Saudi Arabia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
المملكة العربية السعودية
al-Mamlaka al-ʿArabiyya as-Suʿūdiyya |
|
|---|---|
|
Anthem: النشيد الوطني السعودي
"an-Našīd al-Waṭanīy as-Saʿūdī" "Chant of the Saudi Nation" |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Riyadh 24°39′N 46°46′E / 24.650°N 46.767°E |
| Official languages | Arabic |
| Ethnic groups
(2014)
|
90% Arab 10% Afro-Arab (for Saudi citizens only) |
| Religion
(2010)
|
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Unitary Islamic absolute monarchy |
|
• King
|
Salman |
|
• Crown Prince and Prime Minister
|
Mohammed bin Salman |
| Legislature | none |
| Establishment | |
| 1727 | |
|
• Emirate of Nejd
|
1824 |
|
• Emirate of Riyadh
|
13 January 1902 |
|
• Unification
|
23 September 1932 |
| 24 October 1945 | |
|
• Current constitution
|
31 January 1992 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
2,149,690 km2 (830,000 sq mi) (12th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
0.0 |
| Population | |
|
• 2022 census
|
|
|
• Density
|
15/km2 (38.8/sq mi) (174th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2013) | medium |
| HDI (2022) | very high · 40th |
| Currency | Saudi riyal (SR) (SAR) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (AST) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy (AH) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +966 |
| ISO 3166 code | SA |
| Internet TLD |
|
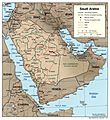
Saudi Arabia is a large country in the Middle East. It covers about 80% of the Arabian Peninsula, which is the world's biggest peninsula. With an area of about 2,150,000 km2 (830,000 sq mi), it is the largest country in the Middle East.
Saudi Arabia shares borders with many countries. To the west is the Red Sea. To the north are Jordan, Iraq, and Kuwait. To the east, you'll find the Persian Gulf, Bahrain, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates. Oman is to the southeast, and Yemen is to the south. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northwest separates Saudi Arabia from Egypt and Israel.
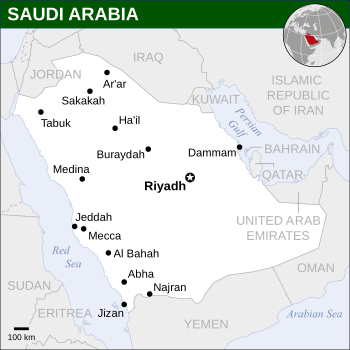
The capital and largest city is Riyadh.
Saudi Arabia is an absolute monarchy, meaning a king rules the country. Sunni Islam is the official religion.
The country is important to Arabs and Islam. It is sometimes called "the Land of the Two Holy Mosques." This refers to Masjid al-Haram in Mecca and Al-Masjid an-Nabawi in Medina. These are the two holiest places in Islam.
Saudi Arabia has about 32 million people. About 16 million of these are Saudi citizens. Arabic is the only official language.
Since 1938, Saudi Arabia has been one of the world's top oil producers. It is also the world's largest oil exporter.
The country's money is called the Saudi Riyal.
Contents
Discovering Saudi Arabia's Past
The area that is now Saudi Arabia used to be four different regions. These were Hejaz, Najd, and parts of Eastern and Southern Arabia. The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia was created in 1932 by Ibn Saud. He brought these regions together. He started by capturing Riyadh in 1902. Riyadh was the original home of his family, the House of Saud.
Since then, Saudi Arabia has been an absolute monarchy. This means the king has all the power. The government follows Islamic laws. It is strongly based on Wahhabism, a specific school of thought in Islam. The country is also known as "The Land of the Two Holy Mosques." These are Masjid al-Haram in Mecca and Al-Masjid al-Nabawi in Medina. These are the two most sacred places in Islam.
How Saudi Arabia is Governed
 |
 |
| Salman Al Saud King and Prime Minister |
Mohammad bin Salman Crown Prince |
Saudi Arabia is an absolute monarchy. The king makes the laws, runs the government, and oversees the courts. Royal decrees are the basis of the country's laws. The king must follow Sharia, which is Islamic law, and the Quran. The Quran and the Sunnah (traditions of Muhammad) are considered the country's constitution. There are no political parties or national elections allowed.
Saudi Arabia joined the United Nations in 1945. It is also a founding member of the Arab League. In 2005, the country joined the World Trade Organization.
