Mediterranean Basin facts for kids
The Mediterranean Basin is a special area of land around the Mediterranean Sea. It's also called the Mediterranean Region. This area has a unique Mediterranean climate, which means it has mild, rainy winters and warm, dry summers. This climate helps certain types of plants grow, like Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub. This region has been very important for many ancient civilizations.
Contents
Geography: Where is the Mediterranean Basin?
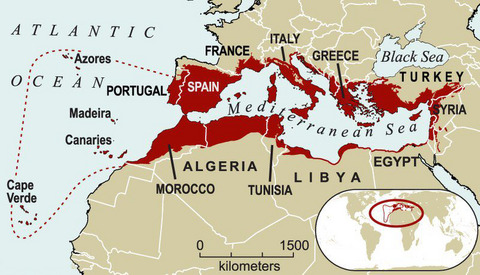
The Mediterranean Basin stretches across parts of three continents: Europe, Africa, and Asia. It's different from the area where rivers flow into the Mediterranean Sea (like the Nile or Rhône). For example, the Mediterranean Basin includes parts of Portugal, Jordan, and Iraq, even though rivers from these places don't always flow into the Mediterranean Sea.
This region has many different types of landscapes. You can find tall mountains, rocky coastlines, thick scrub, dry plains, wetlands by the sea, sandy beaches, and many islands. Even though tourist pictures often show sandy beaches, the Mediterranean area is actually very hilly. You can see mountains from almost anywhere!
The Mediterranean Basin goes from Macaronesia in the west to the Levant in the east. Some definitions might include all of Macaronesia (like the Azores and Cape Verde), while others only include Madeira and the Canary Islands.
In Western Asia, the basin covers the western and southern parts of Anatolia (modern-day Turkey), reaching as far as Iraq. However, it doesn't include the cooler mountains in central Turkey. It also includes the eastern Mediterranean area called the Levant, which is bordered by the Syrian Desert and Negev deserts to the east and south.
In northwestern Africa, the northern part of the Maghreb region has a Mediterranean climate. The Atlas Mountains separate this area from the vast Sahara Desert. In the eastern Mediterranean, the Sahara Desert reaches the southern coast, except for a small northern strip of Cyrenaica in Libya, which has a dry Mediterranean climate.
Europe is to the north of the Mediterranean Sea. The European part of the Mediterranean Basin is mostly Southern Europe. Three large peninsulas in Southern Europe – the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal), the Italian Peninsula (Italy), and the Balkan Peninsula – extend into this climate zone. Mountain ranges like the Pyrenees, Alps, Dinaric Alps, and Balkan Mountains separate the Mediterranean region from the cooler climates of Central and Eastern Europe.
Geology: How the Mediterranean Basin Formed
The Mediterranean Basin was created a very long time ago when the African-Arabian continent slowly moved north and crashed into the Eurasian continent. This collision closed an ancient ocean called the Tethys Sea. As the continents pushed together, huge mountain ranges formed, stretching from the Pyrenees in Spain to the Zagros Mountains in Iran. This mountain-building period happened mostly between 34 and 5.3 million years ago.
Around 6 million years ago, during the late Miocene period, Africa moved in a way that closed off the western end of the Mediterranean Sea. This caused the entire sea to dry up! This event is known as the Messinian Salinity Crisis. The sea then refilled with water from the Atlantic Ocean. Some scientists think this drying and refilling might have happened several times, leading to a lot of salt being left behind.
The end of the Miocene also brought a big change in the Mediterranean Basin's climate. Before, it was a humid, subtropical area with summer rain, supporting forests with laurel trees. But about 3.2 to 2.8 million years ago, during the Pliocene period, the climate changed to what we know as the Mediterranean climate, with less summer rain. The laurel forests disappeared from most areas, and new plants evolved. These plants, like coniferous trees and sclerophyllous trees and shrubs, have small, tough, waxy leaves that help them save water during dry summers. Sadly, much of these natural forests and shrublands have been changed by thousands of years of human activity.
Flora and Fauna: Plants and Animals
The Mediterranean Basin is a very special place for plants. It's part of a larger area called the Mediterranean Floristic Region. This region was first described by a German botanist named August Grisebach in the late 1800s.
One unique plant family, Drosophyllaceae, is found only in this region. Many plant groups (genera) are also found only here, such as:
- Anagyris
- Andryala
- Aphyllanthes
- Argania
- Argantoniella
- Bellardia
- Biserrula
- Bivonaea
- Bolanthus
- Boleum
- Callicotome
- Ceratocapnos
- Ceratonia
- Chamaerops
- Chronanthus
- Cladanthus
- Coridothymus
- Didesmus
- Dorystoechas
- Drosophyllum
- Euzomodendron
- Fedia
- Guiraoa
- Gyrocarion
- Helicodiceros
- Hermodactylus
- Hutera
- Hymenocarpus
- Ionopsidium
- Lafuentea
- Lagoecia
- Leuzea
- Lycocarpus
- Malope
- Morisia
- Ortegia
- Petromarula
- Phillyrea
- Preslia
- Putoria
- Rothmaleria
- Rosmarinus
- Rupicapnos
- Santolina
- Staehelina
- Soleirolia
- Spartium
- Tetraclinis
- Trachelium
- Tremastelma
- Triplachne
- Vella
Many well-known Mediterranean plants include the Aleppo pine, stone pine, Mediterranean cypress, bay laurel, holm oak, kermes oak, strawberry tree, mastic, common myrtle, and oleander.
