Desert climate facts for kids
A desert climate, also called an arid climate, is a very dry type of weather found in certain parts of the world. In these places, there is usually less than 250 millimeters (about 10 inches) of rain each year. This low rainfall is why deserts like the Sahara, the Arabian Desert, and central Australia are so dry.
Desert climates are often found deep inside continents. They can also be on the western sides of continents or behind tall mountain ranges, where mountains block the rain. Even some very cold places, like parts of the Arctic and Antarctic, have desert-like climates because they get so little snow or rain.
Contents
What Makes a Place a Desert?
A "true desert" is a place where very few plants grow, and rain is rare. Because the air in deserts is so dry, there isn't much moisture to hold onto the heat from the sun. This means desert nights are usually very cold. The big difference between day and night temperatures can make it hard for plants and animals to live there.
Some places get more than 250 millimeters of rain each year but are still considered deserts. For example, the Kalahari Desert can get up to 640 millimeters (about 25 inches) of rain a year. It has huge sand dunes, but plants help keep the sand from moving around. Other areas, like Tucson in Arizona, get more rain (about 303 millimeters or 12 inches) but lose more water through evaporation than they receive. Some scientists don't call these places "true deserts."
Types of Desert Climates
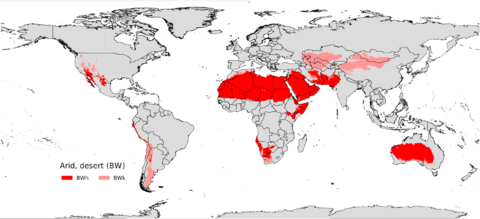
Scientists use the Köppen climate classification system to sort desert climates into different types. There are three main types:
- Hot desert climate (BWh)
- Cold desert climate (BWk)
- Mild desert climate (BWh/BWn)
Hot deserts have very hot summers, with temperatures that can reach 45 °C (113 °F) or even higher. Winters in hot deserts are usually warm. Cold deserts can also have hot summers, but their winters are very cold. They are often found at high altitudes and can be even drier than hot deserts.
Hot Desert Climates
Hot desert climates (BWh) are usually found in the lower middle parts of the world, often between 20° and 33° north and south of the equator. In these areas, air sinks and creates high pressure, which clears away clouds. This leads to hot, dry conditions with lots of sunshine.
You can find hot deserts in many places:
- Large parts of North Africa (like the Sahara Desert)
- Western Asia (like the Arabian Desert)
- Northwestern India and Pakistan (like the Thar Desert)
- Southwestern Africa (like the Namib Desert)
- Inside Australia (like the Great Victoria Desert)
- The southwestern United States and northern Mexico (like the Mojave Desert)
- The southeastern coast of Spain
- The coast of Peru and Chile
This means hot deserts are found on every continent except Antarctica.
During summer, the heat is intense. Average temperatures in the hottest month are usually between 29°C and 35°C (84°F and 95°F). Temperatures of 43–46°C (109–115°F) are common during the day. The highest temperatures ever recorded on Earth, over 50°C (122°F), have happened in hot deserts. This includes the record of 56.7°C (134°F) in Death Valley, USA. Some tropical deserts stay very hot all year, even in winter. Places like Dallol, Ethiopia, have some of the highest average yearly temperatures on Earth, almost 35°C (95°F).
During colder times of the year, night temperatures can drop to freezing or below. This happens because the clear skies allow heat to escape quickly. However, temperatures rarely drop far below freezing in hot deserts.
Hot deserts are places of extremes. They are often among the hottest, driest, and sunniest places on Earth. This is because of constant high pressure, very dry air, and strong sun. These conditions make hot deserts very difficult for most living things.
Cold Desert Climates
Cold desert climates (BWk) usually have hot or warm, dry summers. However, their summers are not as hot as those in hot deserts. Unlike hot deserts, cold deserts have cold, dry winters. Snow is rare in these regions.
The Gobi Desert in northern China and Mongolia is a good example of a cold desert. It gets hot in the summer but has very cold winters, just like the rest of Central Asia. The Atacama Desert in South America has mild summers with only small temperature changes between seasons. Cold deserts are typically found at higher altitudes than hot deserts and are often drier.
Cold deserts are usually located in temperate zones. They are often in the "rain shadow" of high mountains. This means the mountains block rain from reaching the desert. For example, the Patagonian Desert in Argentina is next to the Andes mountains. In Central Asia, mountains block rain from the eastern monsoon winds.
Other major cold deserts include the Kyzyl Kum and Taklamakan Desert in Central Asia. The Ladakh region and the city of Leh in the Himalayas in India also have a cold desert climate. In North America, cold deserts are found in the drier parts of the Great Basin Desert in the United States. In Europe, this climate is only found in some inland parts of southeastern Spain.
The Arctic and Antarctic regions also receive very little precipitation. This is because the air is so cold and dry that most moisture freezes. However, these areas are usually called polar climates because their average summer temperatures are below 10°C (50°F). Even so, they share some desert features like dry land and very barren areas without ice.
How Plants and Animals Adapt
Desert plants and animals have amazing ways to live in these dry climates.
- Some animals can survive on very little water.
- Some plants can store water in their stems or leaves.
- Animals like snakes, lizards, and scorpions use venom to catch food. This saves energy because they don't have to chase their prey.
- Many desert animals are nocturnal. They sleep in cool caves or burrows during the day and hunt at night when it's cooler.
- Plants also have ways to save water. Some have waterproof coverings to prevent drying out.
- The giant Saguaro cactus stores water in its large stem. It can live for over 150 years and grow over 40 feet tall!
- Many desert plants have thorns or spines to protect their water stores from animals.
Related pages
See also
 In Spanish: Clima árido para niños
In Spanish: Clima árido para niños