Left- and right-hand traffic facts for kids
Have you ever noticed that in some countries, cars drive on the left side of the road, while in others, they drive on the right? This is called left-hand traffic (LHT) or right-hand traffic (RHT). It's a basic rule that helps traffic flow smoothly and safely.
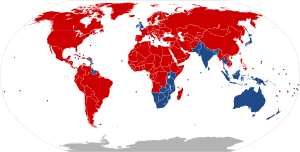
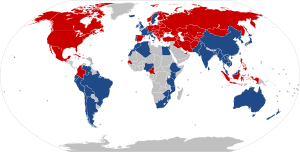
Most countries, about 165 of them, use RHT. The other 75 countries use LHT. Countries with LHT make up about one-sixth of the world's land area. They also have about one-third of the world's people and one-quarter of its roads. A long time ago, in 1919, the number of LHT and RHT countries was almost equal. But since then, many LHT countries have switched to RHT.
Many countries that drive on the left used to be part of the British Empire. But some, like Japan, Thailand, Indonesia, and Suriname, were not. On the other hand, many countries that drive on the right were once part of the French colonial empire.
For trains, LHT is common in Western Europe (except Germany, Denmark, Austria, Spain, and the Netherlands). It's also common in Latin America (except Mexico) and in countries that were part of the British and French Empires. Trains in North America and Central and Eastern Europe usually use RHT.
Even on water, there are rules similar to RHT. According to international rules for ships, boats in narrow channels must keep to the right side. When two power-driven boats meet head-on, both must turn to their right. For airplanes, rules in the US suggest RHT principles, both in the air and on water.
In LHT countries, vehicles drive on the left. Cars usually have the steering wheel on the right side. This means the driver sits closer to the center of the road. The passenger sits closer to the curb. Roundabouts in LHT countries go around in a clockwise direction. In RHT countries, everything is the opposite. Cars drive on the right, the driver sits on the left side of the car, and roundabouts go counterclockwise.
History of Driving Sides
How Driving Sides Started in Europe
Ancient soldiers from Greece, Egypt, and Rome often marched on the left side. In 1998, scientists found old Roman road tracks in England. The tracks were deeper on the left side when leaving a quarry. This suggests that carts drove on the left, as they would be heavier when leaving the quarry. Around the year 1300, Pope Boniface VIII told pilgrims to keep to the left.
The first time LHT was mentioned in English law was in 1756. This rule was for London Bridge. After the French Revolution, all traffic in France started keeping to the right.
Some cities in Europe had different rules than the rest of their country. For example, Rotterdam in the Netherlands was LHT until 1917, even though the rest of the country was RHT. Russia completely switched to RHT in February 1917.
After the Austro-Hungarian Empire broke apart, many new countries slowly changed to RHT. For example, parts of Austria switched between 1921 and 1938. In Romania, some areas were LHT until 1919, while others were already RHT. Nazi Germany made Czechoslovakia and Slovakia switch to RHT in 1938–1939.
In Italy, country roads were RHT, but cities were LHT until 1927. Rome switched to RHT in 1924, and Milan in 1926. However, the Rome Metro, built in 1955, still uses LHT.
Portugal switched to RHT in 1928. Finland, which used to be part of LHT Sweden, switched to RHT in 1858. This was ordered by Russia.

Sweden made a big change to RHT in 1967. Before this, it had been LHT since about 1734. This was unusual because its neighbors drove on the right. Also, about 90% of cars in Sweden were already left-hand drive (LHD). People voted against changing in 1955, but the government decided to do it anyway. The switch happened on Sunday, September 3, 1967, at 5 AM. This day was called Dagen H. After the switch, the number of accidents dropped a lot, but then went back to normal. When Iceland switched the next year, it was called Hægri dagurinn.
The United Kingdom still uses LHT. But its territories like Gibraltar and British Indian Ocean Territory use RHT. In the late 1960s, the UK thought about switching to RHT. But they decided it would be too dangerous and expensive because the country is so built up.
Today, only four countries in Europe still use LHT. All of them are islands and used to be part of the British Empire. These are the UK (including Northern Ireland), Cyprus, the Republic of Ireland, and Malta.
Changes in Africa
Egypt kept RHT even after the British took control. This was because Napoleon had introduced RHT earlier.
The British brought LHT to British West Africa. But after these countries became independent, they switched to RHT. This was because they shared borders with former French colonies that used RHT. Countries like Ghana, Gambia, Sierra Leone, and Nigeria all switched. Britain also brought LHT to Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and South Africa. These countries still use LHT. Sudan switched to RHT in 1973 because its neighbors used RHT.
