraphy, and paper marbling (ebru) are some art forms where modern Turkish artists are leaders in the Islamic world.
Music and Dance

Turkish music can be grouped into three main types: "Turkish folk music", "Turkish art music", and various popular music styles. Popular music styles include arabesque, pop, and Anatolian rock.
The growing popularity of pop music led to several international Turkish pop stars. These include Ajda Pekkan, Sezen Aksu, Tarkan, and Sertab Erener. Famous Turkish jazz and blues musicians and composers include Ahmet Ertegun (who founded Atlantic Records) and Kerem Görsev.
Architecture
Turkey has many ancient Neolithic settlements, like Çatalhöyük. From the Bronze Age, important buildings include Alaca Höyük and the second layer of Troy. There are also many examples of Ancient Greek and Ancient Roman buildings, especially in the Aegean region. Byzantine architecture dates back to the 4th century AD. Its best example is Hagia Sophia. Byzantine style continued to develop after Istanbul was conquered.
During the Seljuk Sultanate of Rum and Turkish principalities periods, a unique architecture appeared. It combined Byzantine and Armenian styles with styles from West Asia and Central Asia. Seljuk architecture often used stone and bricks. They built many caravanserais (roadside inns), madrasas (schools), and mausoleums (tombs).
Ottoman architecture began in northwest Anatolia. Early Ottoman architecture mixed "traditional Anatolian Islamic architecture with local building materials and techniques." After Istanbul was conquered, classical Ottoman architecture developed in the 16th and 17th centuries. The most important architect of this time was Mimar Sinan. His major works include the Şehzade Mosque, Süleymaniye Mosque, and Selimiye Mosque. In the 18th century, Ottoman architecture was influenced by European styles, leading to the Ottoman baroque style. European influence continued in the 19th century, seen in buildings like the Dolmabahçe Palace. The last period of Ottoman architecture includes the First National Architectural Movement.
Since 1918, Turkish architecture has changed a lot. From 1918 to 1950, it moved from the First National Architectural Movement to modernist architecture. Modern buildings were preferred for public spaces. For private homes, the "Turkish house" style was popular. From 1950 to 1980, there was a lot of urbanization and international influence. For homes, "reinforced concrete, slab-block, medium-rise apartments" became common. Since 1980, architecture has been shaped by consumer trends and international styles, like shopping malls and office towers. Luxury homes with a "Turkish house style" are also popular. In the 21st century, urban renewal projects are common. A main goal for these projects is to make buildings safer against natural disasters like earthquakes.
Turkish Food
Turkey has a rich and varied cuisine, which changes from one region to another. Turkish food has been influenced by Anatolian, Mediterranean, Iranian, Central Asian, and East Asian cooking. Turkish and Ottoman cuisine have also influenced other cultures. Dīwān Lughāt al-Turk, from the 11th century, shows how old much of today's Turkish food is. Güveç, Bulgur, and Börek are some of the earliest recorded Turkish dishes. Even though the word "kebab" comes from Persian, Turkic people have long used skewers to cook meat. Turkish cuisine is known for its many kinds of kebabs. Similarly, pilaf dishes were influenced by Turkish cooking. More information about food during the Seljuk and Ottoman periods comes from the writings of Rumi and Evliya Çelebi.
Common foods in Turkey include bread and yogurt. Some types of bread are lavash and pide (a kind of pita bread). Ayran is a drink made from yogurt. In western Turkey, olive oil is used a lot. Grains like wheat, maize, barley, oats, and millet are important. Beans, chickpeas, nuts, aubergines, and lamb are often used ingredients. Doner kebab, which started in Turkey, is made of marinated lamb slices cooked on a vertical rotisserie. Seafood like anchovy is also popular. Dolma and mantı are made by stuffing vegetables or pasta. Sarma is made by rolling edible leaves around a filling. Yahni dishes are vegetable stews. Turkey is one of the countries with the meze tradition, which means serving many small dishes. Honey, pekmez (grape molasses), dried fruit, or fresh fruit are used for sweetening. Filo is a Turkish dough used to make baklava. Turkish delight is a soft, chewy jelly candy.
