Somalia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Federal Republic of Somalia
|
|
|---|---|
|
Anthem: Qolobaa Calankeed
علم أي امة "Every Nation Has Its Own Flag" |
|
 |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Mogadishu 2°2′N 45°21′E / 2.033°N 45.350°E |
| Official languages | |
| Ethnic groups
(2021)
|
|
| Religion | Sunni Islam (official) |
| Demonym(s) | Somali |
| Government | Federal parliamentary republic |
| Hassan Sheikh Mohamud | |
| Hamza Abdi Barre | |
|
• Speaker of the Senate
|
Abdi Hashi Abdullahi |
| Legislature | Federal Parliament |
| Senate | |
| House of the People | |
| Establishment | |
| 2350 BC | |
|
• Macrobia
|
980 BC |
|
• Barbaria
|
100 BC |
|
• Adal Sultanate
|
9th century |
|
• Mogadishu Sultanate
|
10th century |
| 13th century | |
| 13th century | |
|
• Hiraab Imamate
|
16th century |
|
• Geledi Sultanate
|
1695–1911 |
|
• Majeerteen Sultanate
|
1648–1927 |
|
• Sultanate of Hobyo
|
1878–1927 |
|
• Isaaq Sultanate
|
1749–1884 |
| 1884 | |
|
• Italian Somaliland
|
1889 |
|
• Independence and union with the State of Somaliland
|
1 July 1960 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
637,657 km2 (246,201 sq mi) (43rd) |
| Population | |
|
• 2023 estimate
|
18,143,378 (78th) |
|
• Density
|
27.2/km2 (70.4/sq mi) (199th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2017) | 36.8 medium |
| HDI (2022) | low · 193rd |
| Currency | Somali shilling (SOS) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (EAT) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +252 |
| ISO 3166 code | SO |
| Internet TLD | .so |
Somalia (Somali: Soomaaliya; Arabic: الصومال) is officially known as the Federal Republic of Somalia. It is a country located in the Horn of Africa. Somalia shares borders with Djibouti to the northwest and Kenya to the southwest. To its north is the Gulf of Aden (near Yemen), and to the east is the Indian Ocean. Ethiopia lies to its west.
Contents
Somalia's Past
Somalia has a very long and interesting history. In ancient times, it was a major trading hub. During the Middle Ages, powerful Somali empires like the Ajuran Sultanate and Adal Sultanate controlled trade in the region.
From Empires to Colonies
In the late 1800s, European powers took control of Somali lands. The Italians and British divided the area into two colonies: Italian Somaliland and British Somaliland.
Becoming an Independent Nation
In 1960, these two territories joined together. They formed the independent Somali Republic. Later, in 1969, a new government took over, creating the Somali Democratic Republic. This government faced many challenges.
Recent Challenges and New Beginnings
In 1991, the government collapsed, leading to a period of conflict. Over time, efforts were made to bring peace and stability. A new government, the Transitional Federal Government of Somalia (TFG), was formed in 2004. By 2012, a new constitution was adopted, and the country continued its journey towards lasting peace and development.
Somalia's Geography
Somalia is located in the Horn of Africa. It borders Djibouti to the northwest, Ethiopia to the west, and Kenya to the southwest. To the north is the Gulf of Aden, and to the east are the Somali Sea and Guardafui Channel.
Land and Coastline
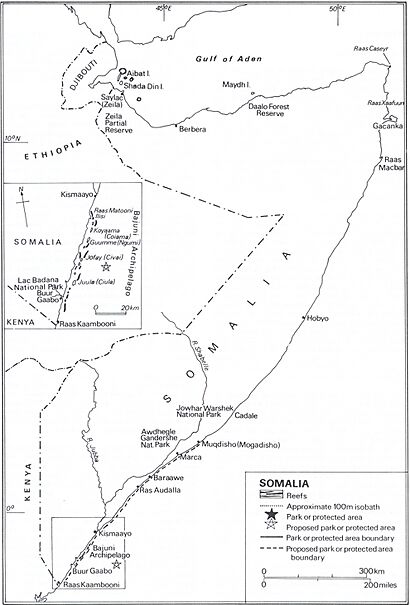
Somalia covers about 637,657 square kilometers. Its land is mostly made up of plateaus (flat areas high above sea level), plains (flat lowlands), and highlands (mountainous areas). Somalia has the longest coastline in mainland Africa, stretching over 3,333 kilometers. On a map, Somalia looks a bit like a "tilted number seven."
Mountains and Rivers
In the north, you'll find the rugged Ogo Mountains. These mountains are close to the Gulf of Aden coast. Somalia has only two rivers that flow all year round: the Jubba and Shabele. Both rivers start in the Ethiopian Highlands and flow south. The Jubba River reaches the Indian Ocean at Kismayo. The Shabele River often disappears into the desert before reaching the sea.

