Colonialism facts for kids

Colonialism is when one country takes control of another land or region far away from its own borders. This new land is then called a colony. Usually, a stronger, richer country takes over a smaller, less powerful area. Sometimes, the words "colonialism" and "imperialism" mean almost the same thing.
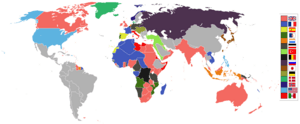
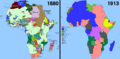
In the 1700s and 1800s, many powerful European countries like Britain, France, Spain, and the Netherlands set up colonies. They did this in Africa, South America, and the Caribbean.
Some countries used colonialism to gain more land for their people to live on. They helped settlers move to these new areas. Often, the local people living there were forced to leave their homes by armies. To keep these settlers safe, the colonizing countries often built military forts or set up police forces.
Other countries used colonialism to get land for farming or to take out valuable resources. These resources included trees (wood), coal, or metals. They might also set up their own government or military bases there.
Sometimes, countries used colonialism to get workers from the poorer country. These workers would then work in factories or on farms. This could be in the richer country or in the colony itself. In the past, powerful countries often forced people from poorer countries to work as slaves.
Contents
The History of Colonialism
Colonialism has a long history. The Phoenicians, an ancient people, created many trading colonies around the Mediterranean Sea. Carthage was one of their largest and most famous colonies.
Later, the Ancient Greeks also expanded their lands with colonies. Ancient Greece was made up of many city-states. Each city was independent and had its own government. These cities also traded goods and sometimes fought wars. To gain more influence or to protect trade routes, a city would send settlers to a new place. These settlers would then build a new city, which was called a colony.
Sometimes, a new colony had to pay taxes to its "mother city." In return, the mother city offered protection. However, these Greek colonies usually ruled themselves. The mother city did not send a governor to control them. Syracuse is a very famous example of a Greek colony.
If Greek settlers found a local tribe living in the new land, they would often fight them. They would force the local people to leave or make them slaves. The new colony would then use the land to grow crops or raise cattle.
The Romans created the word "colonia" from "colonus," meaning "farmer." At first, "colonia" meant a new town where Romans, including farmers and retired soldiers (veterans), moved. Over time, the word "colony" began to mean land ruled by people from a foreign country.
Different Kinds of Colonies
There were several ways countries practiced colonialism.
Settler Colonies
Some countries created Settler colonies. In these places, many people from the colonizing country moved to the new region. They often took the best land. They forced the indigenous peoples (like Native Americans or Maori) to move away. This caused many problems for the local people.
Countries that started as settler colonies include the United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and Argentina.
In some settler colonies, the new settlers married local people. Their children created new groups of people, like the mestizos in Mexico. In other places, settlers and local people lived separately. They did not often live together or marry. Examples include French Algeria (when France controlled Algeria) or Southern Rhodesia.
Dependencies
Another type of colonialism is when a powerful country sets up dependencies. Here, the colonizing country does not send thousands of settlers. Instead, it sets up a governing group (administrators) to control the existing local people or tribes.
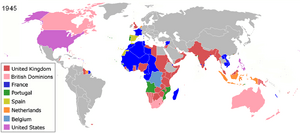
Examples include the British Raj, where the British government controlled India. Another is the Dutch East Indies, where the Netherlands controlled parts of Southeast Asia. The Japanese colonial empire also controlled many Asian territories this way.
Plantation Colonies
With a plantation colony, the powerful country used the poorer country's land to grow crops. The local people were often forced to become slaves and work on these large farms. Examples of plantation colonies include Barbados, Saint-Domingue, and Jamaica.
Trading Post Colonies
Another type of colony was the trading post colony. Rich and powerful countries set these up to have places where they could trade, sell goods, and do business. They often built military forts or police forces to make sure their laws were followed. Examples include Macau, Malacca, Deshima, and Singapore.
Other pages
- Massive colonization took place in Ancient India too. But the history of colonization is attributed to Greece only. In Ancient India Colonization began not with political conquest but with cultural conquest. Hinduism, and after centuries Buddhism became the main source of colonization. It was a colonization that began with cultural expansion leading to economic colonization. Indians were in the role of masters for a few centuries and in the role of slaves for centuries.
- Colonization
Images for kids
-
1541: Spanish Conquistadors founding Santiago de Chile
-
Dutch family in Java, 1927
-
Iberian Union of Spain and Portugal between 1580 and 1640
-
Map of the British Empire (as of 1910)
-
Colonial Governor of the Seychelles inspecting police guard of honour in 1972
-
Harbour Street, Kingston, Jamaica, c. 1820
-
The Battle of Isandlwana during the Anglo-Zulu War of 1879. After an initial defeat the British were able to conquer Zululand.
-
Governor General William Howard Taft addressing the audience at the Philippine Assembly in the Manila Grand Opera House
-
The Russian settlement of St. Paul's Harbour (present-day Kodiak, Alaska), Russian America, 1814
-
Portuguese women in Goa, India, 16th century
-
The Battle of Tétouan, 1860, by Marià Fortuny
-
Spanish General Arsenio Martínez Campos in Havana, Colonial Cuba, 1878
-
Muslim Bosniak resistance during the battle of Sarajevo in 1878 against the Austro-Hungarian occupation
-
Map of the European Union in the world, with Overseas Countries and Territories and Outermost Regions. (N.B. The United Kingdom left left the Union in 2020.)
-
Governor Lord Ranfurly reading the annexation proclamation to Queen Makea on 7 October 1900.
-
Argentine C-130 and control tower, Marambio Airport
-
The Conquest of the Desert extended Argentine power into Patagonia.
-
Siamese Army in Laos in 1893.
-
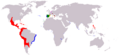
Portuguese trade routes (blue) and the rival Manila-Acapulco galleons trade routes (white) established in 1568
-
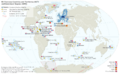
Dutch East India Company was the first-ever multinational corporation, financed by shares that established the first modern stock exchange.
-
Slave traders in Gorée, Senegal, 18th century
-
The First Anglo-Ashanti War, 1823–31
-
Gandhi with Lord Pethwick-Lawrence, British Secretary of State for India, after a meeting on 18 April 1946
-
The annual Notting Hill Carnival in London is a celebration led by the Trinidadian and Tobagonian British community.
-
British Togoland in 1953
-
Governor-General Félix Éboué welcomes Charles de Gaulle to Chad
-
"The East offering its riches to Britannia", painted by Spiridione Roma for the boardroom of the British East India Company
-
Since 1945, immigration to the United Kingdom under British nationality law has been significant, in particular from the former British Empire.
-
Boer family in South Africa, 1886
-
Irish leaving Ireland, many in response to the Great Famine in the 1840s
See also
 In Spanish: Colonialismo para niños
In Spanish: Colonialismo para niños