Medes facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Median Empire
|
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 625 BCE–549 BCE | |||||||||
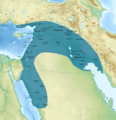
Median Empire, ca. 600 BC
|
|||||||||
| Capital | Ecbatana | ||||||||
| Religion | Zoroastrianism, possibly also Proto-Indo-Iranian religion | ||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| King | |||||||||
| Historical era | Iron Age | ||||||||
|
• Cyaxares united Median tribes
|
c. 625 BCE | ||||||||
| 549 BCE | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
The Medes were an ancient people who lived in the northwestern part of what is now Iran. This area was called Media or Medea by the Greeks. The Medes arrived in this region around 2000 BC, at the end of the Bronze Age. They were among the first Iranian tribes to settle there.
By the 6th century BC, the Medes had built their own powerful empire. It stretched from the southern coast of the Black Sea to parts of central Asia, Afghanistan, and Pakistan. The Medes ruled over many smaller states. One of these was the Persians, who later took over the Median Empire. This new empire became known as the Achaemenid Empire.
The Medes are famous for creating the first Iranian empire. It was the largest empire of its time. Later, Cyrus the Great united the Medes and Persians into one big Iranian empire. This empire is often called the Achaemenid Empire.
Contents
The Median Empire's Rise
The Medes became a strong power in the ancient world. Their empire grew to be very large. It included many different lands and peoples. The Medes were skilled warriors and leaders. They were able to bring many tribes under their rule.
Conquering New Lands
The Median Empire expanded its borders. It reached from the Black Sea in the west to parts of central Asia in the east. This vast territory included modern-day Azerbaijan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan. The Medes controlled important trade routes and rich lands.
Ruling Over Others
Many smaller states had to pay tribute to the Medes. This meant they had to give money or goods to the Median king. The Persians were one of these states. They lived south of the Medes. This relationship would later change history.
The Median Language
The Medes spoke a language related to other Iranian languages. These languages were spoken across a wide area. Ancient writers like Strabo noted how similar these languages were.
Language Connections
Strabo, a Greek historian, wrote about the language of the Medes. He said it was very similar to the languages spoken in Iran and other nearby regions. This shows that the Medes shared a common language family with many of their neighbors.
Words from the Past
The historian Herodotus mentioned a Median word, "Spaka," which meant "Dog." This word is still found in some Iranian languages today. It shows how ancient languages can leave traces in modern ones.
The End of the Empire
The Median Empire lasted for about 76 years. It was a powerful force for a long time. However, its rule eventually came to an end.
Rise of the Persians
The Persians, who were once under Median rule, grew stronger. Their leader, Cyrus the Great, was a brilliant military strategist. He led the Persians in a revolt against the Medes.
A New Empire Begins
In 549 BC, Cyrus the Great defeated the Median king. This marked the end of the Median Empire. Cyrus then created the Achaemenid Empire. This new empire combined the Medes and Persians. It became one of the largest and most famous empires in ancient history. The Medes played an important role in shaping the ancient world.
Images for kids
-
This ancient carving from Persepolis shows a Mede soldier behind a Persian soldier.
-
A map showing the neighboring Neo-Babylonian Empire at its largest size.
See also
 In Spanish: Media (región) para niños
In Spanish: Media (región) para niños
 | Jewel Prestage |
 | Ella Baker |
 | Fannie Lou Hamer |