Syria facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Syrian Arab Republic
|
|
|---|---|
|
Anthem: فِي سَبِيلِ المَجد
Fī Sabīli al-Majd "In Pursuit of Glory" (de facto) حُمَاةَ الدِّيَارِ Ḥumāt ad-Diyār "Guardians of the Homeland" (de jure) |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Damascus 33°30′N 36°18′E / 33.500°N 36.300°E |
| Official languages | Arabic |
| Ethnic groups
(2021)
|
80–90% Arabs 9–10% Kurds 1–10% others |
| Religion
(2020)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Syrian |
| Government | Unitary presidential republic under a provisional government |
| Ahmed al-Sharaa | |
| Vacant | |
| Legislature | People's Assembly |
| Establishment | |
|
• Arab Kingdom of Syria
|
8 March 1920 |
|
• State of Syria under French mandate
|
1 December 1924 |
|
• First Syrian Republic
|
14 May 1930 |
|
• End of the French mandate
|
17 April 1946 |
|
• Part of the United Arab Republic
|
22 February 1958 – 28 September 1961 |
|
• Beginning of Ba'athist rule
|
8 March 1963 |
|
• Ba'athist regime overthrown
|
8 December 2024 |
|
• Current interim constitution
|
13 March 2025 |
|
• Current provisional government established
|
29 March 2025 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
185,180 km2 (71,500 sq mi) (87th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
1.1 |
| Population | |
|
• 2025 estimate
|
|
|
• Density
|
118.3/km2 (306.4/sq mi) (70th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2021 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$50.28 billion |
|
• Per capita
|
$3,300 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$9.8 billion |
|
• Per capita
|
$800 |
| Gini (2022) | ▼ 26.6 low |
| HDI (2023) | medium · 162nd |
| Currency | Syrian pound (SYP) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (AST) |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +963 |
| ISO 3166 code | SY |
| Internet TLD | .sy سوريا. |
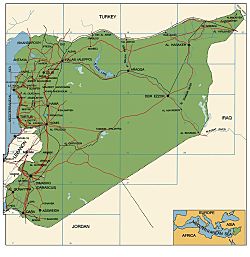
Syria is a country located in the Middle East, which is the western part of Asia. It shares borders with several countries. These are Lebanon, Israel, Jordan, Iraq, and Turkey.
To the west, Syria has a coastline along the Mediterranean Sea. The eastern and northern parts of the country are covered by mountains. Syria's capital city is Damascus, and its largest city is Aleppo.
Since 2011, Syria has been in a difficult situation due to a civil war. Many different countries have been involved in this conflict. This has led to a major refugee crisis. Over 6 million people have had to leave their homes and become refugees.
Most people in Syria follow the Sunni branch of Islam (74%). Other groups include Alawi (12%), Christians (10%), and Druze (3%).
Contents
A Look at Syria's Past
Syria has a very long and rich history. It was once home to the Phoenicians. Later, it became part of powerful empires. These included the Achaemenid Empire, the Roman Empire, and the Eastern Roman Empire.
In those ancient times, people in Syria spoke the Syriac language. The city of Antioch was very important. It was one of the key cities for early Christendom. When the Arab Empire arrived, people started speaking the Arabic language. Today, most Syrians are Muslim, but there are still many Christians.
After World War I ended, France took control of Lebanon and Syria. Meanwhile, Britain gained power over Iraq, Jordan, and Palestine. A border was drawn between Iraq and Syria in 1920. France governed Syria until 1946, when Syria became an independent country.
Syria was briefly part of the United Arab Republic with Egypt from 1958 to 1961. Syria has also had conflicts with Israel. Some areas, like the Golan Plateau, were taken by Israel.
In 2012, a civil war started in Syria. This conflict was against the government of President Bashar al-Assad. Many different countries became involved in the fighting. Over time, several groups formed in Syria to challenge the government. These included the Syrian Interim Government, Syrian Salvation Government, and Rojava.
On December 8, 2024, opposition forces took control of the capital city, Damascus. This event led to the end of Bashar al-Assad's government. It also ended the Assad family's 53-year rule over Syria.
Syria's Land and Climate
Syria is located between 32° and 38° North latitude and 35° and 43° East longitude. The country's climate changes quite a bit. The coast along the Mediterranean Sea is humid. Inland, there is a semi-arid (partly dry) steppe zone. Further east, it becomes a very dry desert.