The Portuguese Empire used LHT and brought it to Mozambique and Angola. Even though Portugal itself switched to RHT in 1928, these African territories stayed LHT. This was because they bordered former British colonies. Other former Portuguese colonies in Africa, like Guinea-Bissau, São Tomé and Príncipe, and Cape Verde, switched to RHT in 1928.
France introduced RHT in French West Africa and the Maghreb region. Countries like Mali, Mauritania, Ivory Coast, Burkina Faso, Benin, Niger, Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia still use RHT. Other former French colonies like Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Djibouti, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo also use RHT.
Rwanda and Burundi are RHT, but they are thinking about switching to LHT. This would match their neighbors in the East African Community. A study in 2009 showed that many Rwandans wanted to switch. They thought RHD cars would be cheaper and easier to fix. Also, it would help traffic rules match other EAC countries. In 2015, Rwanda allowed RHD vehicles.
North American Driving Sides
In Canada, the British introduced LHT. But British Columbia, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island all switched to RHT between 1920 and 1924. Newfoundland, which was a British colony then, switched to RHT in 1947. Areas that were part of New France (like Quebec) have always used RHT.
When the British first settled North America, they drove on the left. But after the United States became independent in 1776, they wanted to be different from Britain. They slowly changed to RHT. This was also influenced by help from France in the War of Independence.
In the late 1700s, large wagons pulled by many horses helped make RHT common in the US. The driver usually sat on the left horse to hold the whip in their right hand. From this position, it was easier to see oncoming wagons if they passed on the left. The first law to keep right in the US was in 1792. New York made RHT official in 1804, New Jersey in 1813, and Massachusetts in 1821. Today, the US is RHT, except for the United States Virgin Islands, which uses LHT like many nearby islands.
Some special vehicles in the US, like postal trucks or garbage trucks, still have the steering wheel on the right side.
In the Caribbean, islands usually drive on the same side as the country that used to rule them. Many islands were British colonies and drive on the left. These include Jamaica, Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Trinidad and Tobago, and The Bahamas.
Asia's Driving Rules
The British brought LHT to British India (now India, Pakistan, Myanmar, and Bangladesh). They also brought it to British Malaya (now Malaysia, Brunei, and Singapore) and British Hong Kong. All these places are still LHT, except Myanmar. Myanmar switched to RHT in 1970, but many of its roads are still set up for LHT. Most cars there are used RHD cars from Japan. Afghanistan was LHT until the 1950s, like its British-influenced neighbors.
The Portuguese Empire introduced LHT to Macau and East Timor. Both places are still LHT. Macau is now part of RHT China, so cars have to switch sides at the Lotus Bridge. East Timor shares an island with Indonesia, which is also LHT. East Timor actually switched to RHT with Portugal in 1928, but then switched back to LHT in 1976 during Indonesian rule.
China uses RHT, except for Hong Kong and Macau. These two regions are LHT because of their history as colonies. In the 1930s, LHT was common in China, but then northern areas became RHT. In 1946, Nationalist China adopted RHT. This rule stayed when the Communist Party took over the mainland.
Both North Korea and South Korea switched to RHT in 1945. This happened after they were freed from Japanese rule.
The Philippines mostly used LHT during its Spanish and American colonial times. It stayed LHT during the Japanese occupation. But during the Battle of Manila in 1945, American forces drove their tanks on the right side to make moving easier. RHT became official in 1945.
Japan was never part of the British Empire, but its traffic also drives on the left. This custom goes back to the Edo period (1603-1868). It became more official in 1872 when Japan's first railway was built with British help. Trains and trams all drove on the left. By 1924, left-side driving was officially written into law. After World War II, Okinawa, which was ruled by the US, used RHT. When it returned to Japan in 1972, it switched back to LHT in 1978. This change was called 730.
Vietnam became RHT as part of French Indochina, and so did Cambodia. In Cambodia, RHD cars were banned in 2001, even though most cars there were RHD.
Oceania's Driving Rules
Many former British colonies in Oceania have always used LHT. These include Australia, New Zealand, Fiji, Kiribati, Solomon Islands, Tonga, and Tuvalu. Also, Nauru and Papua New Guinea, which Australia used to manage, are LHT.
