Oman facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Sultanate of Oman
|
|
|---|---|
|
Anthem: نشيد السلام السلطاني
"as-Salām as-Sultānī" "Sultanic Salutation" |
|
Location of Oman (dark green)
|
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Muscat 23°35′20″N 58°24′30″E / 23.58889°N 58.40833°E |
| Official languages | Arabic |
| Religion
(2023)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Omani |
| Government | Unitary Islamic absolute monarchy |
|
• Sultan
|
Haitham bin Tariq |
| Theyazin bin Haitham | |
| Legislature | Council of Oman |
| Council of State (Majlis al-Dawla) | |
| Consultative Assembly (Majlis al-Shura) | |
| Establishment | |
|
• Azd tribe migration
|
130 |
|
• Al-Julandie
|
629 |
|
• Imamate established
|
751 |
|
• Nabhani dynasty
|
1154 |
|
• Portuguese rule
|
1507–1656 |
|
• Yarubi dynasty
|
1624 |
|
• Al Said dynasty
|
1744 |
| 8 January 1856 | |
|
• Sultanate of Oman
|
9 August 1970 |
|
• Basic Statute
|
6 November 1996 (established); 2011 (amended); 2021 (amended) |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
309,500 km2 (119,500 sq mi) (70th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
negligible |
| Population | |
|
• 2018 estimate
|
4,829,473 (125th) |
|
• 2010 census
|
2,773,479 |
|
• Density
|
15/km2 (38.8/sq mi) (177th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2018) | 30.75 medium |
| HDI (2022) | very high · 59th |
| Currency | Omani rial (OMR) |
| Time zone | UTC+4 (GST) |
| DST is not observed. | |
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +968 |
| ISO 3166 code | OM |
| Internet TLD | .om, عمان. |
|
Website
www.oman.om |
|
The Sultanate of Oman is a country in the southwestern part of Asia. It is located on the southeast coast of the Arabian Peninsula. Oman shares borders with the United Arab Emirates to the northwest, Saudi Arabia to the west, and Yemen to the southwest. It also has a sea border with Pakistan to the northeast. The country's coast meets the Arabian Sea in the south and east, and the Gulf of Oman in the northeast.
Oman is a monarchy, which means it is ruled by a king or queen, in this case, a Sultan. The capital city of Oman is Muscat.
Contents
History of Oman

Evidence shows that early humans lived in Oman a very long time ago. Stone tools found in the Dhofar region are about 106,000 years old. This suggests that people moved from Africa into Arabia during the Late Pleistocene era.
Archaeologists have found many ancient sites from the Stone Age and Bronze Age in Oman. These sites show old pottery, stone tools, metal items, and large buildings.
Around the 8th century BCE, the Yaarub tribe is believed to have ruled the entire region, including Oman.
From the 17th century, Oman became a powerful empire. It competed with the Portuguese and British for control in the Persian Gulf and Indian Ocean. At its strongest in the 1800s, Oman's influence reached Iran, Pakistan, and even as far south as Zanzibar.
In the 20th century, the United Kingdom had a strong influence over Oman. The two countries had a good relationship for over 300 years. The UK valued Oman's location for trade routes.
Oman is an absolute monarchy, meaning the Sultan has complete power. The power is passed down through the male family line. Qaboos bin Said was the Sultan from 1970 until he passed away in 2020. He chose his cousin, Haitham bin Tariq, to be the next Sultan.
Oman is the oldest continuously independent country in the Arab world. It is a member of the United Nations and other important international groups.
Geography and Climate
Oman is located between 16° and 28° North latitude, and 52° and 60° East longitude. A large flat desert made of gravel covers most of central Oman. There are mountain ranges along the north (Al Hajar Mountains) and southeast coast (Qara or Dhofar Mountains).
The main cities are found in these coastal and mountain areas. These include the capital city Muscat, Sohar, and Sur in the north, and Salalah in the south.
Oman's climate is hot and dry in the middle of the country. It is more humid along the coast. Long ago, Oman was covered by ocean, and you can still find many fossilized shells in the desert.
The Musandam area is a special part of Oman that is separated from the rest of the country by the United Arab Emirates. It is located on the important Strait of Hormuz. Another small part of Oman, called Madha, is also inside the UAE.
Climate of Oman
Oman has a hot climate with very little rain. Muscat, the capital, gets about 100 mm (4 inches) of rain each year, mostly in January. The Dhofar region gets more rain during the southwest monsoon season from late June to October. Some coastal areas, like near Masirah island, might not get any rain at all in a year.