Most of Syria is a dry plateau. However, the northwest part near the Mediterranean Sea is quite green. Two important farming areas are Al-Jazira in the northeast and Hawran in the south. The Euphrates River, Syria's most important river, flows through the eastern part of the country.
Syria is considered part of the "cradle of civilization." This means it's one of the places where early human civilizations began. Its land sits on the northwest edge of the Arabian Plate.
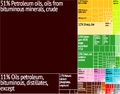
Oil was first found in commercial amounts in Syria in 1956. The main oil fields are in areas like al-Suwaydiyah and Karatchok. These fields are connected to oil fields in Iraq. After 1974, oil became Syria's most important natural resource and main export. Natural gas was also found in 1940.
How Syria is Governed
Syria is now led by a transitional government. The President of Syria is the head of the country. The Prime Minister of Syria leads the government.
The Interim Legislative Council is responsible for making laws. This council also approves how the government spends money.
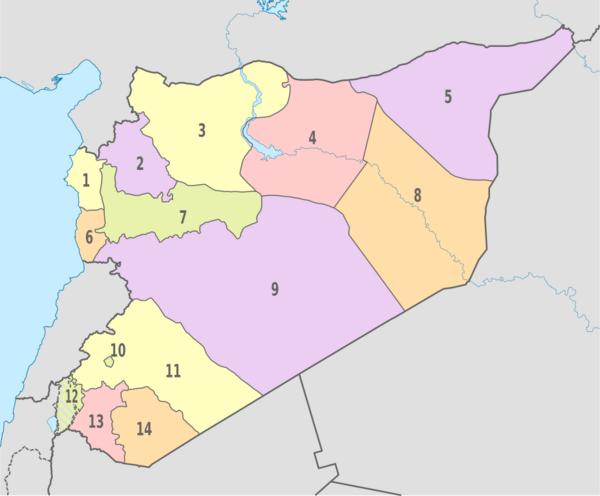
Syria is divided into 14 main areas called governorates. These are further split into 61 districts. The districts are then divided into smaller sub-districts.
| No. | Governorate | Capital | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Latakia | Latakia | |
| 2 | Idlib | Idlib | |
| 3 | Aleppo | Aleppo | |
| 4 | Raqqa | Raqqa | |
| 5 | Al-Hasakah | Al-Hasakah | |
| 6 | Tartus | Tartus | |
| 7 | Hama | Hama | |
| 8 | Deir ez-Zor | Deir ez-Zor | |
| 9 | Homs | Homs | |
| 10 | Damascus | Damascus | |
| 11 | Rif Dimashq | Douma | |
| 12 | Quneitra | Quneitra | |
| 13 | Daraa | Daraa | |
| 14 | Al-Suwayda | Al-Suwayda |
Syria's Economy

Syria is considered a middle-income country. Before the civil war, its economy relied heavily on oil and farming. The oil industry brought in about 40% of the money from exports. Recent discoveries suggest there might be large amounts of oil under the Mediterranean Sea near Syria and Cyprus.
Farming also played a big role, making up about 20% of the country's economy. It also provided jobs for 20% of the people. However, oil reserves are expected to decrease, and Syria has started to import more oil than it produces.
Since the civil war began, Syria's economy has shrunk significantly. The value of the Syrian currency has also dropped. The government now relies more on financial support from countries like Iran, Russia, and China.
Getting Around in Syria
Syria has four international airports. These are in Damascus, Aleppo, Lattakia, and Qamishli. These airports are main hubs for Syrian Air and other airlines.
Most of Syria's goods are transported by Syrian Railways. This railway system connects with Turkey's railways. Syria's railway system is well-maintained, even for a developing country. It has many express services and modern trains.
The country also has a large road network, which includes expressways. There are also some waterways that can be used for transport, but they are not very important for the economy.
People and Cultures of Syria
Most people in Syria live in the Euphrates River valley. They also live along the coastal plain, which is a fertile strip between the mountains and the desert. Before the civil war, about 99 people lived per square kilometer.
By 2014, about 9.5 million Syrians, which is half the population, had been displaced. This happened since the start of the Syrian Civil War in March 2011. About 4 million of these people became refugees outside the country. By 2020, over 5.5 million Syrians were refugees, and 6.1 million were displaced inside Syria.
Ethnic Groups in Syria
Syrians are a native Levantine people. They are closely related to people in nearby countries like Lebanon, Palestine, Jordan, and Israel. Syria's population is about 18.5 million (2019 estimate).
Syrian Arabs make up about 74% of the population. This group includes about 600,000 Palestinians living in Syria. The native Assyrians and Western Aramaic-speakers number around 400,000. Many Assyrians still speak Neo-Aramaic dialects.
