Jamaica facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Jamaica
Jumieka (Jamaican Patois)
|
|
|---|---|
|
Motto: "Out of Many, One People"
|
|
|
Anthem: "Jamaica, Land We Love"
|
|
 |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Kingston 17°58′17″N 76°47′35″W / 17.97139°N 76.79306°W |
| Official languages | English |
| Vernacular language | Jamaican Patois |
| Ethnic groups |
|
| Religion |
|
| Demonym(s) | Jamaican |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
• Monarch
|
Charles III |
| Patrick Allen | |
| Andrew Holness | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Independence
from the United Kingdom
|
|
|
• Granted
|
6 August 1962 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
10,991 km2 (4,244 sq mi) (160th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
1.5 |
| Population | |
|
• 2019 estimate
|
2,734,092 (137th) |
|
• 2011 census
|
2,697,983 |
|
• Density
|
266/km2 (688.9/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2021) | ▲ 40.2 medium |
| HDI (2022) | high · 115th |
| Currency | Jamaican dollar (JMD) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +1-876 +1-658 (Overlay of 876) |
| ISO 3166 code | JM |
| Internet TLD | .jm |
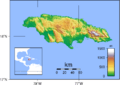
Jamaica is a beautiful island country located in the Caribbean Sea. It covers about 10,990 square kilometers (4,244 square miles). This makes it the third-largest island in the Greater Antilles. It is also the fourth-largest island country in the Caribbean.
Jamaica is about 145 kilometers (90 miles) south of Cuba. It lies 191 kilometers (119 miles) west of Hispaniola. Hispaniola is the island where Haiti and the Dominican Republic are located.
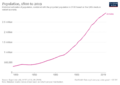
Jamaica is the third most populated English-speaking country in the Americas. Only the United States and Canada have more people. It is also the fourth most populated country in the Caribbean. Kingston is the capital and largest city. It has a population of about 937,700 people.
Most Jamaicans have African roots. There are also many people with European, Chinese, Indian, and Lebanese backgrounds. Many people have mixed backgrounds too. Since the 1960s, many Jamaicans have moved to other countries for work. They live in places like Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
The official language of Jamaica is English. People also speak Jamaican Creole English.
Contents
Government and How Jamaica is Run

Jamaica is a parliamentary democracy. This means people vote for leaders who represent them in a parliament. It is also a constitutional monarchy. This means King Charles III is the head of state.
King Charles III is also the head of state for 15 other countries. He mostly lives in the United Kingdom. In Jamaica, he is represented by the Governor-General. The Prime Minister of Jamaica chooses the Governor-General. The King then appoints them.
The Governor-General also appoints all members of the Cabinet. This is done based on the Prime Minister's advice. Both the King and the Governor-General have mostly ceremonial roles. This means they perform important duties but don't make daily government decisions.
Exploring Jamaica's Geography and Weather
Jamaica is the third-largest island in the Greater Antilles. It is smaller than Cuba and Hispaniola, but larger than Puerto Rico. The island is 235 kilometers (146 miles) long from east to west. Its width varies from 35 kilometers (22 miles) to 82 kilometers (51 miles).
Jamaica is mostly one main island. There are also a few small islands close to the coast.
Mountains and Rivers of Jamaica
The Blue Mountains are the longest mountain range in Jamaica. They are home to the island's highest point, Blue Mountain Peak. This peak stands at 2,256 meters (7,402 feet) tall.
The Black River is one of Jamaica's longest rivers. It is about 53.4 kilometers (33.2 miles) long. It was once called Rio Caobana.
Famous Natural Attractions
Kingston Harbour is the seventh-largest natural harbor in the world. This large harbor helped Kingston become the capital city in 1872.
Popular places to visit include Dunn's River Falls in St. Ann. There are also YS Falls in St. Elizabeth. The Blue Lagoon in Portland is believed to be an old volcano crater. Port Royal was hit by a big earthquake in 1692. This event helped shape the island's Palisadoes.
Jamaica's Tropical Climate
Jamaica has a tropical climate. This means it is usually hot and humid.
The island is in the hurricane belt of the Atlantic Ocean. Because of this, Jamaica sometimes gets strong storms. Hurricanes Charlie and Gilbert hit Jamaica directly in 1951 and 1988. In the 2000s, hurricanes Ivan, Dean, and Gustav also brought severe weather.
Protecting Jamaica's Nature
Jamaica has many different natural areas. These include dry and wet forests, rainforests, wetlands, caves, rivers, and coral reefs. The government protects some of these important areas.
Some protected areas are the Cockpit Country, Hellshire Hills, and Litchfield forest reserves. In 1992, Jamaica's first marine park was created in Montego Bay. It covers almost 15 square kilometers (5.8 square miles).
