Aden facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Aden
|
|
|---|---|
|
Temporary capital and City
|
|
|
Clockwise from top: Aban Mosque in Crater, Queen Victoria Statue, Port of Aden, Abyan Beach, Crater District, Mualla District
|
|
Aden map
|
|
| Country | Yemen |
| Region | Aden Region |
| Governorate | Aden |
| First settled | 7th century BC |
| British occupation | 19 January 1829 |
| Aden Settlement | 1829 |
| Province of Aden | 1932–1937 |
| Colony of Aden | 1 April 1937 |
| State of Aden within the FSA | 18 January 1963 |
| Independence | 30 November 1967 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 760 km2 (290 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 6 m (20 ft) |
| Population
(2017)
|
|
| • Total | 863,000 |
| • Estimate
(2023)
|
1,079,670 |
| • Density | 1,135.52/km2 (2,941.0/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Adeni/Adenies |
| Ethnicities | |
| • Majority | Arabs |
| • Minorities | Afro-Arabs, Indians, Somalis |
| Languages | |
| • Official | Arabic MSA (Education and Government) |
| • Spoken | Adeni Arabic (Majority) English (Widely used) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (AST) |
| Area code(s) | 02 |
![]() Kingdom of Awsan
Kingdom of Awsan
![]() Himyarite Kingdom
Himyarite Kingdom
![]() Kingdom of Aksum
Kingdom of Aksum
![]() Sasanian Yemen
Sasanian Yemen
![]() First Islamic state
First Islamic state
![]() Rashidun Caliphate
Rashidun Caliphate
![]() Umayyad Caliphate
Umayyad Caliphate
![]() Abbasid Caliphate
Abbasid Caliphate
![]() Ziyadid dynasty
Ziyadid dynasty
![]() Najahid dynasty
Najahid dynasty
![]() Sulayhid dynasty
Sulayhid dynasty
![]() Zurayid dynasty
Zurayid dynasty
![]() Ayyubid dynasty
Ayyubid dynasty
![]() Rasulid dynasty
Rasulid dynasty
![]() Tahirid Sultanate
Tahirid Sultanate
![]() Mamluk Sultanate
Mamluk Sultanate
![]() Portuguese Aden
Portuguese Aden
![]() Yemen Eyalet
Yemen Eyalet
![]() Qasimid State
Qasimid State
![]() Yemen Vilayet
Yemen Vilayet
![]() Qasimid State
Qasimid State
![]() Sultanate of Lahej 1728–1839
Sultanate of Lahej 1728–1839
![]() Aden Province 1839–1937
Aden Province 1839–1937
![]() Aden Colony 1937–1963
Aden Colony 1937–1963
![]() Aden protectorate 1937–1963
Aden protectorate 1937–1963
![]()
![]() State of Aden within the FSA 1963–1967
State of Aden within the FSA 1963–1967
![]() South Yemen 1967–1990
South Yemen 1967–1990
![]() Republic of Yemen 1990–1994
Republic of Yemen 1990–1994
![]() Democratic Republic of Yemen 1994
Democratic Republic of Yemen 1994
![]() Republic of Yemen 1994–present
Republic of Yemen 1994–present

Aden (Arabic: عَدَنْ, romanized: ʿAdan) is a port city in Yemen, located in the southern part of the Arabian Peninsula. It sits near the eastern entrance to the Red Sea, about 170 km (110 mi) east of the Bab-el-Mandeb strait and north of the Gulf of Aden. Aden's location makes it a super important shipping spot, connecting Africa, Asia, and the Middle East. In 2023, about 1,080,000 people lived in Aden, making it one of Yemen's biggest cities.
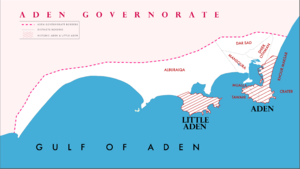
Aden is split into eight areas: Tawahi, Mualla, Crater, Khur Maksar, Al Mansura, Dar Sad, Sheikh Othman, and Al Buraiqa. These areas together form the Aden Governorate today. When the British were in charge, Aden mostly referred to the coastal areas like Tawahi, Mualla, Crater, and parts of Khur Maksar. The western harbor area, called Little Aden, is now part of the Al Buraiqa District.
Before Yemen became independent, Aden had several main centers. These included Crater, the old port; Ma'alla, the newer port; Tawahi, once known as "Steamer Point"; and the Gold Mohur resorts. Khormaksar, which is on the narrow strip of land connecting Aden to the mainland, is home to foreign offices, the main buildings of Aden University, and Aden International Airport. On the mainland, you'll find Sheikh Othman, an old oasis area, and Al-Mansura, a town planned by the British. There's also Madinat ash-Sha'b, which used to be the capital of the South Arabian Federation. Today, it has a large power and desalination plant, plus more university buildings.