The second largest ethnic group in Syria is the Kurds. They make up about 9% to 10% of the population, or about 2 million people. This includes about 40,000 Yazidis.
There are also smaller groups like Albanians, Bosnians, Georgians, Greeks, Persians, Pashtuns, and Russians. However, most of these groups have adopted Arab culture and language to some extent.
Languages Spoken in Syria
Arabic is the official language of Syria. Besides Arabic, other languages are spoken in the country. These include Kurdish, Turkish, Neo-Aramaic (with four different dialects), Circassian, Chechen, Armenian, and Greek. None of these minority languages are official.
English and French are also widely spoken as second languages. English is used more often than French.
Religions in Syria

Sunni Muslims make up about 74% of Syria's population. Sunni Arabs account for about 59–60% of the population. There are also around 1.2 million Christians in Syria.
Syrian Culture and Traditions
Syria has a traditional society with a very long and rich cultural history. Family, religion, education, self-discipline, and respect are all very important values. Syrians enjoy traditional arts, especially dances. These include the al-Samah, different types of Dabkeh, and the sword dance. Weddings and the birth of children are special times for showing off these folk customs.
Syrian Literature

Syrian writers have made important contributions to Arabic literature. They have a proud history of both spoken and written poetry. Many Syrian writers moved to Egypt and played a key role in the "nahda." This was an Arab literary and cultural rebirth in the 1800s.
Some well-known modern Syrian writers include Adonis, Muhammad Maghout, Haidar Haidar, Ghada al-Samman, Nizar Qabbani, and Zakariyya Tamer.
After the 1966 coup, there was more censorship. Because of this, historical novels became a way for writers to express their opinions. They would criticize the present by writing about the past. Syrian folk stories often use magical realism. This also allows for hidden criticism of current events. Salim Barakat, a Syrian writer living in Sweden, is famous for this style. Modern Syrian literature also includes science fiction and stories about future ideal societies. These can also be used to express different ideas.
Syrian Music
The music scene in Syria, especially in Damascus, has always been very important in the Arab world. This is especially true for classical Arab music. Syria has produced several famous Arab singers. These include Asmahan, Farid al-Atrash, and Lena Chamamyan.
The city of Aleppo is known for its muwashshah. This is a type of sung poetry from Andalusia. Sabri Moudallal helped make it popular. Aleppo is also known for popular singers like Sabah Fakhri.
Syrian Food

Syrian food is very rich and uses many different ingredients. The dishes are often linked to the specific regions of Syria where they first appeared. Syrian cuisine mostly includes dishes from the Southern Mediterranean, Greece, and Southwest Asia.
Some Syrian dishes also show influences from Turkish and French cooking. Examples include shish kebab, stuffed zucchini, and yabraʾ (stuffed grape leaves). The word yabraʾ comes from the Turkish word yaprak, which means leaf.
Some of the main dishes in Syrian cuisine are kibbeh, hummus, tabbouleh, fattoush, labneh, shawarma, mujaddara, shanklish, pastırma, sujuk, and baklava. Baklava is a sweet pastry made with thin layers of dough, chopped nuts, and honey.
Syrians often serve a selection of appetizers called meze before the main meal. Popular appetizers include Za'atar, minced beef, and cheese manakish. The Arabic flatbread khubz is always eaten with meze.
Drinks in Syria vary depending on the time of day or occasion. Arabic coffee is a very popular hot drink. It is usually made in the morning for breakfast or in the evening. It is often served to guests or after a meal. Arak, an alcoholic drink, is well-known. It is mostly served on special occasions. Other Syrian drinks include ayran, jallab, white coffee, and a local beer called Al Shark.
Related Pages
Images for kids
-
God head from the kingdom of Yamhad (around 1600 BC).
-
The ancient city of Palmyra.
-
The Roman theatre of Bosra in Syria.
-
A Fresco from Qasr al-Hayr al-Gharbî, built in the early 7th century.
-
Hafez al-Assad greets Richard Nixon in Damascus in 1974.
-
Dmitry Medvedev arriving in Damascus in May 2010.
-
Burj Islam, a beach north of Latakia.
-
An oil refinery in Homs.
-
The headquarters of Damascus University in Baramkeh.
See also
 In Spanish: Siria para niños
In Spanish: Siria para niños
 | Toni Morrison |
 | Barack Obama |
 | Martin Luther King Jr. |
 | Ralph Bunche |