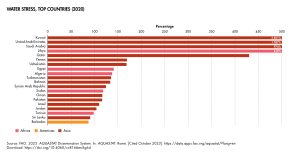Yemen facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of Yemen
|
|
|---|---|
|
Motto: ٱللَّهُ، ٱلْوَطَنُ، ٱلثَوْرَةُ، ٱلْوَحْدَةُ
Allāh, al-Waṭan, ath-Thawrah, al-Waḥdah "God, the Homeland, Revolution, Unity" |
|
|
Anthem: الجمهورية المتحدة
al-Jumhūriyyah al-Muttaḥidah "United Republic" |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Sanaa |
| Government seat | Aden |
| Official language and national language |
Arabic |
| Ethnic groups
(2000)
|
|
| Religion
(2020)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Yemeni Yemenite |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic under a provisional government |
|
• President of the Presidential Leadership Council
|
Rashad al-Alimi |
| Shaea al-Zindani | |
|
• President of the House of Representatives
|
Sultan al-Barakani |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Shura Council | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Establishment | |
|
• Unification
|
22 May 1990 |
|
• Current constitution
|
16 May 1991 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
455,503 km2 (175,871 sq mi) (54th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
negligible |
| Population | |
|
• 2023 estimate
|
|
|
• Density
|
71.8/km2 (186.0/sq mi) (143rd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2014) | 36.7 medium |
| HDI (2023) | low · 184th |
| Currency | Yemeni rial (YER) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (AST) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +967 |
| ISO 3166 code | YE |
| Internet TLD | .ye, اليمن. |
The 2011 Yemeni revolution was part of the Arab Spring protests. People protested against unemployment, corruption, and the president's plan to stay in power longer. In November 2011, President Saleh agreed to step down and transfer power to his deputy, Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi.
Hadi became president in 2012. However, the central government remained weak. The Houthi insurgency grew stronger. In September 2014, Houthi forces took over the capital, Sana'a. They forced Hadi to agree to a "unity" government. In January 2015, the Houthis dissolved parliament and declared their own ruling committee.
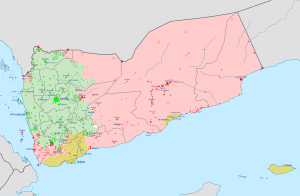
Controlled by the Government of Yemen (under the Presidential Leadership Council since April 2022) and allies Controlled by Houthis-led Supreme Political Council Controlled by the UAE-backed Southern Transitional Council Controlled by Al-Qaeda (AQAP) and Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant-affiliated Ansar al-Sharia Controlled by Hadrami Elite Forces. Controlled by Tareq Saleh's National Resistance Forces
President Hadi fled to Aden in February 2015. He declared Aden the temporary capital. The Houthis continued to advance south. On March 26, 2015, Saudi Arabia and its allies began airstrikes against the Houthis. This started a large-scale military intervention.
Yemen has been suffering from a severe famine since 2016 due to the civil war. Many children have died from starvation. There has also been a widespread cholera outbreak. The conflict and blockades have made the humanitarian crisis much worse. By the end of 2021, the war had caused over 377,000 deaths, with about 70% of those being children under five.
In December 2017, former president Ali Abdullah Saleh was killed by Houthis. In April 2022, President Hadi resigned, and the Presidential Leadership Council took power.
In January 2024, the United States and its allies launched military actions against Houthi targets in Yemen. In late 2025, the Southern Transitional Council (STC) launched a military campaign, but it was defeated in early 2026 by a Yemeni government counter-offensive.
Contents
Yemen's Geography

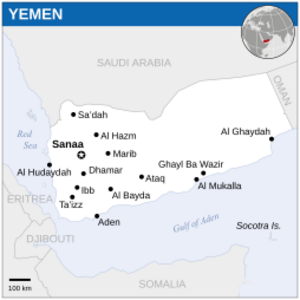
Yemen covers about 455,000 square kilometers. It is located in the southern part of the Arabian Peninsula. It borders Saudi Arabia to the north, the Red Sea to the west, the Gulf of Aden to the south, and Oman to the east.
Several islands belong to Yemen, including the Hanish Islands, Kamaran, and Perim in the Red Sea. Socotra island, in the Arabian Sea, is also part of Yemen. Many of these islands are volcanic. Socotra is geographically closer to Africa and has unique plants and animals.
Regions and Climate
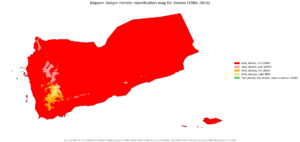
| BWh Hot desert BWk Cold desert BSh Hot semi-arid BSk Cold semi-arid CWb Subtropical highland |
Yemen has four main geographic regions:
- The coastal plains in the west, called Tihamah, are very dry and flat.