Samoa, which was a German colony, had used RHT for over 100 years. But it switched to LHT in 2009. This was the first country in almost 30 years to switch. The change was made so Samoans could buy cheaper RHD cars from Australia, New Zealand, or Japan. It also helped Samoa match other South Pacific nations. Some people protested the change, but it happened smoothly on Monday, September 7, 2009, at 6 AM. The day of the switch and the next day were public holidays to reduce traffic.
South American Driving Sides
Brazil was a Portuguese colony. It had mixed driving rules until 1928, when all regions switched to RHT. This was the same year Portugal switched. Other Central and South American countries that switched from LHT to RHT include Argentina, Chile, Panama, Paraguay, and Uruguay.
Suriname and its neighbor Guyana are the only two countries in South America that still use LHT.
Changing Sides at Borders
Even though many LHT countries are islands, cars sometimes need to cross borders into RHT areas. These borders are mostly in Africa and southern Asia. The Vienna Convention on Road Traffic has rules for foreign cars in countries that have signed it.
LHT Thailand has three RHT neighbors: Cambodia, Laos, and Myanmar. At most borders, a simple traffic light helps cars switch sides. But some places have special interchanges that allow traffic to switch without stopping.
There are four road crossings between Hong Kong (LHT) and Mainland China (RHT). The Takutu River Bridge connects LHT Guyana and RHT Brazil. It's the only border in the Americas where traffic changes sides.
The United Kingdom is separated from Europe by the English Channel. But many vehicles travel between the UK and France through the Channel Tunnel.
How Road Vehicles Are Set Up
Driver's Seat Position
In RHT countries, cars are usually LHD, meaning the driver sits on the left side. In LHT countries, it's the opposite; cars are RHD, and the driver sits on the right. The driver's side, which is closer to the center of the road, is sometimes called the offside. The passenger side, closer to the curb, is called the nearside.
Most windshield wipers are designed to clean the driver's side better. They have a longer blade on the driver's side. On LHD cars, they wipe from right to left (from inside the car). On RHD cars, they do the opposite.
In the past, the driver's seat position wasn't always fixed. Before 1910, most American cars were RHD. But in 1908, Henry Ford made the Ford Model T LHD for RHT America. He said it was safer because the driver could see oncoming cars better. By 1915, other car makers followed Ford's lead.
Sometimes, the driver sits on the nearside (curbside) for special reasons. For example, street sweepers or delivery vehicles might have the driver on the nearside. This helps the driver see the edge of the road or make deliveries more easily. Some special trucks can even switch their steering wheel from left to right.
Motorcycles are usually mounted from the left side. Their kickstands are also usually on the left. This makes it easier to get on from the safer curbside in LHT countries.
Headlights and Other Lights
Most low-beam headlights shine light unevenly. They are designed for one side of the road. For LHT countries, headlights shine more light towards the front-left. For RHT countries, they shine more light towards the front-right. This helps drivers see obstacles and signs without blinding oncoming traffic.
In Europe, headlights must be adjustable if a car is driven temporarily on the other side of the road. This can be done by adding special strips or lenses to the headlight. Some modern headlights can even adjust automatically using GPS. They change their beam pattern when the car moves from an LHT country to an RHT country, or vice versa.
Rear Fog Lights
In the European Union, cars must have one or two red rear fog lights. If there's only one, it must be on the driver's side of the car.
Rail Traffic Rules
In most countries, trains travel on the same side of the tracks as cars on the road. However, sometimes railways were built using LHT British technology. Then, the country's road traffic switched to RHT, but the trains stayed LHT. This happened in countries like Argentina, Belgium, France, Italy, and Sweden.
In Indonesia, it's the opposite: trains use RHT, but roads use LHT. China mostly uses LHT for long-distance trains but RHT for metro systems. In Spain, trains use RHT, but the metros in Madrid and Bilbao use LHT. Trams usually follow the same side as road traffic because they often share roads.
Countries and Their Driving Sides
Out of 195 countries recognized by the United Nations, 141 use RHT and 54 use LHT for roads. The table below shows which side each country drives on. It also notes if a country switched sides and why.