Aden has a huge natural harbor that forms its modern port. Long ago, this led to the creation of Aden's famous Cisterns of Tawila. These reservoirs were built to collect rainwater for the city's people to drink. Little Aden is where the oil refinery and tanker port are located. These were first built and run by British Petroleum until 1978, when they were handed over to the South Yemeni government.
Aden was the capital of South Yemen until it joined with North Yemen on May 22, 1990. Since 2014, it has been the temporary capital of Yemen. Some government members stay there, mostly at al-Maashiq Palace. It is also where the Southern Transitional Council is based, which controls the city.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The name "Aden" means "to reside" or "a home for ships." So, "Aden" can mean "resident" or "a place where people settle." This makes sense because it has always been a welcoming place for ships and traders.
Many old geographers and historians have written about Aden:
- Yaqut al-Hamwi said it's a famous city on the Indian Sea coast in Yemen. He noted it had little water but was a vital port for ships from India, making it a busy trade town.
- Ibn Manzur described it as a city on the edge of the sea in the furthest part of Yemen.
- Ibn Khaldun called Aden one of Yemen's strongest cities, located by the Indian Sea. He mentioned it has been a trade hub for a very long time, often visited by silk merchants.
Aden's Long History
Aden is a very old port. The ancient Greeks called it Arabia Emporion, meaning "Arabic trade port." Because of its great location on the sea route between India and Europe, many rulers wanted to control Aden throughout history. In the 1st century BC, it was known as Eudaemon, meaning "blissful" or "prosperous." It was a key stop for trade in the Red Sea. However, it faced tough times when new shipping methods allowed ships to sail directly to India, bypassing Aden.
The Bible, in the Book of Ezekiel, also mentions Aden as a place of trade. At first, Aden was a small peninsula without many natural resources. But its position between Egypt and India made it very important for ancient global trade.
The city was home to the ancient Kingdom of Osan from the 8th to 7th centuries BC. Later, the Himyarites took control of Aden around 275 AD. They are believed to have built the huge water storage systems, known as the "Cisterns of Aden," which could hold a massive amount of water.
The Himyarite Kingdom fell in the 6th century AD. The Byzantines and later the Sasanian Empire also controlled the city. A local legend in Yemen even says that Aden might be as old as human history itself, and some believe that Cain and Abel are buried there.
Culture and Life
How People Speak
When Yemenis became Muslim, they started using the Arabic alphabet. Today, people in Yemen speak Arabic with a special Yemeni accent. There are three main types of Yemeni Arabic: the Sana'i dialect, the Hadrami dialect, and the Ta'izzi-Adeni dialect. Each of these has its own unique sounds and words.
Music and Poetry
"Adeni art," or Adeniyat, is a special kind of Arabic music. Famous old artists from Aden include Iskander Thabet Saleh and Muhammad Murshid Naji. Many poets have also come from Aden, like Abdul Rahman Ibrahim Muhammad and Lotfi Jaafar Aman.
Adeni music has always been very important in the city. Musicians were called "al-Mutariba," meaning "people of music." Adeni music really started to grow around 1920 when the Aden Protectorate army formed. Their music groups would play at special events and weddings.
Sports and Games
Early Sports
Sports in Aden began way back in 1902 with the Adeni Tennis Club. Soon after, the "Recreational Club United" was started. Aden was actually the first city in the Arabian Peninsula to have organized sports. The very first sports club in Yemen and the Arab world was "Al-Ittihad Al-Muhammadi Club," founded in 1905.
More clubs appeared in the 1920s and 1930s, like "Al-Husseini Sports Club" and "Nujoom Al-Layl Club." At first, football games were just friendly matches between teams from different areas. But in 1934, a sports association was formed to organize everything. This group, led by the British Governor, started the first club tournament, the "Rosario Cup Championship." Six clubs played, and Al-Ittihad Al-Mohammadi Club won!
Modern Sports
After Aden became independent, the "Football Federation" was created in 1968. Many smaller clubs were combined into larger ones. By 1975, there were only 5 main sports clubs left, including the famous "Al-Tilal Sports Club," which used to be Al-Ittihad Al-Muhammadi Club.
Football is the most popular sport in Aden. The city has 9 stadiums and 10 sports clubs. In November 2010, Aden even hosted the 2010 Arabian Gulf Football Cup, a big football tournament for countries in the region.
Cool Places to Visit
Aden has many interesting historical and natural places to see:
- The old British churches.
- The Zoroastrian Temple.
- The Cisterns of Tawila—an ancient system for collecting water.
- Sira Fortress—a historic fort.
- The Aden Minaret.
