Oil refinery facts for kids

An oil refinery (also called a petroleum refinery) is a big factory where crude oil (raw oil from the ground) is changed into many useful petroleum products. This happens through a special process called fractional distillation and other steps. Some of the important products made at a refinery include gasoline (for cars), diesel fuel (for trucks and buses), asphalt (for roads), heating oil (for homes), kerosene (for lamps and jet fuel), and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG, for cooking and heating).
Contents
What is Crude Oil?
Crude oil is a thick, dark liquid found deep underground. It's a mix of many different things, and it's not very useful on its own. Think of it like a raw ingredient that needs to be cooked and separated before it can be used. Refineries are like giant kitchens that turn this raw oil into everyday products we use.
How a Refinery Works
Separating Oil into Products
The main job of an oil refinery is to separate crude oil into its different parts. This is done using a process called fractional distillation.
- First, the crude oil is heated to very high temperatures, turning it into a hot vapor (a gas).
- This hot vapor then goes into a tall tower called a distillation column.
- As the vapor rises in the tower, it cools down. Different parts of the oil cool and turn back into liquid at different heights.
- Lighter products, like gasoline, rise to the top of the tower.
- Heavier products, like asphalt, stay at the bottom.
- This way, the refinery can collect different products from different levels of the tower.
Making Products Better
After separation, some products might need more work. Refineries use other processes to make these products even better. For example, they might remove impurities or change the chemical structure of some parts of the oil. This ensures that the gasoline burns cleanly or that the asphalt is strong enough for roads.
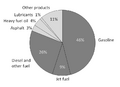
Products We Use Every Day
Oil refineries make many things that are important in our daily lives.
- Gasoline and Diesel Fuel: These are the fuels that power most cars, trucks, and buses.
- Kerosene: Used for jet fuel, heating, and sometimes in lamps.
- Heating Oil: Keeps homes warm in cold weather.
- Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG): Used for cooking, heating, and sometimes in vehicles.
- Asphalt: The sticky, black material used to build roads and roofs.
- Lubricants: Like motor oil, which keeps engines running smoothly.
- Chemicals: Many plastics, medicines, and other products start with chemicals made from oil.
Safety at Refineries
Because refineries handle flammable materials and use high temperatures, safety is very important. Refineries have strict rules and special equipment to prevent accidents and protect workers. They use advanced technology to monitor processes and ensure everything runs safely.
Images for kids
-
A petrochemical refinery in Grangemouth, Scotland
-
The oil refinery in Haifa, Israel, is capable of processing about 9 million tons (66 million barrels) of crude oil a year. Its two cooling towers are landmarks of the city's skyline.
-
Storage tanks and towers at Shell Puget Sound Refinery (Shell Oil Company), Anacortes, Washington
-
Refinery of Slovnaft in Bratislava
-
Sample of crude oil (petroleum)
-
Cylinders of liquified petroleum gas
-
Sample of gasoline
-
Sample of kerosene
-
Sample of diesel fuel
-
Pile of asphalt-covered aggregate for formation into asphalt concrete
See also
 In Spanish: Refinería de petróleo para niños
In Spanish: Refinería de petróleo para niños