Water pollution facts for kids
Water pollution means that harmful things get into water, like lakes, rivers, and oceans. This usually happens because of human activities, and it makes the water unsafe or unhealthy to use. These harmful things, called pollutants, come from places like sewage, factories, farms, and even rain washing stuff off city streets.
Water pollution can affect water on the surface (like rivers) or underground (like groundwater). It causes big problems, like harming animals and plants that live in water (aquatic ecosystems). It can also spread diseases if people drink or use polluted water for farming. Polluted water also means we lose important things water usually gives us, like clean drinking water.
To stop water pollution, we need good systems, plans, and rules. New technologies can help too, like better ways to treat sewage, factory waste, and farm runoff. They also help control soil erosion and manage rainwater in cities.
What Is Water Pollution?
Water pollution happens when substances or energy change the water in a way that harms its normal uses. Water is called polluted when human-made contaminants damage it. Because of these harmful things, the water can no longer be used for things like drinking. It also struggles to support the living things in it, like fish.
What Pollutes Water?
Pollution from Sewage
Sewage is wastewater from homes and businesses. Even treated sewage can carry harmful things into water bodies. These include:
- Chemicals from soaps and beauty products.
- Hormones and fake chemicals (like phthalates) that act like hormones. These can harm water animals and even people if the water is used for drinking.
- Bug killers (insecticides) and weed killers (herbicides), often from farms.
If water pollution comes from sewage, the main problems are:
- Solid bits: These make the water look bad and can form sludge.
- Organic matter: This uses up oxygen in the water, which can kill fish.
- Nutrients: Things like nitrogen and phosphorus can make too much algae grow. This can harm fish and make babies sick (from nitrates).
- Germs (Pathogens): These cause diseases.
| Pollutant | What it is | What it can do |
|---|---|---|
| Suspended solids | Tiny bits floating in water |
|
| Organic matter | Natural materials that break down |
|
| Nutrients | Things like nitrogen and phosphorus |
|
| Pathogens | Germs like bacteria and viruses | Causes waterborne diseases |
| Non-biodegradable organic matter | Chemicals that don't break down easily |
|
| Inorganic dissolved solids | Salts and minerals |
|
Germs (Pathogens)
The main types of germs that pollute water are bacteria, viruses, protozoans, and worms. It's hard to find these tiny germs directly. So, scientists often look for "indicator organisms" like E. coli. These show that human or animal waste might be in the water.
Germs in polluted water can cause diseases in people or animals. Some common ones include:
- Cryptosporidium parvum
- Giardia lamblia
- Salmonella
- Norovirus
- Parasitic worms (like Schistosoma)
These germs often come from human or animal waste getting into the water. This can happen if there aren't good toilets or sewage systems. It also happens when sewage plants don't clean water enough, or when heavy rains cause sewers to overflow. Farms with many animals can also be a source if their waste isn't managed well.
Organic Chemicals
Harmful organic chemicals often enter water bodies. These include:
- Oil and gas: From spills or rain washing fuel off roads.
- Industrial solvents: Chemicals used in factories, if not stored properly.
- PFAS: These are "forever chemicals" that stay in the environment for a very long time.
Inorganic Pollutants

Inorganic pollutants are chemicals that don't contain carbon. They include:
- Ammonia: From food processing waste.
- Heavy metals: From cars (washed off by rain) and old mines.
- Nitrates and phosphates: From sewage and farms (these are nutrients).
- Silt (sediment): Tiny bits of soil washed into water from construction sites, logging, or land clearing.
- Salt: When road salt used in winter washes into fresh water, it can make it too salty.
Medicine Pollution
Medicines and their broken-down parts can also pollute water. These include things like antidepressants and antibiotics. They can affect water animals and even people if the water is used for drinking.
Trash and Plastics

Trash can get into water from untreated sewage, overflowing sewers, or people throwing garbage away. Wind can also blow trash from landfills into water. This leads to large pieces of trash polluting the water. It also creates tiny pieces called microplastics that are hard to see.
Microplastics stay in the environment for a long time, especially in oceans and rivers. They cause water pollution and harm animals. A lot of ocean microplastics come from clothes made of polyester, acrylic, or nylon when they are washed.
Rainwater, untreated sewage, and wind are the main ways microplastics travel from land to sea. Synthetic fabrics, car tires, and city dust are the biggest sources of microplastics. These three sources cause more than 80% of all microplastic pollution.
Kinds of Surface Water Pollution
Surface water pollution affects rivers, lakes, and oceans. When it affects oceans, it's called marine pollution. Nutrient pollution is when too many nutrients get into the water.
Around 4.5 billion people worldwide did not have safe sanitation in 2017. This lack of proper toilets often leads to water pollution. During heavy rains or floods, human waste can be washed from the ground into rivers and lakes. Simple pit toilets can also flood.
In 2022, Europe and Central Asia were responsible for about 16% of the microplastics that ended up in the seas globally.
How Water Pollution Harms Us and Nature

Harm to Ecosystems
Water pollution is a huge global problem because it damages all water ecosystems – fresh water, coastal areas, and oceans. The harmful things in water include many chemicals, germs, and even physical changes like warmer temperatures. While some chemicals are natural, too much of them can be harmful. For example, high amounts of natural substances can hurt water plants and animals.
Things that use up oxygen in water, like decaying plants or human-made chemicals, can also cause problems. Other natural and human-made substances can make water cloudy. This blocks sunlight, stopping plants from growing, and can clog the gills of fish.

Health Problems and Waterborne Diseases
A study from 2017 said that "polluted water spread stomach illnesses and parasitic infections and killed 1.8 million people." These are called waterborne diseases. Being around pollutants in water for a long time can also increase the risk of cancer or other serious health issues.
Too Many Nutrients (Eutrophication)
Too much nitrogen pollution can cause eutrophication, especially in lakes. Eutrophication means there are too many nutrients in an ecosystem. This leads to a lack of oxygen in the water and makes the water quality much worse. This can harm fish and other animals living in the water.
Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification is another impact of water pollution. It means the Earth's oceans are becoming less alkaline (more acidic). This happens because the oceans absorb a lot of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air.
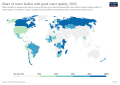
Where Does It Happen?
Water pollution is a problem in both developing countries and developed countries around the world.
Images for kids
-
The Brayton Point Power Station in Massachusetts discharges heated water to Mount Hope Bay.
-
A polluted river draining an abandoned copper mine on Anglesey.
-
Environmental scientists preparing water autosamplers.
See also
 In Spanish: Contaminación hídrica para niños
In Spanish: Contaminación hídrica para niños
- Pollution
- Trophic state index (water quality indicator for lakes)
 | Jessica Watkins |
 | Robert Henry Lawrence Jr. |
 | Mae Jemison |
 | Sian Proctor |
 | Guion Bluford |