The Mediterranean Basin is the largest of the world's five regions with a Mediterranean climate. It has many different plant communities, which change depending on rainfall, how high up they are, and the type of soil.
- Scrublands grow in the driest areas, especially near the coast where there's a lot of wind and salt. These low, soft-leaved scrublands have different names like garrigue (French) or phrygana (Greek).
- Shrublands are dense areas of evergreen shrubs and small trees. They are very common around the Mediterranean. They are called maquis (French) or macchia (Italian). Sometimes, shrublands are the natural plant type, but often they are areas where forests used to be, but were cut down or overgrazed.
- Savannas and grasslands are also found, usually with many annual grasses.
- Woodlands usually have oak and pine trees, mixed with other evergreen and cone-bearing trees.
- Forests have a closed canopy (the tops of the trees touch) and grow in areas with more rainfall or along rivers. Mediterranean forests usually have evergreen trees, mostly oaks and pines. Higher up in the mountains, these forests change to mixed forests with broadleaf and tall conifer trees, similar to forests in cooler climates.
The Mediterranean Basin has amazing biodiversity, with 22,500 types of vascular plants found nowhere else in the world. Because it has so many unique species and is also threatened, it's called a "biodiversity hotspot." The total area of the Mediterranean Basin is huge, but only a small part of it remains untouched by humans.
Some endangered mammals in the Mediterranean Basin include the Mediterranean monk seal, the Barbary macaque (a type of monkey), and the Iberian lynx (a wild cat).
Ecoregions: Different Natural Areas
The WWF (World Wide Fund for Nature) has identified 22 different natural areas, or ecoregions, within the Mediterranean Basin. Most of these areas have plants with tough, leathery leaves (sclerophyll plants) that help them survive the dry summers.
- Aegean and Western Turkey sclerophyllous and mixed forests (Greece, Turkey, North Macedonia, Bulgaria)
- Anatolian conifer and deciduous mixed forests (Turkey)
- Canary Islands dry woodlands and forests (Spain)
- Corsican montane broadleaf and mixed forests (France)
- Crete Mediterranean forests (Greece)
- Cyprus Mediterranean forests (Cyprus)
- Eastern Mediterranean conifer–sclerophyllous–broadleaf forests (Lebanon, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Palestine, Syria, Turkey)
- Iberian conifer forests (Spain)
- Iberian sclerophyllous and semi-deciduous forests (Portugal, Spain)
- Illyrian deciduous forests (Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Greece, Italy, Montenegro, Slovenia)
- Italian sclerophyllous and semi-deciduous forests (France, Italy, San Marino)
- Mediterranean acacia–argania dry woodlands (Western Sahara, Morocco, Canary Islands (Spain))
- Mediterranean dry woodlands and steppe (Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Tunisia)
- Mediterranean woodlands and forests (Algeria, Libya, Morocco, Tunisia)
- Northeastern Spain and Southern France Mediterranean forests (France, Monaco, Spain)
- Northwest Iberian montane forests (Portugal, Spain)
- Pindus Mountains mixed forests (Albania, Greece, Kosovo, North Macedonia)
- South Apennine mixed montane forests (Italy)
- Southeastern Iberian shrubs and woodlands (Spain)
- Southern Anatolian montane conifer and deciduous forests (Lebanon, Israel, Jordan, Syria, Turkey)
- Southwest Iberian Mediterranean sclerophyllous and mixed forests (Portugal, Spain)
- Tyrrhenian–Adriatic sclerophyllous and mixed forests (Croatia, France, Italy, Malta)
History: People in the Mediterranean Basin
Neanderthals lived in western Asia and parts of Europe that weren't covered by glaciers, starting about 230,000 years ago. Modern humans arrived in western Asia from Africa less than 100,000 years ago. Later, modern humans, known as Cro-Magnons, moved into Europe around 50,000 to 40,000 years ago.
The last big ice age ended about 12,000 years ago. After that, there was a warm period.
Around 9,000 years ago, people in the eastern Mediterranean started to grow food crops like wheat, chickpeas, and olives. They also began to raise sheep and goats. This led to the creation of the first farming villages. These farming ideas then spread to southeastern Europe. Later, other crops like poppy and oats were grown in Europe. Farming communities grew all around the Mediterranean Basin. Large stone structures called Megaliths were built in Europe between 4500 and 1500 BCE.
Between 9,000 and 7,000 years ago, the summer monsoon became stronger, bringing more rain to the Sahara. This turned the Sahara into a green grassland with lakes and rivers. However, after a time of changing weather, the Sahara became a desert again by about 4,000 BCE.
Agriculture: What Grows Here?
Wheat is the most important grain grown around the Mediterranean Basin. Other crops like pulses (beans, lentils) and vegetables are also grown. The most famous tree crop is the olive. Figs are another important fruit tree. Citrus fruits, especially lemons, are grown in areas where there is irrigation. Grapes are also a major crop, used for eating and for making wine. In areas with irrigation, rice and summer vegetables are grown.
See also
 In Spanish: Cuenca del Mediterráneo para niños
In Spanish: Cuenca del Mediterráneo para niños
- Ancient Egypt
- Ancient Greece
- Ancient Rome
- Life zones of the Mediterranean region
- Mediterranean wine climate
- MISTRALS
- Ottoman Empire
- Phoenicia
- Zanclean flood