- Little Ben, a smaller version of the famous Big Ben clock tower in London. It was built during the time of British rule.
- The Landing Pier at Steamer Point, a 19th-century building where important visitors, like Queen Elizabeth in 1954, would arrive.
- The Palace of the Sultanate of Lahej/National Museum—This museum has one of the largest collections of historical items in Yemen.
- The Aden Military Museum, which shows the city's military history.
- The Rimbaud House, where French poet Arthur Rimbaud lived from 1880 to 1891.
- The old forts of Jebal Hadid and Jebal Shamsan.
- The beautiful beaches of Aden and Little Aden, like Lover's Bay Beach and Gold Beach.
- Al-Aidaroos Mosque.
- Main Pass (now Al-Aqba Road), the only road into Aden through Crater. It used to be an arched bridge built during the Ottoman Empire.
Money and Travel
Aden is an important industrial city with many factories. The most important is the oil refinery, which started working in 1954. This refinery has a port for oil tankers, many storage tanks, and a place to refuel ships.
Historically, Aden was a major trading center for the Arabian Peninsula. It imported goods from Africa, Europe, the United States, and India. The port also exported local products. Ships passing by would stop in Aden to get coal and salt.
Getting Around
Aden's port has always been a major travel hub. Passenger ships arrive in the Al-Tawahi District. The city also has Aden International Airport, which is about 10 kilometers (6 miles) away. This airport is the main base for Al-Saeeda Airlines and is the second largest airport in Yemen. It's known for its good location, surrounded by the Arabian Sea.
The airport was first built by the British military in 1927. After World War II, it was expanded into the international airport we know today. In 1977, Aden, like the rest of South Yemen, changed from driving on the left side of the road to the right side, matching its neighboring countries.
In the early 1900s, Aden was a big center for exporting coffee grown in the Yemeni highlands. It also exported frankincense, wheat, barley, and millet. Aden also produced salt from seawater. Two companies, one Italian and one Indian, were involved in salt production, exporting over 120,000 tons of salt between 1916 and 1917.
Economy Today
Aden's economy has faced challenges, especially with electricity. The city relies on diesel generators, which need imported fuel. The main power plant, al-Hasswa, often struggles to produce enough electricity for the region.
Special Economic Zone
A special "free zone" was opened in Aden in 1991. This area is like Yemen's economic doorway, connecting Asia and Africa. Its location near the main global trade routes makes it perfect for shipping goods to East Africa, the Red Sea, India, and the Arabian Gulf. It's a great place for storing and distributing products.
Land and Weather
Where is Aden?
Aden is on the coast of the Gulf of Aden. It's about 363 kilometers (225 miles) from Yemen's capital, Sana'a. The city is only about 6 meters (20 feet) above sea level. It's surrounded by Lahj Governorate to the north and east, and Abyan Governorate to the northwest. Aden has its international airport and a sea port. It also has roads connecting it to other Yemeni cities.
Land Features
Aden is a coastal city, meaning it's right by the sea, specifically the Gulf of Aden, which leads to the Indian Ocean. The city's shape, with two peninsulas, helps create cool land and sea breezes. This also affects how much the temperature changes between day and night, and between summer and winter.
The land in Aden slopes towards the south. In the southern part, you'll find highlands like Jabal Shamsan, which is over 500 meters (1,640 feet) tall. Other highlands like Jabal Ihsan and Jabal Al-Muzalqim in Little Aden are not as tall. These mountains are made of volcanic rock. Even though they cover a lot of the city, they don't have a big impact on Aden's climate.
What's the Weather Like?
Aden has a hot desert climate. This means it's very hot and dry, with almost no rain all year. However, it is humid because it's right by the sea.