Climate and Seasons
Somalia is close to the equator, so its climate doesn't change much throughout the year. It's generally hot, with monsoon winds and irregular rainfall. Temperatures usually range from 30°C to 40°C. Some areas, like Berbera, are among the hottest in the world.
Somalia has four main seasons based on wind patterns:
- Jilal (December to March): The driest and harshest season.
- Gu (April to June): The main rainy season. This brings life back to the land.
- Xagaa (July to September): The second dry season.
- Dayr (October to December): The shortest rainy season.
Protecting the Environment
Somalia is a mostly dry country with a small amount of land suitable for farming. People in Somalia are working to protect their environment. In the past, there were efforts to plant trees to stop sand dunes from spreading.
One important environmental activist, Fatima Jibrell, worked to save old acacia trees. These trees were being cut down to make charcoal, which caused deforestation and turned land into desert. Thanks to her efforts, exporting charcoal was banned in the Puntland region in 2000. This helped reduce charcoal exports by a lot.
Somalia's Wildlife
Somalia is home to many different animals because of its varied landscapes and climates.
Mammals and Birds
You can find animals like cheetahs, lions, giraffes, baboons, and elephants. Somalia also has a very large number of dromedary camels. About 727 types of birds live in Somalia, with some found only there.
Marine Life and Reptiles
Somalia's coastal waters are great for fishing, especially for tuna. Many different fish and crustaceans live there. The country also has about 235 types of reptiles, with nearly half living in the northern areas. Some reptiles are found only in Somalia.
Government and Politics
Somalia is a republic where people elect their representatives. The President of Somalia is the country's leader and the head of the armed forces. The President chooses a Prime Minister to lead the government.
How Laws are Made
Somalia has a national parliament called the Federal Parliament of Somalia. It has two parts: the House of the People and the Senate. Members of parliament are elected for four-year terms. They choose the President and other leaders. The parliament also makes and approves laws.
The Justice System
Somalia's legal system is based on its constitution, which was adopted in 2012. The courts are organized into three levels: the Constitutional Court, federal courts, and state courts. Judges are appointed by a special commission. Somali law uses a mix of modern civil law, Islamic law, and traditional customary law.
Somalia's Economy
Somalia's economy combines traditional ways of making money with more modern methods.
Farming and Livestock
A large part of Somalia's economy comes from agriculture. About 80% of the people are nomads or semi-nomads. They raise animals like goats, sheep, camels, and cattle. Livestock farming makes up about 40% of the country's economy and more than half of its export earnings. Other important exports include fish and bananas.

Tourism and Attractions
Somalia has many interesting places to visit. These include historical sites, beautiful beaches, waterfalls, and national parks. Some famous spots are the Laas Geel caves with ancient rock art, and the Cal Madow mountains.
Transportation
Somalia has a network of roads that are about 22,100 kilometers long. A major highway connects cities in the north with towns in the south.
The country has 62 airports, with seven having paved runways. Important airports include Aden Adde International Airport in Mogadishu and Hargeisa International Airport in Hargeisa.
With Africa's longest coastline, Somalia also has several important seaports. These are found in cities like Mogadishu, Bosaso, and Kismayo.
People and Culture
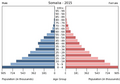
Somalia has an estimated population of over 18 million people.
Ethnic Groups and Languages
About 85% of the people are ethnic Somalis. They have a long history of living in clans and forming sultanates. Other groups make up the rest of the population, mostly in the southern parts of the country.
Somali and Arabic are the official languages. Somali is the main language for most people. English is also widely spoken and taught in schools.
Somali Food

Somali food is a mix of different influences, including Arab, Indian, and Italian flavors. This is because Somalia has always been a busy trading country.
Common foods include rice and pasta, along with meats like lamb, beef, and chicken. Spices such as cumin and cardamom are used a lot. Somali cuisine also features hearty stews, traditional flatbreads like "Canjeero/Lahooh," and tasty pastries.
A special part of Somali food is the use of camel meat and milk. These are considered special treats and are very important in Somali cooking.
Somali rice, often eaten for lunch or dinner, is usually seasoned and mixed with meat, vegetables, and sometimes even raisins for a sweet touch. It can also be colored with saffron to look more appealing.
Pasta and lasagne are also popular, especially in the south. This shows the lasting influence of Italian rule.
Tea and coffee are very popular drinks. Somalis were among the first people to enjoy coffee and were important in the global coffee trade. Somali coffee, called 'Qahwo', and tea, 'Shah', are special because they are made with a mix of different spices.
After meals, homes are often filled with the smell of frankincense or incense (unsi). This is burned in a special burner called a dabqaad.
Somali Music
Somalia has a rich musical history based on traditional folklore. Most Somali songs use a five-note scale, unlike the seven-note scales common in Western music. While it might sound a bit like music from nearby countries, Somali music has its own unique sounds and styles. Somali songs are usually created by a team: a lyricist, a songwriter, and a singer.
Somali Architecture

Somali architecture shows a long history of engineering and design. It includes ancient, medieval, and modern styles, often blending traditional Somali-Islamic designs with newer Western ones.
In ancient Somalia, pyramid-like structures called taalo were used for burials. Hundreds of these stone monuments can still be seen today. Houses were built with dressed stone, similar to those in ancient Egypt. There were also large stone walls around settlements.
When Islam came to Somalia, it brought new architectural ideas from Arabia and Persia. Buildings started using coral stone, sun-dried bricks, and limestone. Many new buildings, like mosques, were built on the foundations of older structures.
Images for kids
-
Men from Punt carrying Gifts, Tomb of Rekhmire.
-
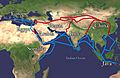
The Silk Road extending from China to southern Europe, Arabia, Somalia, Egypt, Persia, India, and Java.
-
The Ajuran Sultanate maintained commercial ties with the Ming dynasty and other kingdoms.
-
Mogadishu, capital of Italian Somaliland, with the Catholic Cathedral at the center and the Arch monument in honor of King Umberto I of Italy.
-
An avenue in downtown Mogadishu in 1963.
-
Major General Mohamed Siad Barre, Chairman of the Supreme Revolutionary Council, meeting with President of Romania Nicolae Ceauşescu.
-
Air Somalia Tupolev Tu-154 in Sharjah, United Arab Emirates. Somalia today has several private airlines.
-
500 Somali shilling banknote.
-
The Citadel of Gondershe.
See also
 In Spanish: Somalia para niños
In Spanish: Somalia para niños