Exploring Saudi Arabia's Geography
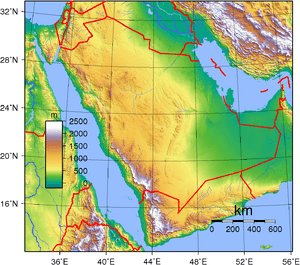
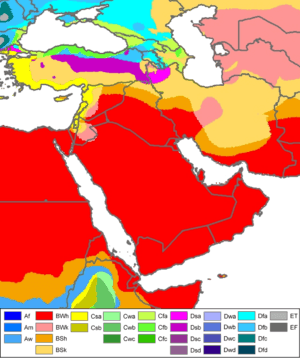
Saudi Arabia's land is mostly desert and dry shrubland. It has many linked deserts. This includes the 647,500 km2 (250,001 sq mi) Rub' al Khali, also known as the "Empty Quarter." This is the world's largest continuous sand desert.
Saudi Arabia is the biggest country in the world without any permanent rivers. However, there are many dry riverbeds called wadis. Fertile areas are found in these wadis, basins, and oases. The main land feature is a central plateau. It rises sharply from the Red Sea and slopes down towards the Persian Gulf.
Along the Red Sea coast, there is a narrow plain called the Tihamah. Next to it is a tall cliff. The southwest area of Asir is mountainous. It has Mount Sawda, which is the highest point in the country at 3,133 m (10,279 ft).
Except for the Asir region, Saudi Arabia has a desert climate. This means very hot days and cool nights. Summer temperatures average around 113 °F (45 °C). They can reach as high as 129 °F (54 °C). In winter, temperatures rarely drop below 32 °F (0 °C). Spring and autumn are milder, averaging around 84 °F (29 °C).
Rainfall is very low. The Asir region is different because of monsoons from the Indian Ocean. These usually happen between October and March. About 300 mm (12 in) of rain falls during this time. This is about 60% of the yearly rain.
Amazing Animals of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is home to many wild animals. These include the Arabian leopard, wolf, striped hyena, and baboon. Other animals are the mongoose, hare, sand cat, and jerboa. Animals like gazelles, oryx, and leopards were common until the 1800s. Too much hunting made them almost disappear.
Birds include falcons, eagles, hawks, and vultures. There are also sandgrouse and bulbuls. Many types of snakes live here, and some are venomous.
The Red Sea has a rich and diverse ecosystem. More than 1200 types of fish have been found there. About 10% of these fish are found nowhere else. This includes 42 types of deepwater fish.
The Red Sea has 2,000 km (1,240 mi) of coral reefs. These reefs are 5000–7000 years old. They are made mostly of stony corals. These reefs form platforms and sometimes lagoons along the coast. They are also visited by ocean fish, including some of the 44 types of shark.
The Red Sea also has many reefs away from the shore. Many of these are unusual. They are thought to be shaped by the high amount of tectonic activity in the area.
Domesticated animals include the famous Arabian horse and the Arabian camel. People also raise sheep, goats, cows, donkeys, and chickens. Saudi Arabia's plants are mostly herbs and shrubs. They need very little water to grow in the desert. The date palm is also very common.
Saudi Arabia's Economy

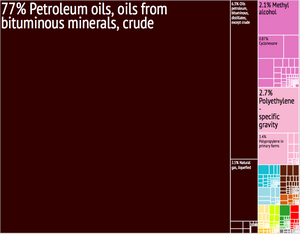
Saudi Arabia has the world's second-largest proven oil reserves. It is also the biggest exporter of oil. The country has the fifth-largest proven natural gas reserves. Because of this, Saudi Arabia is called an "energy superpower." In 2016, its natural resources were worth about US$34.4 trillion. This is the third highest value in the world.
Saudi Arabia's economy relies heavily on oil. About 63% of its government money and 67% of its export earnings come from oil. The country depends a lot on workers from other countries. About 80% of private sector jobs are held by non-Saudis.
Besides oil and gas, Saudi Arabia also has gold mining. This happens in the ancient Mahd adh Dhahab region. There are other important mineral industries too. The country has an agricultural sector, especially in the southwest. It grows vegetables, fruits, and dates, and raises livestock. Many temporary jobs are created by the two million people who visit for the annual hajj pilgrimage.
Farming and Food

Large-scale farming started in the 1970s. The government began a big program to use modern farming methods. They built rural roads, irrigation systems, and storage facilities. They also supported farming research and training.
This led to a huge increase in food production. Saudi Arabia now produces enough of its own meat, milk, and eggs. The country exports wheat, dates, dairy products, and more to markets worldwide. Dates, once a main food, are now mostly grown for humanitarian aid.