| Country | Road traffic | Road switched sides | Notes, exceptions |
|---|---|---|---|
| RHT | |||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | Was French Algeria until 1962. | ||
| RHT | Located between France and Spain. | ||
| RHT | 1928 | Was a Portuguese colony until 1975. | |
| LHT | Was a British colony. Caribbean island. | ||
| RHT | 1945 | The day of the switch, June 10, is still celebrated as Road Safety Day. | |
| RHT | |||
| LHT | Was made of British colonies before 1901. Includes Norfolk Island. | ||
| RHT | 1921–38 | ||
| RHT | |||
| LHT | Was a British colony. Caribbean island. | ||
| RHT | 1967 | Was a British protectorate. Switched to match its neighbors. | |
| LHT | Was part of British India before 1947. | ||
| LHT | Was a British colony. Caribbean island. | ||
| RHT | 1899 | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | 1961 | Was a British colony. Switched to match its neighbors. | |
| RHT | Was part of French West Africa. | ||
| LHT | Was under British protection. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | 1918 | Switched after the Austro-Hungarian Empire ended. | |
| LHT | |||
| RHT | 1928 | ||
| LHT | Was under UK protection. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | Was part of French West Africa. | ||
| RHT | Was a Belgian colony. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | 1961 | ||
| RHT | 1920–24 | ||
| RHT | 1928 | Was a Portuguese colony. | |
| RHT | Was a French colony. | ||
| RHT | Was a French colony. | ||
| RHT | 1920s | ||
| RHT/LHT | 1946 | Mainland China is RHT. Hong Kong and Macau are LHT due to their colonial history. | |
| RHT | |||
| RHT | Was a French colony. | ||
| RHT | Was a French colony. | ||
| RHT | Was a Belgian colony. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | Was part of French West Africa. | ||
| RHT | 1926 | Switched as part of Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. | |
| RHT | |||
| LHT | Was under UK rule. Island nation. | ||
| RHT | 1939 | Switched during German occupation. | |
| RHT | Includes Faroe Islands and Greenland. | ||
| RHT | |||
| LHT | Was a British colony. Caribbean island. | ||
| RHT | |||
| LHT | 1976 | Was a Portuguese colony. Switched to RHT in 1928, then back to LHT in 1976 during Indonesian rule. | |
| RHT | |||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | 1964 | Was an Italian colony. | |
| RHT | |||
| LHT | Was a British colony. Drives on the same side as neighboring South Africa. | ||
| RHT | 1964 | ||
| LHT | Was a British colony. Island nation. | ||
| RHT | 1858 | ||
| RHT | 1792 | Includes many overseas territories like French Polynesia and Réunion. | |
| RHT | |||
| RHT | 1965 | Was a British colony. Switched to RHT because it's surrounded by former French colonies. | |
| RHT | Many cars are RHD due to imports from Japan. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | 1974 | Was a British colony. Switched to RHT. RHD cars were banned for new registrations just before the switch. | |
| RHT | |||
| LHT | Was a British colony. Caribbean island. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | 1928 | Was a Portuguese colony. | |
| LHT | Was a British colony. One of the few LHT countries in the Americas. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | Located inside Rome. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | 1941 | Was LHT like most of Austria-Hungary, but switched during World War II. | |
| RHT | 1968 | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | |||
| LHT | Was part of British India. | ||
| LHT | Roads are LHT, but railways use RHT. | ||
| LHT | Was part of the United Kingdom. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | 1924–26 | ||
| LHT | Was a British colony. Caribbean island. | ||
| LHT | |||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | |||
| LHT | Was part of the British East Africa Protectorate. | ||
| LHT | Was a UK colony. Pacific islands. | ||
| RHT | 1946 | Was LHT under Japanese rule. Switched to RHT after Japan surrendered. | |
| RHT | 1946 | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | Many cheaper RHD cars are imported from Japan. | ||
| RHT | RHT was used when it was part of French Indochina. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | Was a French Mandate. | ||
| LHT | Surrounded by LHT South Africa. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | Was an Italian colony. | ||
| RHT | Located between Switzerland and Austria. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | Was a French colony. | ||
| LHT | Was a British colony. | ||
| LHT | Was a British colony. | ||
| LHT | Was a British colony. Island nation. | ||
| RHT | Was part of French West Africa. | ||
| LHT | Was a British colony. Island nation. | ||
| RHT | Was under American control. | ||
| RHT | Was part of French West Africa. | ||
