Muslim conquests facts for kids
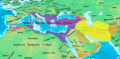
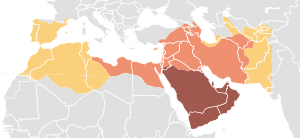
The Arab Muslim conquests were a series of military expansions that happened after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad in 632 AD. These conquests, also known as the Islamic or Arab conquests, led to the rapid growth of a large Arab Muslim empire. This empire stretched from India in the east, across Central Asia, the Middle East, and North Africa, all the way to Spain and Portugal in the west.
These conquests caused the fall of the Sassanid Empire (a powerful Persian empire) and greatly reduced the size of the Byzantine Empire. The success of the Arab armies can be understood by looking at the situation at the time. Both the Sassanid and Byzantine empires were very tired from fighting each other for many years. This made it hard for them to stop the fast-moving Arab armies, who often came from the desert.
Also, many people living under these empires, like Jews and Christians in Persia, and certain Christian groups in Syria, were not happy with their rulers. They sometimes even welcomed the Arab invaders, often because of religious disagreements within their own empires.
Contents
How the Arab Empire Expanded
The Arab Muslim conquests happened over many years, with different areas being taken over at different times.
Wars with the Byzantine Empire
The wars between the Arab Muslims and the Byzantine Empire lasted for a long time. First, the Rashidun Caliphate fought them, and then the Umayyad Caliphate continued the fight.
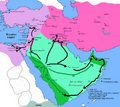
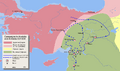
Under the Rashidun Caliphate, important areas like Syria (637 AD), Armenia (639 AD), Egypt (639 AD), and parts of North Africa (652 AD) were conquered.
Later, under the Umayyad Caliphate, the conquest of North Africa continued (665 AD). There was also a major siege of Constantinople (the capital of the Byzantine Empire) in 717-718 AD, and the city of Tbilisi was conquered in 736 AD. Much later, in 827 AD, southern Italy was also conquered.
Conquests in Asia
The last ruler of the powerful Sassanid Empire in Iran was defeated by the Rashidun armies in 633 and 636 AD. However, the Sassanid army was completely destroyed in 642 AD, marking the end of their empire.
During the 7th century, the Umayyad Caliphate also fought successfully against early Rajput kingdoms in northern India and expanded into Central Asia.
In 711 AD, a Muslim army defeated a local ruler near what is now Hyderabad, Sindh in Sindh (modern-day Pakistan). By 712 AD, Umayyad rule was established there. The Umayyads soon controlled most of what is now Pakistan, from Karachi to the borders of Kashmir. However, some semi-independent Arab states soon formed in the region.
Conquest of Spain and Portugal
The conquest of the Iberian Peninsula (modern-day Spain, Portugal, Gibraltar, and Andorra) began in 711 AD. Armies, mostly made up of Berbers and some Arabs, landed at Gibraltar on April 30th and moved northward.
This new territory was called Al-Andalus by the Arabs. It first became an Emirate and then an independent Umayyad Caliphate. This happened after the Umayyad dynasty in Damascus was overthrown by the Abbasids. Starting in 1031 AD, Christian kingdoms in the north began a long process called the Reconquista (meaning "reconquest"). This ended in 1492 AD when Granada, the last Muslim kingdom in Al-Andalus, fell to the Spanish kings.
Later Muslim Expansions
In Sub-Saharan Africa, especially in the Sahel region, Muslim territories continued to expand. Muslim traders played a big role in spreading Islam to new areas.
In more recent times, three powerful Muslim empires rose: the Ottoman Empire (in the Middle East and parts of Europe), the Safavid Empire (in Persia and Central Asia), and the Mughal Empire (in India). These empires competed with each other and eventually declined as European colonial powers grew stronger.
Decline of Empires
The Mughal Empire in India began to decline after the death of its emperor Aurangzeb in 1707. It was officially ended by the British after the Indian Rebellion of 1857.
Related Topics
Images for kids
-
The Battle of Talas between the Tang dynasty and the Abbasid Caliphate, around 751 AD.
-
A Byzantine manuscript showing Greek fire being used.