Levant facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Levant |
|
|---|---|
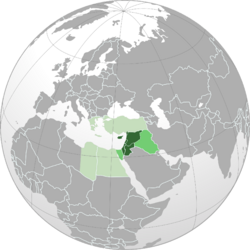
Countries and regions of the Levant in its broad, historical meaning (equivalent to the Eastern Mediterranean) Countries of the Levant in 20th-century usage Countries and regions sometimes included in 21st-century usage
|
|
| Countries and regions | Narrow definition:
Broad definition: |
| Population | Narrow definition: 44,550,926 |
| Demonym | Levantine |
| Languages | Arabic, Aramaic, Armenian, Circassian, Domari, Greek, Hebrew, Kurdish, Turkish |
| Time Zones | UTC+02:00 (EET) and UTC+03:00 (TRT/AST) |
| Largest cities | |
The Levant is a historical name for a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region. It's part of what we now call West Asia and the Middle East.
In its most common meaning today, the Levant includes Cyprus and the lands along the Mediterranean Sea in western Asia. This area is sometimes called "Greater Syria." It covers countries like Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, the Palestinian territories, and parts of Turkey.
This region is very important because it acts as a land bridge connecting Africa and Eurasia. In the past, the Levant was sometimes thought to include all countries along the Eastern Mediterranean, from Greece to Libya.
The word "Levant" comes from the Italian word levante, which means "rising." It refers to the sun rising in the east. This term became popular in English in the late 1400s. It's similar to the Arabic word al-Mashriq, which also means "the eastern place where the Sun rises."
In 1581, England created the Levant Company to trade with the Ottoman Empire. After World War I, the term "Levant States" was used for the French rule over Syria and Lebanon. This is why "Levant" often refers to modern Syria, Lebanon, Palestine, Israel, Jordan, and Cyprus.
Today, the term "Levant" is often used when talking about ancient history or archaeology. It means the same as "Syria-Palestine." This area is bordered by the Taurus Mountains in Turkey to the north, the Mediterranean Sea to the west, the Arabian Desert to the east, and the Sinai Peninsula to the south.
Many people consider "Levant" to be an old-fashioned word for the modern region. However, it's still used in fields like archaeology (e.g., Levantine archaeology) and when talking about food (e.g., Levantine cuisine). Also, Latin Christians from this area are still called Levantine Christians.
The Levant is known as the "crossroads of Western Asia, the Eastern Mediterranean, and Northeast Africa." People living in the Levant share not only their location but also similar foods, customs, and a long history.
Contents
What Does the Word 'Levant' Mean?
The word "Levant" first appeared in English in 1497. It originally meant "the East" or "Mediterranean lands east of Italy." It comes from the French word levant, which means "rising." This refers to the sun rising in the east. The word ultimately comes from the Latin word levare, meaning "to lift" or "to raise."
Many languages have similar words for "east" that mean "sunrise" or "morning land." For example, in Greek, Anatolē means "the direction of sunrise," which is where the name Anatolia comes from.
Over time, the meaning of "Levantine" changed. At first, it referred to Europeans living in the eastern Mediterranean. Later, it started to describe local people and minority groups in the region.
The term became common in English in the 1500s when English merchants began trading in the area. The English Levant Company was set up in 1581 to trade with the Ottoman Empire.

In the early 1800s, travel writers sometimes included parts of the Ottoman Empire and independent Greece (especially the Greek islands) in the Levant. In archaeology, the term referred to the overlapping cultures in this region from prehistoric times onwards. The French rule over Syria and Lebanon (1920–1946) was even called the "Levant states."
Where is the Levant Today?
Today, archaeologists and historians often use "Levant" to talk about the region's history. Scholars prefer this term because it describes a "wider cultural area" and avoids the "political meanings" that come with names like "Syria-Palestine."
The term is also used for modern events and people in the same region. Countries sometimes considered part of the Levant include Cyprus, Egypt, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, Syria, and Turkey. Many researchers include the island of Cyprus in their studies of the Levant. This is because Cyprus has always had strong ties to the mainland, especially due to its valuable copper resources.
Academic journals like the Journal of Levantine Studies and The Levantine Review have started using the word "Levant" to analyze politics and society in the region.
Defining the Levant for Archaeology
In archaeology, the Levant is often defined as the area known in Arabic as bilad al-sham, or "the land of Syria."