- The western highlands are heavily terraced for farming and receive the most rainfall in Arabia.
- The central highlands are a high plateau, drier than the western highlands but still good for farming with irrigation. Sana'a is in this region.
- The Rub' al Khali desert in the east is very low and receives almost no rain.
Yemen's highest point is Jabal An-Nabi Shu'ayb, at about 3,666 meters (12,028 feet). Yemen faces severe water scarcity, especially in the highlands. This is a major challenge for the country.
Biodiversity
Yemen has diverse natural environments. Its plants are a mix of tropical African and Saharo-Arabian types. Many unique plants are found in the coastal plains.
Among its animals, the Arabian leopard is very rare in the mountains. Socotra Island is especially known for its unique plants and animals, many of which are found nowhere else in the world. This includes the famous Dragon Blood Trees.
Culture in Yemen

Yemen has a rich cultural heritage. Its architecture is famous for unique designs, especially the tall mud-brick buildings in cities like Shibam.
Media and Arts
Radio broadcasting in Yemen started in the 1940s. Television is the most important way people get news, especially since many people cannot read. The Yemeni film industry is still quite new.
Yemeni theatre has a long history, dating back to the early 20th century. Both amateur and professional groups perform plays. Many Yemeni writers have created dramatic works. Plays by famous international authors have also been performed in Yemen.
Sports and Activities
Football is the most popular sport in Yemen. The Yemeni national football team plays in international games. Yemen also has many football clubs.
Yemen's mountains offer great opportunities for outdoor sports like biking, rock climbing, and hiking. The coastal areas and Socotra are good for water sports like surfing and scuba diving. Socotra is known for some of the best surfing spots.
A unique traditional sport is camel jumping, popular among the Zaraniq tribe. Competitors run and leap over as many camels as they can. Yemen hosted the 20th Arabian Gulf Cup football tournament in 2010.
World Heritage Sites
Yemen has four World Heritage sites recognized by UNESCO:
- The Old Walled City of Shibam is known as "Manhattan of the Desert" because of its tall mud-brick skyscrapers. It's an old example of vertical city planning.
- The Old City of Sana'a has been lived in for over 2,500 years. It became a major Islamic center and has many old mosques and houses.
- The historic town of Zabid was Yemen's capital from the 13th to 15th centuries. It was an important center of learning for the Arab and Islamic world.
- The Socotra Archipelago is a group of islands with amazing biodiversity. Many of its plants and animals are found nowhere else on Earth, including the Dragon's Blood Tree.
Government and Politics
Yemen is a republic with a two-house parliament. The 1991 constitution states that power is shared between an elected president, an elected Assembly of Representatives, and an appointed Shura Council. The president is the head of state, and the prime minister is the head of government. In Sana'a, the Houthi-controlled areas have their own government, which is not recognized internationally.
The president is elected for a seven-year term, and members of parliament serve for six years. People aged 18 and older can vote. Only Muslims can hold elected office.
Ali Abdullah Saleh was the first elected president of unified Yemen in 1999. He was re-elected in 2006. However, protests in 2011 led to his resignation in 2012. He remained influential in Yemeni politics.
The legal system in Yemen is based on Sharia (Islamic law). There are also commercial courts and a Supreme Court.
Foreign Relations
Yemen is a member of the United Nations, the Arab League, and other international organizations. After the 1994 civil war, Yemen worked to improve relations with its neighbors. In 2000, Yemen and Saudi Arabia settled a long-standing border dispute.
In March 2020, the U.S. and its allies reduced aid to Yemen. This caused many UN programs to close or shrink, affecting millions of people. The UN has called the situation in Yemen the world's worst humanitarian crisis. In January 2024, the U.S. and its allies launched military strikes against Houthi targets in Yemen.
Military Forces
Yemen's armed forces include the Army, Navy, and Air Force. Yemen has one of the largest military forces on the Arabian Peninsula. In 2007, compulsory military service was brought back.
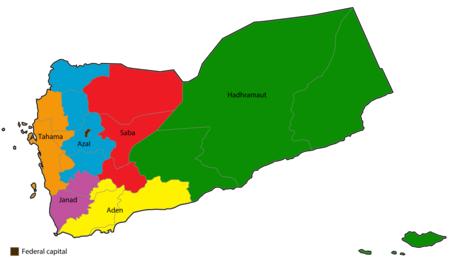
Administrative Divisions
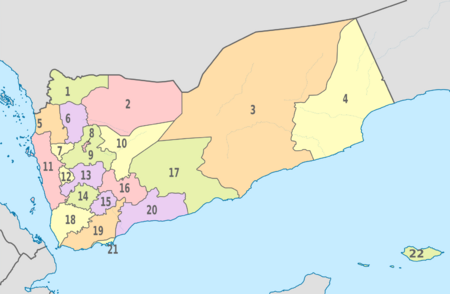
Yemen is divided into 21 governorates, plus the capital city of Sana'a. These governorates are further divided into districts, sub-districts, and villages.