| Climate data for Aden | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 31.1 (88.0) |
31.7 (89.1) |
35.0 (95.0) |
37.8 (100.0) |
41.1 (106.0) |
41.1 (106.0) |
41.1 (106.0) |
42.8 (109.0) |
38.3 (100.9) |
38.9 (102.0) |
35.0 (95.0) |
32.8 (91.0) |
42.8 (109.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 28.5 (83.3) |
28.6 (83.5) |
30.2 (86.4) |
32.2 (90.0) |
34.1 (93.4) |
36.6 (97.9) |
35.9 (96.6) |
35.3 (95.5) |
35.4 (95.7) |
33.0 (91.4) |
30.7 (87.3) |
28.9 (84.0) |
32.4 (90.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 25.7 (78.3) |
26.0 (78.8) |
27.2 (81.0) |
28.9 (84.0) |
31.0 (87.8) |
32.7 (90.9) |
32.1 (89.8) |
31.5 (88.7) |
31.6 (88.9) |
28.9 (84.0) |
27.1 (80.8) |
26.0 (78.8) |
29.1 (84.4) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 22.6 (72.7) |
23.2 (73.8) |
24.0 (75.2) |
25.6 (78.1) |
27.7 (81.9) |
28.8 (83.8) |
28.0 (82.4) |
27.5 (81.5) |
27.8 (82.0) |
24.6 (76.3) |
23.2 (73.8) |
22.9 (73.2) |
25.5 (77.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 15.6 (60.1) |
17.2 (63.0) |
18.9 (66.0) |
18.9 (66.0) |
21.1 (70.0) |
23.9 (75.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
23.3 (73.9) |
25.0 (77.0) |
18.9 (66.0) |
18.3 (64.9) |
16.7 (62.1) |
15.6 (60.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 6 (0.2) |
3 (0.1) |
5 (0.2) |
2 (0.1) |
1 (0.0) |
0 (0) |
3 (0.1) |
3 (0.1) |
5 (0.2) |
1 (0.0) |
3 (0.1) |
5 (0.2) |
36 (1.4) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 20 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 72 | 72 | 74 | 74 | 72 | 66 | 65 | 65 | 69 | 68 | 70 | 70 | 70 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 241.8 | 203.4 | 217.0 | 240.0 | 303.8 | 282.0 | 241.8 | 269.7 | 270.0 | 294.5 | 285.0 | 257.3 | 3,106.3 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 7.8 | 7.2 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 9.8 | 9.4 | 7.8 | 8.7 | 9.0 | 9.5 | 9.5 | 8.3 | 8.5 |
| Source: Deutscher Wetterdienst | |||||||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 °C (77 °F) | 25 °C (77 °F) | 26 °C (79 °F) | 27 °C (81 °F) | 29 °C (84 °F) | 30 °C (86 °F) | 29 °C (84 °F) | 29 °C (84 °F) | 30 °C (86 °F) | 28 °C (82 °F) | 27 °C (81 °F) | 25 °C (77 °F) |
Nature and Animals
Coasts and Beaches
Most of Aden's coast is made up of sandy beaches. Some popular ones include Golden Coast, Abyan Bakhour Maksar, Al-Ghadeer Beach, and Kud Al-Nimr Beach.
Islands Nearby
Around Aden's peninsulas, there are about 21 islands. Most of them are rocky, and some have coral reefs. Many of these islands are good for fishing. Some islands, like Al-Ummal Island and Sirah Island, are popular for various activities.
Wildlife
Yemen is rich in different bird species, especially because it has many suitable coastal areas, wetlands, and islands. The Aden region is known as an important place for birds. It's a home for three types of birds that are globally at risk of disappearing: the great eagle, the gull eagle, and the eastern king eagle.
Many other birds live in Aden's wetlands and the Caltex swamp area. These include great flamingos, dwarf flamingos, rock egrets, spoonbills, hooked terns, and seagulls.
Public Services
Learning and Schools
Aden has 95 schools, including 13 kindergartens and 82 basic education schools. There are also 29 secondary schools. In 2004, over 104,000 students were in basic education, and over 20,000 in secondary education.
For older students, there are 13 vocational and technical centers. Aden also has one government university, the University of Aden, with 9 colleges. In 2010, more than 29,000 students were studying there.
Mail Services
Aden has had mail services since June 15, 1839, just a year after the British took control. The official post office opened in 1857. At first, Aden used postage stamps from Britain and India. When it became the Aden Colony in 1937, it started issuing its own stamps with pictures and the name "Aden" on them.
News and Media
Newspapers
The weekly newspaper Al-Amal (meaning "Hope") started in Aden in 1957. Its motto was "Freedom, Bread, and Peace." The British authorities only allowed 1,500 copies to be printed each week, and the newspaper was soon banned.
In 1958, Al-Ayyam (meaning "The Days") newspaper was founded in Aden. It was an independent daily newspaper in Arabic. Its first issue came out on July 30, 1958, and its founder was Brigadier General Muhammad Ali Bashraheel. The newspaper stopped publishing after independence but started again in 1990 after Yemen united.
Radio and TV
Radio Aden began broadcasting on August 17, 1954. It is still on air today, with morning and evening shows. The British also started Aden Channel TV on September 11, 1964. At first, TV broadcasts only reached populated areas, especially where British soldiers and their families lived.
In 1979, the TV headquarters moved to a new building. In 1981, they started broadcasting in color, and later that year, the channel began broadcasting via satellite. After Yemen united in 1990, Aden Channel became the second official TV channel for Yemen.
Notable People
- Shafiqa Zawqari (born 1942) - author
Images for kids
-
1955 British passport for former Aden protectorate citizens – Qu'aiti State in Hadhramaut
See also
 In Spanish: Adén para niños
In Spanish: Adén para niños