Ancient Near East facts for kids
The Ancient Near East was a very important part of the world, often called one of the "cradles of civilization." This means it was one of the first places where human societies grew into complex civilizations. People here first started farming all year round. This led to the creation of the first big cities.
Many things we know today began in the Ancient Near East. This includes ideas like different social classes and strong central governments. Empires also started here, along with organized religions and even organized warfare.
This region also saw the invention of the first writing systems. The first alphabet and the first money were created here. Early laws and important discoveries in astronomy and mathematics also came from this area. And don't forget the invention of the wheel!
Over time, the states in the Ancient Near East grew bigger and bigger. Eventually, powerful empires took control of many different cultures. These empires were often very focused on their armies.
Ancient civilizations in this area believed strongly in their spiritual ideas. They thought that gods and goddesses influenced everything on Earth. They also believed in telling the future, which was called divination. Important events and predictions were often written down in places like ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia.
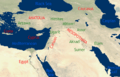
The Ancient Near East covered a large area. It included places like Mesopotamia (modern Iraq and nearby countries). It also included ancient Egypt, and parts of Iran (like Elam and Persia). Other areas were Anatolia (modern Turkey) and the Levant (modern Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine, and Jordan). Cyprus and the Arabian Peninsula were also part of it.
The history of the Ancient Near East usually starts with the rise of Sumer around 4000 BC. It covers the Bronze Age and the Iron Age. Historians have different ideas about when this period ended. Some say it was when the Achaemenid Empire conquered the region in the 6th century BC. Others say it was with the Macedonian Empire in the 4th century BC. Some even say it ended with the Muslim conquests in the 7th century AD.
The name "Ancient Near East" came about in the 1800s. It helped people tell the difference between the "Near East" and the "Far East." These were important regions for the British Empire at the time.
Time Periods of the Ancient Near East
Historians divide the long history of the Ancient Near East into different time blocks. This helps us understand the changes that happened over many centuries.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Antiguo Oriente Próximo para niños
In Spanish: Antiguo Oriente Próximo para niños