The Portland Bight Protected Area was set up in 1999. The next year, the Blue and John Crow Mountains National Park was created. This park covers about 300 square miles (777 square kilometers) of wilderness. It is home to thousands of plant species and rare animals.
Plant Life in Jamaica
Jamaica's plant life has changed a lot over hundreds of years. When the Spanish arrived in 1494, most of the country was covered in thick forests. European settlers cut down many trees for building and ships. They also cleared land for farming.
Many new plants were brought to the island. These include sugarcane, bananas, and citrus trees. Areas with heavy rainfall have bamboo, ferns, ebony, mahogany, and rosewood trees. Dry-area plants like cactus grow along the south and southwest coasts. Some parts of the west and southwest have large grasslands with scattered trees.
Jamaican Culture: Music, Art, and More
Though Jamaica is a small country, its culture is known worldwide. Many popular music styles started here. These include reggae, ska, mento, rocksteady, dub, and more recently, dancehall and ragga. All these styles came from the island's lively music scene.
Jamaica also helped shape punk rock music through reggae. Reggae has even influenced American rap music. This is because both styles have rhythmic, African roots. Some famous rappers, like The Notorious B.I.G., Busta Rhymes, and Heavy D, have Jamaican family.
World-famous reggae musician Bob Marley was Jamaican. So was Millie Small, who sang "My Boy Lollipop."
Delicious Jamaican Food
Jamaica is famous for its Jamaican jerk spice. This spice is used in many dishes. Other popular foods include curries and rice and peas. These are very important parts of Jamaican cooking.
Jamaica is also home to Red Stripe beer. And don't forget Jamaican Blue Mountain Coffee, which is known around the world.
Sports in Jamaica: A Nation of Athletes
Sports are a big part of life in Jamaica. The island's athletes often do much better than expected for a small country. The most popular local sport is cricket. However, Jamaicans are especially good at track and field athletics on the world stage.
Cricket and Track & Field
Jamaica has produced some of the world's best cricketers. The country hosted some games for the 2007 Cricket World Cup. The Jamaica national cricket team plays in regional games. They also provide players for the West Indies team. Sabina Park is the only place on the island where Test cricket matches are played. The Greenfield Stadium is also used for cricket. Chris Gayle is a very famous Jamaican batsman who plays for the West Indies.
Since gaining independence, Jamaica has always had amazing track and field athletes. Kids in Jamaica start athletics very young. Most high schools have strong athletics programs. Their best athletes compete in national and international events. It's common for young athletes in Jamaica to become famous even before they reach the international stage.
Over the last 60 years, Jamaica has had many world-class sprinters. These include Olympic and World Champion Usain Bolt. He holds the world record for the men's 100m at 9.58 seconds. He also holds the 200m record at 19.19 seconds. Jamaica also has several great amateur and professional boxers.
Other Popular Sports
Association football (soccer) and horse-racing are also popular in Jamaica. The national football team played in the 1998 FIFA World Cup.
The Jamaica national bobsled team was once a strong competitor in the Winter Olympics. They even beat many well-known teams. Chess and basketball are widely played in Jamaica. They are supported by the Jamaica Chess Federation (JCF) and the Jamaica Basketball Federation (JBF). Netball is also very popular. The Jamaica national netball team, called The Sunshine Girls, is often ranked among the top five teams in the world.
Jamaica's Economy and How it Works
Jamaica has a mixed economy. This means it has both government-owned and private businesses. Key parts of Jamaica's economy include agriculture, mining, manufacturing, tourism, and financial and insurance services.
Tourism and mining bring in the most foreign money. About half of Jamaica's economy comes from services, especially tourism. Around 1.3 million foreign tourists visit Jamaica every year.
Because of its location in the Caribbean Sea, Jamaica is on a major shipping route to the Panama Canal. This means many container ships pass through. The container terminal at the Port of Kingston has grown a lot recently to handle more ships. Jamaica also has nine lighthouses to help ships navigate safely.
Images for kids
-
Henry Morgan was a famous Caribbean pirate and plantation owner.
-
Marcus Garvey, a national hero who started the Back to Africa Movement.
-
Jamaica's national bird, a red-billed streamertail.
-
A Jamaican boa snake.
-
Northern suburbs of Kingston, Jamaica's capital.
-
Mandeville Church (built 1816), an Anglican church in Manchester Parish.
-
Usain Bolt is one of the most famous sprinters in the world.
-
A US Airways aircraft landing at Montego Bay (2013).
See also
 In Spanish: Jamaica para niños
In Spanish: Jamaica para niños
 | James B. Knighten |
 | Azellia White |
 | Willa Brown |