British India facts for kids
British India was a large part of India in South Asia that was controlled by the British for a long time. This period lasted for hundreds of years.
From the 1600s until 1858, these areas were managed by the English East India Company. This was a powerful trading company. After 1858, the British government took direct control. This period, from 1858 to 1947, was known as the British Raj.
Some parts of British India were directly ruled by a person called the Governor-General of India. This person was chosen by the British government in London. They were also a Viceroy, which means they acted as the deputy of the British monarch, like Queen Victoria.
In other areas, called princely states, local rulers continued to govern. However, they were under the protection and influence of the British.
After 1876, when Queen Victoria became the Empress of India, British India became part of the British Indian Empire. This empire also included hundreds of Indian princely states. These states had never been fully conquered by the British. They still managed their own affairs, but they were protected by the British. This whole empire is sometimes called the British Raj.
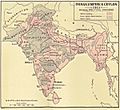
British India included the areas that are now Bangladesh, India, Myanmar (also known as Burma), and Pakistan. This was true from 1858 until August 13, 1947.
Provinces of British India
When India gained independence in 1947, British India had seventeen main areas called provinces. These were:
- Ajmer-Merwara-Kekri
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Assam
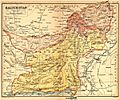
- Baluchistan
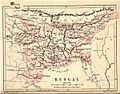
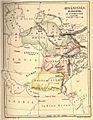
- Bengal Province
- Bihar
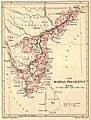
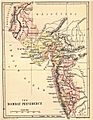
- Bombay Province
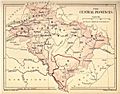
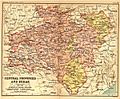
- Central Provinces and Berar
- Coorg
- Delhi Province
- Madras Province
- North-West Frontier Province (from 1901 to 1955)
- Panth-Piploda
- Orissa
- Punjab
- Sind Province
- United Provinces of Agra and Oudh
After 1947, India was divided into two new countries: the Union of India and the Dominion of Pakistan.
Twelve of the original provinces became part of India. These were Ajmer-Merwara-Kekri, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Assam, Bihar, Bombay, Central Provinces and Berar, Coorg, Delhi, Madras, Panth-Piploda, Orissa, and the United Provinces.
Three provinces went to Pakistan: Baluchistan, North-West Frontier, and Sindh.
Two provinces, Bengal and Punjab, were split between India and Pakistan.
In 1950, after India created its new Constitution, the provinces in India were changed. They became new states and union territories. Pakistan kept its five provinces. Later, East Bengal, which was renamed East Pakistan in 1956, became the independent country of Bangladesh in 1971.
Images for kids
-
A drawing of Fort William in Calcutta, which was the capital of the Bengal Presidency in British India in 1735.
-
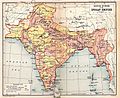
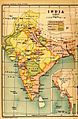
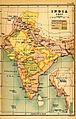
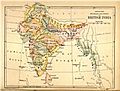
A map of the British Indian Empire in 1909. It shows British India in pink and the princely states in yellow.
-
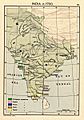
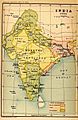
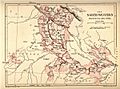
The Indian peninsula in 1700, showing the Mughal Empire and early European trading posts.
-
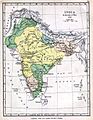
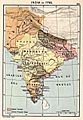
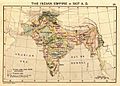
The Indian peninsula in 1760, after the Battle of Plassey. It shows the Maratha Empire and other important states.
-
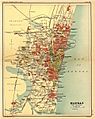
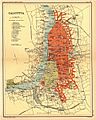
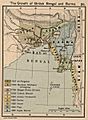
The city of Calcutta (shown here in a 1908 map) was started in 1690 as Fort William.
-
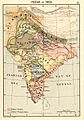
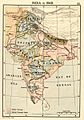
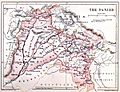
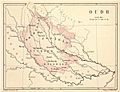
Punjab was taken over in 1849.
-
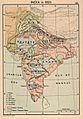
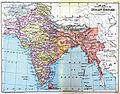
The Indian Empire in 1907.
See also
 In Spanish: Presidencias y provincias de la India británica para niños
In Spanish: Presidencias y provincias de la India británica para niños
 | Georgia Louise Harris Brown |
 | Julian Abele |
 | Norma Merrick Sklarek |
 | William Sidney Pittman |