- North: The Taurus Mountains in Turkey.
- East: The eastern deserts, including the Euphrates River and the Syrian Desert. This means it doesn't usually include Mesopotamia or the main Arabian Peninsula.
- South: The Wadi al-Arish in the Sinai Peninsula.
- West: The Mediterranean Sea.
Subregions of the Levant
The Levant is often divided into two main parts:
- The Litani River in Lebanon separates the Northern Levant from the Southern Levant.
- Cyprus is also included as a third important subregion. Even though it's an island, its close location and natural resources, like copper, led to strong cultural connections with the mainland.
People and Cultures of the Levant
| Historical population of the Levant | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 14 | 4,300,000 | — |
| 164 | 4,800,000 | +11.6% |
| 500 | 4,127,000 | −14.0% |
| 900 | 3,120,000 | −24.4% |
| 1200 | 2,700,000 | −13.5% |
| 1700 | 2,028,000 | −24.9% |
| 1897 | 3,231,874 | +59.4% |
| 1914 | 3,448,356 | +6.7% |
| 1922 | 3,198,951 | −7.2% |
| Source: | ||
The largest religious group in the Levant are Muslims. Most of them identify as Arabs and speak Levantine Arabic. This is a dialect of Arabic that developed from older Arabic dialects in Syria. Recent studies show that people from the Levant get most of their family history from ancient people who spoke Semitic languages during the Bronze Age and Iron Age.
Other Arab groups include the Bedouins who live in the Syrian Desert. There are also non-Arab groups like Circassians, Chechens, Turks, Jews, Turkmens, Assyrians, Kurds, and Armenians.
The Muslim conquest of the Levant in the 600s brought Islam to the region. Most Muslims in the Levant are Sunni. There are also smaller Islamic groups like the Alawites and Nizari Ismailis in Syria, and Twelver Shiites in Lebanon.
Christian groups in the Levant include Greek Orthodox, Syriac Orthodox, and various Eastern Catholic groups like the Maronites. There are also Roman Catholics and Protestants. Armenians mostly belong to the Armenian Apostolic Church. Some people called Levantines or Franco-Levantines are also Roman Catholic.
Other religious groups in the Levant are Jews, Samaritans, Yazidis, and Druze.
This region is also very important for Abrahamic religions (Judaism, Christianity, and Islam). It has many holy sites like Masjid Al-Aqsa, the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, and the Western Wall in Jerusalem. Other important sites include the Sayyidah Zainab Mosque in Damascus and Antioch in Hatay.
Languages Spoken in the Levant
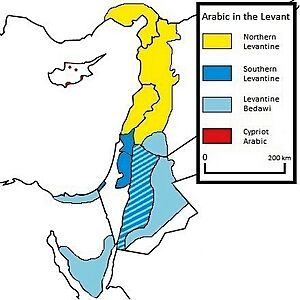
Most people in the Levant speak Levantine Arabic. This includes different types like North Levantine Arabic (spoken in Lebanon, Syria, and parts of Turkey) and South Levantine Arabic (spoken in Palestine and Jordan). Each of these has its own local differences. Other Arabic dialects, like Levantine Bedawi Arabic, are also spoken.
In Israel, the official language is Hebrew. Arabic was also an official language until 2018. The Arab minority in Israel speaks a dialect of Levantine Arabic that is very similar to what is spoken in the Palestinian territories.
In Cyprus, the two official languages are Turkish and Greek. Greek is spoken more in the south, and Turkish in the north. Two minority languages are recognized: Armenian and Cypriot Maronite Arabic. The latter is a mix of old Arabic with influences from Turkish and Greek, spoken by about 1,000 people.
Some communities also speak Aramaic, Greek, Armenian, Circassian, French, Russian, or English.
See also
 In Spanish: Levante mediterráneo para niños Overlapping regional designations
In Spanish: Levante mediterráneo para niños Overlapping regional designations
Subregional designations
- Southern Levant
Others
- French post offices in the Ottoman Empire ("Levant" stamps)
- History of the Levant
- Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (Referred to in current events as ISIL or ISIS)
- Levantine Sea
- Levantines (Latin Christians), Catholic Europeans in the Levant
- Wildlife of the Levant
Other places in the east of a larger region
- Levante, Spain
- Riviera di Levante, Italy
 | Laphonza Butler |
 | Daisy Bates |
 | Elizabeth Piper Ensley |