Temperatures can reach around 50°C (122°F) during the hot season, from May to September.
Plants and Animals
You can find desert shrubs and grasses in Oman, similar to other parts of southern Arabia. However, the central desert plateau has very few plants. The Dhofar region and the mountains have more plants because they get more monsoon rain in the summer. Coconut palms grow well in Dhofar's coastal plains. Frankincense trees grow in the hills, along with oleander and different types of acacia.
The Al Hajar Mountains are a unique area with special wildlife, including the Arabian tahr.
Native mammals in Oman include the leopard, hyena, fox, wolf, hare, oryx, and ibex. Many birds live here too, such as vultures, eagles, storks, and falcons.
Oman has several endangered species. Laws have been made to protect them. These include the Arabian leopard, Arabian oryx, mountain gazelle, goitered gazelle, Arabian tahr, and several types of sea turtles like the green sea turtle and hawksbill turtle.
Oman is also becoming a popular place for whale watching. You might see the rare Arabian humpback whale, sperm whales, and pygmy blue whales here.
Government and Law
Oman is an absolute monarchy. This means the Sultan holds all the power in the country. He makes the laws and leads the government and military.
The legal system in Oman is based on Sharia law, which comes from Islamic teachings. Family matters like divorce and inheritance are handled by Sharia court departments.
Oman has a two-part legislature called the Council of Oman. The upper part is the Council of State, and its members are chosen by the Sultan. This council gives advice. The lower part is the Consultative Assembly, and its members are elected by the people. They serve for four years. Political parties are not allowed in Oman.
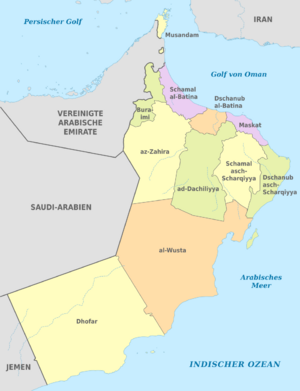
Regions and Cities
Oman is divided into eleven main areas called governorates. Each governorate is then divided into smaller areas called wilayats.
- Ad Dakhiliyah
- Ad Dhahirah
- Al Batinah North
- Al Batinah South
- Al Buraimi
- Al Wusta
- Ash Sharqiyah North
- Ash Sharqiyah South
- Dhofar
- Muscat
- Musandam
Major Cities in Oman
|
Largest cities or towns in Oman
|
||
|---|---|---|
| Rank | Pop. | |
| 1 | Muscat | 797,000 |
| 2 | Seeb | 237,816 |
| 3 | Salalah | 163,140 |
| 4 | Bawshar | 159,487 |
| 5 | Sohar | 108,274 |
| 6 | Suwayq | 107,143 |
| 7 | Ibri | 101,640 |
| 8 | Saham | 89,327 |
| 9 | Barka | 81,647 |
| 10 | Rustaq | 79,383 |
Economy and Tourism
Oman has a varied economy, but it still relies a lot on selling oil.
Oil and Gas
Oman has about 5.5 billion barrels of oil reserves, making it the 25th largest in the world. Oil is taken out of the ground and processed by Petroleum Development Oman (PDO). Oman also has a lot of natural gas.
Tourism in Oman
Tourism is growing very fast in Oman. It is expected to become one of the country's biggest industries. The World Travel & Tourism Council says Oman is the fastest-growing tourist spot in the Middle East.
Oman has many different environments, from deserts to mountains and coasts. It is known for adventure and cultural tourism. Muscat, the capital, was named the second best city to visit in the world in 2012 by Lonely Planet.
Omani Culture

Oman shares many cultural features with its Arab neighbors. However, its geography and history make it unique. Oman has a rich cultural mix because of its past connections to the Swahili Coast and the Indian Ocean.
Oman has a long history of shipbuilding. Maritime travel was very important for Omanis to connect with ancient civilizations. Sur was a famous shipbuilding city.
Traditional Dress
Omani men wear the dishdasha, a simple, long, collarless gown. It is usually white but can be other colors. A tassel called a furakha is sewn into the neckline and can be perfumed. On special occasions, men might wear a black or beige cloak called a bisht over the dishdasha. This cloak often has fancy silver or gold embroidery.
Omani men also wear two types of headwear:
- The ghutra or "Musar" is a square piece of woven wool or cotton fabric with embroidered patterns.
- The kummah is a cap worn during free time.