Sports in Turkey

The most popular sport in Turkey is association football. Galatasaray won the UEFA Cup and UEFA Super Cup in 2000. The Turkey national football team won the bronze medal at the 2002 FIFA World Cup, the 2003 FIFA Confederations Cup, and UEFA Euro 2008.
Other popular sports include basketball and volleyball. The men's national basketball team and women's national basketball team have been successful. Anadolu Efes S.K. is the most successful Turkish basketball club in international competitions. Fenerbahçe reached the final of the EuroLeague three times in a row and became European champions in 2017.
The final of the 2013–14 EuroLeague Women basketball championship was played between two Turkish teams, Galatasaray and Fenerbahçe. Galatasaray won that game. Fenerbahçe won the 2023 FIBA Europe SuperCup Women after two Euroleague wins in a row.
The women's national volleyball team has won several medals. Women's volleyball clubs like VakıfBank S.K., Fenerbahçe, and Eczacıbaşı have won many European championship titles and medals.
The traditional national sport of Turkey is yağlı güreş (oil wrestling). It has been popular since Ottoman times. The annual Kırkpınar oil wrestling tournament in Edirne Province has been held since 1361. This makes it the oldest continuously held sporting event in the world. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, oil wrestling champions like Koca Yusuf became famous internationally. They won world heavyweight wrestling titles in Europe and North America. Other wrestling styles, like freestyle wrestling and Greco-Roman wrestling, are also popular. Turkish wrestlers have won many European, World, and Olympic titles in these styles.
Images for kids
-
Some henges at Göbekli Tepe were built as early as 9600 BC. This was thousands of years before Stonehenge in England.
-
The Lion Gate in Hattusa, the capital of the Hittite Empire. This city's history goes back to 6000 BC.
-
The Library of Celsus in Ephesus was built by the Romans around 114–117 CE. The Temple of Artemis in Ephesus was one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
-
The Hagia Sophia in Istanbul was first a church, then a mosque, and is now a museum. It was built by the Byzantine emperor Justinian I in 532–537 CE.
-
The Mevlana Museum in Konya was built by the Seljuk Turks in 1274. Konya was the capital of the Seljuk Sultanate of Rum.
-
Eighteen female MPs joined the Turkish Parliament in the 1935 elections. Turkish women gained the right to vote earlier than women in some Western European countries.
-
During politically unstable times, the Turkish military sometimes took direct power, or influenced it through leaders like Cemal Gürsel.
-
A view from the Gezi Park protests in Taksim, Istanbul on June 4, 2013.
-
Leaders of the G-20 at the 2015 Antalya summit in Turkey.
-
Turkey was one of the first members of the Council of Europe in 1949. It became an associate member of the EEC in 1963, joined the EU Customs Union in 1995, and started talks to join the European Union in 2005.
-
The Turkish Armed Forces are the second largest military force in NATO, after the US Armed Forces. Turkey joined NATO in 1952.
-
Sümela Monastery on the Pontic Mountains. These mountains have diverse forests and wildlife.
-
Skyscrapers in the Levent business district in Istanbul, Turkey's largest city.
-
Atatürk (center) at the Sümerbank Textile Factory in Nazilli, October 9, 1937.
-
Map showing Turkish speakers according to the 1965 census.
-
Sultan Ahmed Mosque in Istanbul is also known as the Blue Mosque because of its blue İznik tiles.
-
The Bulgarian St. Stephen Church in Fatih, Istanbul, is made of prefabricated cast iron.
-
The Grand Synagogue in Edirne.
-
Istanbul University was founded in 1453. It became Turkey's first university in 1933.
-
Imperial College of Medicine, now the Haydarpaşa campus of Marmara University.
-
Whirling Dervishes of the Sufi Mevlevi Order performing a Sema ceremony in Konya. This ceremony is a UNESCO-listed cultural heritage.
-
A 13th-century Turkish carpet from the Anatolian Seljuk Sultanate period.
-
Tevfik Fikret is seen as the founder of modern Turkish poetry.
-
TRT World is the international news platform of the Turkish Radio and Television Corporation.
-
Nuri Bilge Ceylan, a Turkish film director and screenwriter, won the 2014 Palme d'Or.
See also
 In Spanish: Turquía para niños
In Spanish: Turquía para niños