Ecosystem facts for kids
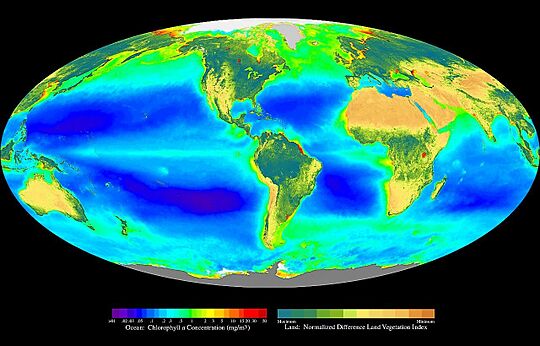
An ecosystem is like a big neighborhood where all living things, like plants and animals, interact with their non-living surroundings. This includes things like water, soil, and air. Living parts are called biotic and non-living parts are abiotic. They are all connected through how nutrients move around and how energy flows.
Ecosystems are shaped by different things. Some are outside factors, like the climate, which sets the general rules. Other factors are inside the ecosystem, like how plants grow or how decomposers break down dead material. Ecosystems are always changing. They can bounce back from things like a big storm or a fire. This ability to recover and stay healthy is called ecological resilience.
Scientists study ecosystems in many ways. They watch them over long periods or do experiments. Biomes are large types of ecosystems, like forests or deserts. In an ecosystem, plants use photosynthesis to make food, bringing energy into the system. Animals help move energy and materials by eating plants and other animals. Tiny microbes and decomposers break down dead stuff, returning important nutrients to the soil and air.
Ecosystems give us many important things. These are called "goods" and "services." Goods include things like water, food, and wood. Services are benefits like clean air, clean water, and even beautiful places to visit. Sadly, human activities can harm ecosystems through pollution, habitat fragmentation, and introducing new species. When an ecosystem loses its main features, it can "collapse." But we can help by working on ecosystem restoration.
What is an Ecosystem?
An ecosystem includes all the living things and their non-living surroundings that interact together. The living parts (biotic) and non-living parts (abiotic) are connected by how nutrients cycle and how energy moves.
Ecosystem processes are how energy and materials move from one part of the ecosystem to another. These processes happen at many different sizes, from a small pond to a huge forest.
How the Idea of Ecosystems Started
The word "ecosystem" was first used in 1935 by a British scientist named Arthur Tansley. He wanted to show how important it is that living things and their environment constantly exchange materials. He described an ecosystem as the complete system, including all organisms and the physical factors around them.
How Ecosystems Work


Inside and Outside Influences
Ecosystems are shaped by factors both outside and inside them. Outside factors, like the climate, control the overall look and function of an ecosystem. For example, how much rain falls and the temperature decide what kind of biome (like a forest or desert) an ecosystem will be.
The type of soil also matters. It affects what nutrients are available. The shape of the land, called topography, can change how water moves and how small climates form.
Other outside factors include how long an ecosystem has existed and what kinds of living things are nearby. If new species are brought into an ecosystem, they can change how it works.
Inside factors are things that both control and are controlled by the ecosystem. These include how dead material breaks down, how plants compete for resources, and how disturbances like fires affect the area.
How Plants Make Food: Primary Production
Primary production is how living things create organic matter from non-organic sources. This mostly happens through photosynthesis. Plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to make carbohydrates (food) and oxygen. This process provides energy for almost all life on Earth.
The total amount of photosynthesis by all plants in an ecosystem is called gross primary production (GPP). Plants use about half of this energy for their own growth and survival. The rest is called net primary production (NPP), which is the energy available for other living things. Photosynthesis can be limited by things like how much light is available, how much water there is, and the temperature.
Energy Flow in Ecosystems
Energy and carbon enter ecosystems through plants making food. This energy then moves to other organisms. Animals eat plants, or other animals, or dead plant matter. Eventually, energy is released through breathing (respiration).
In land ecosystems, most of the energy from dead plants is broken down by decomposers. In water ecosystems, more plant material is eaten by herbivores (plant-eaters).
The path of who eats whom is called a food chain. For example, a plant is eaten by an insect, which is eaten by a bird. But in real life, it's more complex. Animals often eat many different things, creating a food web.
Breaking Down Dead Stuff: Decomposition
Decomposition is the process where dead organic matter (like dead plants and animals) is broken down. This releases nutrients back into the soil and carbon dioxide back into the air. Without decomposition, dead material would pile up, and nutrients would run out.
Decomposition happens in a few ways:
- Leaching: Water washes away soluble parts of dead material.
- Fragmentation: Animals and weather break dead material into smaller pieces. This helps microbes get to it.
- Chemical alteration: Bacteria and fungi use enzymes to chemically break down the dead material.
How Fast Things Decompose
How fast decomposition happens depends on the environment (temperature, moisture), the type of dead material, and the microbes present. Warmer, moist conditions with enough oxygen usually lead to faster decomposition. Very wet or very dry conditions slow it down.
Ecosystem Changes and Recovery
Ecosystems are always changing. They face disturbances like storms, fires, or floods. An ecosystem's ability to stay close to its normal state despite these disturbances is called its resistance. Its ability to recover and keep its main functions after a disturbance is called ecological resilience.
After a disturbance, an ecosystem goes through a process called ecological succession. If a major event like a volcanic eruption leaves bare rock, it's called primary succession. If a less severe event like a forest fire happens, it's secondary succession, and recovery is faster.
Nutrient Cycling
Ecosystems constantly exchange energy and carbon with the environment. But mineral nutrients, like nitrogen and phosphorus, mostly cycle between plants, animals, microbes, and the soil.
Most nitrogen enters ecosystems through nitrogen fixation, where bacteria convert nitrogen gas from the air into a form plants can use. Plants need nitrogen to grow. Phosphorus enters ecosystems from the weathering of rocks.
When plants and animals die, decomposers release these nutrients back into the soil. Plants, fungi, and bacteria then compete for these nutrients. Some bacteria convert nitrogen into different forms, like ammonium, nitrite, and nitrate. Other bacteria can turn nitrates back into nitrogen gas, which returns to the atmosphere.
Fungi that live with plant roots, called mycorrhizal fungi, help plants get phosphorus and nitrogen from the soil.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health