Farmers also grow barley, sorghum, and millet. By 2016, Saudi Arabia stopped growing wheat to save water.
The country has some of the most modern and largest dairy farms in the Middle East. Milk production is very high. The local company Almarai is the biggest dairy company in the Middle East.
Saudi Arabia has increased fruit and vegetable production. They use better farming methods and improved roads. The country exports many fruits and vegetables to its neighbors. Popular crops include watermelon, grapes, citrus fruits, and tomatoes. In Jizan, a well-watered area, they grow tropical fruits like pineapples and mangoes.
The olive tree grows naturally in Saudi Arabia. In 2018, the Al Jouf Agricultural Development Company received an award. It was from Guinness World Records for having the largest modern olive farm. The farm covers 7730 hectares and has 5 million olive trees. It produces 15000 tons of olive oil.
The Al Jouf farms are in Sakaka, a city with a history of over 4,000 years. The Al Jouf region has millions of olive trees. The number is expected to reach 20 million soon.
However, using non-renewable groundwater has caused problems. By 2012, about four-fifths of the total groundwater was used up.
Exploring Tourism in Saudi Arabia
Most tourism in Saudi Arabia is for religious pilgrimages. However, leisure tourism is growing. In 2012, about 14.3 million people visited Saudi Arabia. This made it the 19th most-visited country in the world. Tourism is a key part of the Saudi Vision 2030 plan. A 2018 report said that both religious and non-religious tourism could grow a lot.
Starting in December 2018, visitors could get an electronic visa. This visa was for attending sports events and concerts. The "sharek" visa process began with the Saudia Ad Diriyah E Prix race.
In September 2019, Saudi Arabia announced new plans. People from about 50 countries can now get tourist visas to visit.
-
The old city of Jeddah.
-
A farm in Al-Qassim Province.
-
The Rub' al Khali desert.
Regions and Cities
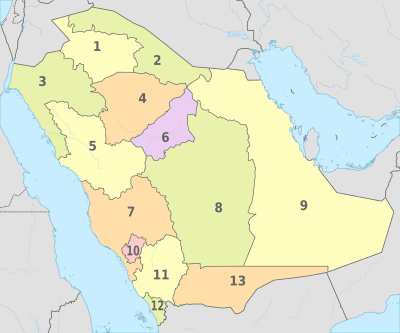
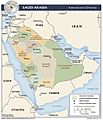
Saudi Arabia is divided into 13 provinces. These provinces are then split into 118 smaller areas called governorates.
| No. | Region | Capital | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Al Jawf | Sakaka | |
| 2 | Northern Borders | Arar | |
| 3 | Tabuk | Tabuk | |
| 4 | Ha'il | Ha'il | |
| 5 | Al Madinah | Medina | |
| 6 | Al Qasim | Buraidah | |
| 7 | Makkah | Mecca | |
| 8 | Al Riyadh | Riyadh | |
| 9 | Eastern Province | Dammam | |
| 10 | Al Bahah | Al Bahah | |
| 11 | Asir | Abha | |
| 12 | Jizan | Jizan | |
| 13 | Najran | Najran |
Major Cities
These are the largest cities in Saudi Arabia.
|
Largest cities or towns in Saudi Arabia
Data.gov.sa (2013/2014/2016) |
||
|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Pop. |
| 1 | Riyadh | 6,506,700 |
| 2 | Jeddah | 3,976,400 |
| 3 | Mecca | 1,919,900 |
| 4 | Medina | 1,271,800 |
| 5 | Hofuf | 1,136,900 |
| 6 | Ta'if | 1,109,800 |
| 7 | Dammam | 975,800 |
| 8 | Buraidah | 658,600 |
| 9 | Khobar | 626,200 |
| 10 | Tabuk | 609,000 |
Saudi Arabian Culture
Saudi Arabia has very old customs and traditions. These often come from Arab civilization. Islam and Arab traditions are big parts of the culture. Its history as an old trade center also plays a role. The culture is very family-focused. People value family traditions and staying close to relatives.
Important Heritage Sites
Some people in Saudi Arabia are very careful about worshiping historical or religious places. They worry it might lead to idolatry. Many important Muslim sites are in the western Hejaz region. Because of this, about 95% of Mecca's old buildings have been taken down. These buildings were often over a thousand years old.
Critics say that over the last 50 years, 300 historic sites linked to Muhammad have been lost. Now, fewer than 20 buildings from Muhammad's time remain in Mecca.