Many men carry an assa, which is a stick. The Janbiya (dagger) is also part of the national dress. Men wear it at their waist for formal events and festivals. A picture of a Janbiya is on Oman's national flag.
Omani women wear colorful national costumes with different styles depending on the region. Their traditional outfit includes the kandoorah, a long tunic with embroidered sleeves. They wear this over loose trousers called a sirwal. Women also wear a head shawl, usually called a lihaf.
Today, women often wear a loose black cloak called an abaya over their clothes for everyday use. In some areas, especially among the Bedouin people, the burqa is still worn. Most Omani women wear a hijab to cover their hair.
Music and Art
Omani music is very diverse due to Oman's history as an empire. There are over 130 different types of traditional Omani songs and dances. The Oman Centre for Traditional Music works to preserve these. The Royal Oman Symphony Orchestra was started in 1985 and is made up of Omani musicians.
Traditional art in Oman comes from its long history of crafts. Modern art began with tribal handicrafts and painting in the 1960s. Omani artists are now gaining international recognition.
Bait Muzna Gallery was the first art gallery in Oman, opening in 2000. It helps new Omani artists show their work. The National Museum of Oman opened in 2016 and shows Oman's heritage from two million years ago to today. It even has information in Arabic Braille for people who are visually impaired.
Omani Food
Omani food is varied and has been influenced by many cultures. Omanis usually eat their main meal in the middle of the day. The evening meal is lighter. During Ramadan, dinner is often served later in the evening.
Arsia is a special festival meal made of mashed rice and meat (sometimes chicken). Another popular festival dish is shuwa. This is meat cooked very slowly, sometimes for up to two days, in an underground clay oven. The meat becomes very tender and is flavored with spices.
Fish is also common in main dishes, especially kingfish. Mashuai is a whole roasted kingfish served with lemon rice.
Rukhal bread is a thin, round bread. It is eaten with any meal, often with Omani honey for breakfast or crumbled into curry for dinner. Chicken, fish, lamb, and mutton are often used in Omani dishes.
The Omani halwa is a very popular sweet. It is made from cooked sugar and nuts. There are many flavors, like black halwa and saffron halwa. Halwa is a symbol of Omani hospitality and is traditionally served with coffee.
Languages Spoken
Arabic is the official language of Oman. Besides Arabic, many other languages are spoken, especially by people from other countries. These include English, Malayalam, Baluchi, Urdu, Tamil, Bengali, Hindi, and Tulu.
English is widely used in business and is taught in schools from a young age. Most signs and writings at tourist sites are in both Arabic and English.
Sports in Oman
Oman has a Ministry of Sports Affairs that helps organize sports. The Omani national football team has won the Arabian Gulf Cup twice.
Traditional Omani sports include dhow racing (boat racing), horse racing, camel racing, bull fighting (where bulls butt heads), and falconry (hunting with falcons). Newer sports like association football, basketball, waterskiing, and sandboarding are also very popular with young people.
Oman has hosted many international sports events. These include the 2010 Asian Beach Games, the 2011 FIFA Beach Soccer World Cup qualifiers, and the 2012 Beach Handball World Championships. In 2014, the first "El Clasico" football match played outside of Spain took place in Oman.
Oman has tried to qualify for the FIFA World Cup several times. In cricket, Oman qualified for the 2016 ICC World Twenty20 and co-hosted the 2021 ICC Men's T20 World Cup with the United Arab Emirates. In 2024, Oman took part in the Touch Rugby World Cup for the first time.
Gallery
- Muscat, Oman
-
A mosque in Muscat, Oman
-
Mutrah Fort, Muscat, Oman
-
Al Ameen Mosque, Muscat, Oman
-
Sultan Qaboos Grand Mosque, Muscat, Oman
-
Sultan's Ship, Mutrah, Muscat, Oman
-
Al Amarat Hills, Muscat, Oman
-
Al Azaiba Beach, Muscat, Oman
-
Library of Sultan Qaboos Grand Mosque, Muscat, Oman
Images for kids
-
The Portuguese Empire ruled Oman for 143 years (1507–1650).
-
The Sultan's Palace in Zanzibar, which was once Oman's capital.
-
Sultan Said bin Taimur ruled from 1932 to 1970.
-
Nizwa Fort attacked by the British Royal Air Force during the Jebel Akhdar War.
See also
 In Spanish: Omán para niños
In Spanish: Omán para niños
 | Madam C. J. Walker |
 | Janet Emerson Bashen |
 | Annie Turnbo Malone |
 | Maggie L. Walker |