The variety of life, or biodiversity, is very important for how an ecosystem works. The different species, their numbers, and how they interact all affect ecosystem processes.
Having many different species can help an ecosystem. For example, more species might help the soil hold onto nitrogen better. However, adding too many similar species might not make a big difference. But adding a very different species, especially one that isn't native, can have a large impact.
Some species, called keystone species, have a much bigger effect on an ecosystem than their numbers suggest. An ecosystem engineer is an organism that creates, changes, or destroys a habitat, like beavers building dams.
Studying Ecosystems
Ecosystem Ecology

Ecosystem ecology is the study of how living things and their environment interact as one system. Ecosystems can be tiny, like a patch of moss, or huge, like an entire ocean.
One famous study, the Hubbard Brook Ecosystem Study in New Hampshire, started in 1963. Scientists studied a whole watershed (an area of land where all water drains to a common point) as an ecosystem. This long-term research helped discover acid rain in North America in 1972.
Scientists use different ways to study ecosystems. They might do theoretical studies, monitor real ecosystems for a long time, compare different ecosystems, or do experiments.
Classifying Ecosystems
Biomes are broad categories of ecosystems, like tropical forests or arctic tundra. These are defined by their climate and general structure.
Ecosystem classifications look at all parts: the living things, the non-living environment, their interactions, and the physical space they occupy. There are different ways to classify ecosystems, depending on what scientists want to focus on, such as human impact or unique features.
People and Ecosystems
Humans live within and depend on ecosystems. Our actions can have a big impact, even affecting global factors like climate.
Benefits from Ecosystems
Ecosystems provide many things we need, called "goods" and "services." Goods are tangible products like water, food, fuel, and medicinal plants. They also include things like places for tourism and recreation.
Ecosystem services are the benefits we get from healthy ecosystems. These include clean air and water, maintaining the water cycle, keeping oxygen in the atmosphere, and helping plants grow through pollination. They also provide beauty and inspiration.
The Millennium Ecosystem Assessment, a big international study, looked at the state of Earth's ecosystems. It found that human activities are greatly impacting ecosystems, making them less able to recover and provide services. The report called natural systems our "life-support system."
Harm to Ecosystems
As the human population grows and we use more resources, our impact on ecosystems increases. Natural resources are limited and vulnerable. Problems for ecosystems include environmental pollution, climate change, and biodiversity loss. On land, we also see air pollution, soil degradation, and deforestation. In water, issues include overfishing, marine pollution, and the effects of climate change on oceans.
Many ecosystems are harmed by human actions, leading to soil loss, air and water pollution, and habitat fragmentation. When an ecosystem loses its main features, it is considered collapsed. This is different from a species going extinct because it might be possible to restore a collapsed ecosystem.
Managing Ecosystems
When we manage natural resources by looking at the whole ecosystem, not just one species, it's called ecosystem management. A key idea is to make sure ecosystems can keep providing goods and services for a very long time. This can be used for protecting wild areas or for managing farms and forests.
Restoring Ecosystems for a Better Future
Ecosystem restoration aims to help damaged ecosystems recover. Projects that combine conservation with helping people's livelihoods are called integrated conservation and development projects. These projects try to solve environmental and human needs together.
Types of Ecosystems
There are many different kinds of ecosystems around the world. They can be grouped into two main types:
- Aquatic ecosystems (water-based)
- Marine ecosystems (like oceans, coral reefs, and estuaries)
- Freshwater ecosystems (like rivers, lakes, and ponds)
- Terrestrial ecosystems (land-based)
- Forests
- Deserts
- Grasslands
- Tundra (cold, treeless areas)
- Taiga (boreal forests)
Related topics
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Ecosistema para niños
In Spanish: Ecosistema para niños