Seven cultural sites in Saudi Arabia are UNESCO World Heritage Sites. These include the Al-Hijr Archaeological Site and Historic Jeddah. Other sites are the Turaif district in Diriyah and Al-Ahsa Oasis. There is also Rock Art in the Hail Region, the Ḥimā Cultural Area, and 'Uruq Bani Ma'arid.
In 2014, a law was passed to protect Saudi Arabia's ancient sites. The country is also investing money to preserve its history. This is part of the Saudi Vision 2030 plan. Saudi Arabia also helps protect heritage in conflict areas.
In 2017, Crown Prince Mohammad bin Salman said Saudi Arabia would return to "moderate Islam." A new center was set up to check interpretations of the Prophet Mohammed's sayings. This is to stop them from being used to justify terrorism.
In 2018, the Crown Prince met with religious leaders. He promised to encourage talks between different faiths. In 2019, Saudi Arabia gave US$25 million to UNESCO. This money is for preserving heritage.
In November 2024, archaeologists found an ancient city in the Khaybar oasis. The city, called al-Natah, is about 4,000 years old. It was lived in during the Bronze Age, around 2,400 BC. It had about 500 houses. Metal weapons were found in nearby graves.
Traditional Dress
Saudi Arabian clothing follows the rules of hijab. This is an Islamic idea of modesty, especially in how people dress. The clothes are usually loose and flowing. They cover the body and are good for Saudi Arabia's desert climate.
Traditionally, men wear a long white garment. It is made from wool or cotton and is called a thawb. On their heads, they wear a keffiyeh or a ghutra. These are square cloths held in place by a rope ring called an agal. For cold days, Saudi men wear a camel-hair cloak called a bisht.
In public, women must wear a black abaya. This is a black outer garment that covers everything except their hands and feet. Most women also cover their heads out of religious respect. This rule applies to non-Muslim women too. Not following it can lead to police action, especially in more traditional areas. Women's clothes are often decorated with patterns, coins, and shiny threads.
Women's Rights and Changes

Before 2019, all women in Saudi Arabia needed a male guardian. This was usually a father, brother, husband, or uncle. In 2019, this law changed for women over 21. They no longer need a male guardian's permission for some things. The new law also gave women rights over their young children.
Before, girls and women could not travel or do official business without their guardian's permission. They also needed permission for some medical procedures. In 2019, Saudi Arabia allowed women to travel abroad. They can also register for divorce or marriage and apply for official documents without a male guardian's permission.
Delicious Saudi Cuisine

Saudi Arabian cuisine is similar to food in nearby countries. It has been influenced by Turkish, Indian, Persian, and African foods. Islamic dietary laws are followed. Pork is not allowed, and other animals are prepared according to halal rules.
Kebabs and falafel are popular. So is shawarma, which is grilled meat like lamb or chicken. Kabsa, a rice dish with meat or seafood, is a national dish. Mandi is another popular dish. Flat, unleavened taboon bread is eaten with almost every meal. Dates, fresh fruit, yogurt, and hummus are also common.
Coffee, served in the Arabic style, is the traditional drink. Tea and fruit juices are also popular. People started drinking coffee in the 15th century in Sufi monasteries in Arabia.
Interesting Facts About Saudi Arabia
- The exact size of Saudi Arabia is not fully known. This is because its borders with the United Arab Emirates and Oman are not precisely marked.
- Saudi Arabia is the only country with coastlines on both the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf.
- Most of its land is dry desert, lowlands, and mountains.
- The Saudi Arabian flag is green. It has the Islamic declaration of faith written in white. There is also a sword below the writing.
- Camels are very important animals in Saudi Arabia. They are used for travel, milk, and meat.
- Falconry, which is hunting with falcons, is a traditional sport.
- Saudi Arabia is building a future city called Neom. It will use only renewable energy.
Images for kids
-
Qaṣr Al-Farīd, a large rock-cut tomb at Hegra, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
-
The Umayyad Caliphate at its largest (661–750).
-
The Battle of Badr, 13 March 624 CE.
-
Abdulaziz Ibn Saud, the first king of Saudi Arabia.
-
Harrat Khaybar seen from the International Space Station.
-
The hajj is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca.
-
A pilgrim praying at Masjid al-Haram in Mecca.
-
The Masjid al-Haram is the holiest Islamic site, in Mecca.
-
The Mosque of the Prophet in Medina.
-
King Abdullah practicing falconry.
-
Uruguay – Saudi Arabia match at the 2018 FIFA World Cup.
-
The desert of Al-Rub' Al-Khali.
See also
 In Spanish: Arabia Saudita para niños
In Spanish: Arabia Saudita para niños