In 2014, a plan was proposed to divide Yemen into six federal regions. This idea contributed to the Houthis' takeover of the government.
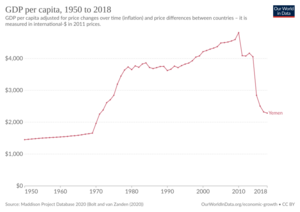
Yemen's Economy
Since its unification in 1990, Yemen has been one of the poorest countries in the Middle East. Services are the largest part of its economy, followed by industry and agriculture. Oil production makes up a big part of the economy and government income. After the civil war started in 2014, Yemen's economy suffered greatly.
Agriculture
Most Yemenis work in agriculture. Important crops include grain, vegetables, fruits, and coffee. A major problem is the growing of qat, a plant that uses a lot of water. This has led to water shortages and higher food prices. Efforts are being made to replace qat farms with coffee plantations.
Industry
Yemen's industry focuses on crude oil production, food processing, and handicrafts. It also has large reserves of natural gas. The country's first liquefied natural gas plant started production in 2009.
Trade
In 2013, Yemen's main exports were crude oil, coffee, and liquefied natural gas. These were mostly sent to China, Thailand, and India. Yemen imported machinery, food, and chemicals, mainly from the EU, UAE, and China.
Water Supply and Sanitation

Yemen faces a severe water scarcity. It is the poorest and most water-scarce country in the Arab world. Groundwater levels have dropped dramatically. The civil war has made it even harder to improve water access. Many Yemenis struggle to get enough water for drinking and bathing.
UNICEF and its partners are working to provide safe drinking water to millions of people in Yemen. They are also helping to build better water systems.
People of Yemen
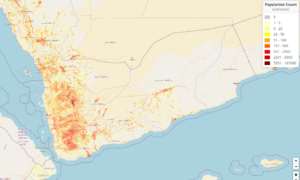
Yemen's population is about 34.7 million people. A large portion of the population is under 15 years old. The population is expected to grow significantly by 2050.
Demographics and Groups
Yemen is largely a tribal society. Most minority groups left when North and South Yemen were formed. There are also people of Indian and Persian origin. Many people of Arab descent in Southeast Asia, East Africa, and India have roots in southern Yemen.
Yemen is considered the birthplace of the Arabs and the Arabic language. Yemen is also a country that hosts refugees, mainly from Somalia, Iraq, and Ethiopia. Many Yemenis have also been displaced within the country due to conflict. A large number of Yemenis live in neighboring Saudi Arabia and the United Kingdom.
Languages Spoken
Modern Standard Arabic is the official language. Yemeni Arabic is the everyday language. In some eastern areas and on Socotra Island, other non-Arabic languages are spoken. English is an important foreign language, especially in the south.
Religion
| Religion in Yemen | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunni Islam | 56.36% | |||
| Zaydi Islam | 42.1% | |||
| Others | 1.54% | |||
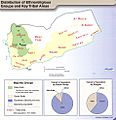
Islam is the official religion in Yemen. Most Yemenis are Muslim, divided into two main groups: Sunni (about 53%) and Shia (about 45%). Sunnis are mostly in the south and southeast, while Shias (mainly Zaydis) are in the north and northwest.
There are very small numbers of non-Muslims, including Christians and Jews. Most Yemeni Jews have moved to Israel. Yemen is known for having a very religious population.
Education

In 2010, about 64% of adults in Yemen could read and write. The government aims to reduce illiteracy even further. Education is supposed to be free and compulsory for children aged six to 15, but this is not always enforced.
Yemen has increased its spending on education. There are also projects to improve education, especially for girls in rural areas.
Health Care
While Yemen has tried to improve its health care system, it is still not fully developed. Spending on health care is low compared to other countries in the Middle East. There are few doctors and hospital beds for the population. Health services are especially hard to find in rural areas. Emergency services are often not available.
Images for kids
-
Yemen's tribal areas and Shia/Sunni regions. Shia Muslims predominant in the green area of Yemen's West, with the rest of Yemen being Sunni Muslims
See also
 In Spanish: Yemen para niños
In Spanish: Yemen para niños