| LHT | Was a British colony. Island nation. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | Was under American control. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | Was under French control. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | Was a French colony. | ||
| LHT | Was a Portuguese colony. | ||
| RHT | 1970 | Was part of British India. Switched to RHT in 1970. | |
| RHT | 1906 | Includes Curaçao, Sint Maarten, and Aruba. | |
| LHT | 1918 | Was managed by South Africa. | |
| LHT | 1918 | Was managed by Australia, New Zealand, and the UK. Island nation. | |
| LHT | Shares a border with LHT India. | ||
| LHT | Was a British colony. Pacific island. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | Was part of French West Africa. | ||
| RHT | 1972 | Was a British colony. Switched to RHT because of its French-speaking neighbors. | |
| RHT | |||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | |||
| LHT | Was part of British India. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | 1943 | ||
| LHT | Switched to LHT after Australia took over German New Guinea. | ||
| RHT | 1945 | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | 1946 | Was LHT during Spanish and American rule. Switched to RHT in 1945 during the Battle of Manila. | |
| RHT | |||
| RHT | 1928 | Its colonies like Macau and Mozambique did not switch. | |
| RHT | Was a British protectorate. Switched to match its neighbors. | ||
| RHT | 1919 | Parts that were once Austria-Hungary were LHT until 1919. | |
| RHT | In the Far East, many RHD cars are imported from Japan. | ||
| RHT | |||
| LHT | Was a British colony. Caribbean island. | ||
| LHT | Was a British colony. Caribbean island. | ||
| LHT | Was a British colony. Caribbean island. | ||
| LHT | 2009 | Switched to LHT to allow cheaper car imports from Australia, New Zealand, and Japan. | |
| RHT | Surrounded by Italy. | ||
| RHT | 1928 | Was a Portuguese colony. | |
| RHT | 1942 | ||
| RHT | Was part of French West Africa. | ||
| RHT | 1926 | Switched as part of Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. | |
| LHT | Was a British colony. Island nation. | ||
| RHT | 1971 | Was a British colony. Switched to RHT because of its French-speaking neighbors. | |
| LHT | Was a British colony. | ||
| RHT | 1939–41 | Switched during German occupation. | |
| RHT | 1926 | Switched as part of Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. | |
| LHT | Was a British colony. Island nation. | ||
| RHT | Former British Somaliland was LHT, but it joined with former Italian Somaliland which was RHT. | ||
| LHT | Was a British colony. | ||
| RHT | 1973 | Was part of Sudan then. | |
| RHT | 1924 | Madrid was LHT until 1924. The Madrid Metro still uses LHT. | |
| LHT | Was British Ceylon. | ||
| RHT | 1973 | Was Anglo-Egyptian Sudan. | |
| LHT | 1920s | Was a Dutch colony. One of the few LHT countries in the Americas. | |
| RHT | 1967 (3 September) | The day of the switch was called Dagen H. Most cars were already LHD. | |
| RHT | |||
| RHT | Was under French and Italian control. | ||
| RHT | 1946 | Was LHT under Japanese rule. Switched to RHT in 1946. | |
| RHT | |||
| LHT | Was part of the British East Africa Protectorate. | ||
| LHT | One of the few LHT countries not a former British colony. | ||
| RHT | |||
| LHT | Was a British protectorate. Polynesian island nation. | ||
| LHT | Was a British colony. Caribbean island. | ||
| RHT | French RHT was used from 1881. | ||
| RHT | 1920s | ||
| RHT | |||
| LHT | Was a British colony. Island nation. | ||
| LHT | Was a British Uganda Protectorate. | ||
| RHT | 1922 | ||
| RHT | Was a British protectorate. Switched to match its neighbors. | ||
| LHT/RHT | 1929 (in Gibraltar) |
Includes Crown dependencies and Overseas Territories. Most are LHT. Gibraltar is RHT because it borders Spain. The British Indian Ocean Territory is also RHT. | |
| RHT/LHT | The United States Virgin Islands is LHT, like many Caribbean islands. | ||
| RHT | 1945 | Switched to RHT on September 2, 1945. | |
| RHT | |||
| RHT | Was managed by France and the United Kingdom. | ||
| RHT | |||
| RHT | Became RHT as French Indochina. | ||
| RHT | Was occupied by Spain. | ||
| RHT | 1977 | South Yemen changed to RHT in 1977. North Yemen was already RHT. | |
| LHT | Was a British colony. | ||
| LHT | Was a British colony. |
Gallery
-
Left-hand traffic on the M25 motorway in the UK.
-
Left-hand traffic in Vienna, Austria, around 1930.
-
A road sign in the British county of Kent placed on the right side of the road.
Images for kids
-
Right-hand traffic on Jamsil Bridge in South Korea.
-
Left-hand traffic on the M1 motorway in the UK.
-
Left-hand traffic on Kwun Tong Road in Hong Kong.
See also
 In Spanish: Sentido de la circulación para niños
In Spanish: Sentido de la circulación para niños