Terrace (earthworks) facts for kids


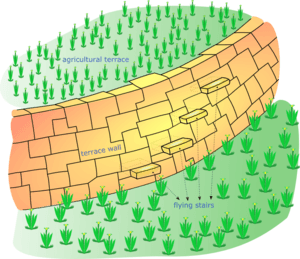
In farming, a terrace is a special kind of field. It's a flat area cut into the side of a hill or mountain. Imagine giant steps on a slope. Farmers create these steps to make farming easier and better. This way of shaping the land is called terracing.
Terraced fields are great for growing crops on hilly land. They help stop soil from washing away (called erosion). They also slow down water running off the land. This means more water stays for the plants. Terraces are often used for crops that need a lot of water, like rice. The Rice Terraces of the Philippine Cordilleras are so important that UNESCO named them a World Heritage Site.
Contents
Where are Terraces Used?
Terraced fields are used all over the world. You can find them in places like East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, and the Mediterranean Basin. They are also common in Africa and South America.
In Asia, farmers use terraces a lot for growing rice. They also grow wheat and barley on them. In drier places like the Mediterranean, terraces help grow grapes for wine. They are also used for olive trees and other plants.
Terraces in Ancient Times
People have been building terraces for a very long time. In the Yemen Highlands, terraces were built around 3000 BC. That was at the start of the Bronze Age.
Some historians think the famous Hanging Gardens of Babylon might have been built on terraces. These gardens may have looked like a stepped mountain. The ancient Romans also used terraces. At the Villa of the Papyri in Herculaneum, gardens were built in terraces. This gave amazing views of the Bay of Naples.
Terrace farming was also common in West Africa before the 1400s. Groups like the Mafa and Dogon used them.
Terraces in More Recent Times
For a long time, it was hard to use machines on steep terraced fields. But in the 1970s, farmers in the European Alps started using special tractors. These tractors were designed to work safely on slopes. They helped manage pastures and harvest grass.
By the 2000s, these machines got even better. New wheels and electronic controls allowed them to work on very steep slopes. They could do many tasks, like harvesting and baling hay.
In Asian countries, smaller, simpler machines have become popular. These two-wheel tractors are light enough to move between terraces. Farmers use them to prepare the soil for crops like maize, wheat, and potato. They also help with rice farming. These machines can even power water pumps or threshers. In Nepal, these affordable machines are helping farmers in the Himalayas.
Terraces in South America
In the Andes mountains of South America, farmers have used terraces for over a thousand years. These terraces are called andenes. They grow crops like potatoes and maize. The Wari culture first developed terraced farming before the year 1000 AD. The Inca people later used and improved these ideas.
The terraces helped farmers use the thin soil well. They also allowed water to flow through the fields for irrigation. The Inca built amazing systems of canals and aqueducts. These brought water to dry land and made the soil more fertile. Terraced farms fed the people in big Inca cities like Machu Picchu.
Terraces in the Canary Islands
Terraced fields are very common on islands with steep hills. The Canary Islands have many terraces called cadenas (chains). These terraces are built with strong stone walls. They often include stairs and channels for water.
Terraces in Japan
In Japan, there are many beautiful terraced rice fields. Some of these are part of the 100 Selected Terraced Rice Fields. While some are slowly disappearing, volunteers help farmers keep these traditional fields going. People also visit them for sightseeing.
Terraces in Myanmar
In the mountains of Myanmar, terrace farming is known as "staircase" or "ladder farming." This name describes how the fields look like steps on a hill.
Gallery
-
Rice terraces in Hoang Su Phi, Ha Giang, Viet Nam.
-
Terraced fields in the Upper Mustang region of Nepal
-
Terraced field in Kabal Swat valley, Pakistan.
-
Rice terrace in Bali
-
Jatiluwih rice terrace in Bali, Indonesia.
-
Rice cultivation, Lower Himalayas, Nepal.
See also
 In Spanish: Bancal para niños
In Spanish: Bancal para niños
- Anden
- Honghe Hani Rice Terraces
- Banaue Rice Terraces
- Rice Terraces of the Philippine Cordilleras
- Terrace garden
 | Claudette Colvin |
 | Myrlie Evers-Williams |
 | Alberta Odell Jones |