Biome facts for kids
In ecology, a biome is a huge area on Earth with a special mix of plants and animals. These living things are perfectly suited to their environment. This includes things like the climate, how high up it is, and the shape of the land.
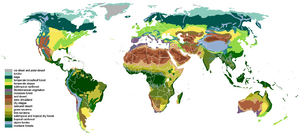
A biome is made up of many smaller areas called ecoregions. It includes all the plants, animals, and even the soil. Often, you can tell a biome apart by its main type of vegetation, like a forest or a grassland.
The different kinds of life in each biome, especially the animals and smaller plants, depend on non-living things like temperature and moisture. Biomes with more plant growth, water, and warmth usually have more different kinds of life.
Biomes are generally split into two main groups:
- Terrestrial (land) biomes
- Aquatic (water) biomes
Sometimes, biomes have different names depending on where they are in the world. For example, a temperate grassland is called a steppe in central Asia. It's known as a savanna or veld in southern Africa. In North America, it's a prairie, and in South America, it's a pampa. In Australia, it might be called outback or scrub.
Contents
Land Biomes: Where Life Thrives
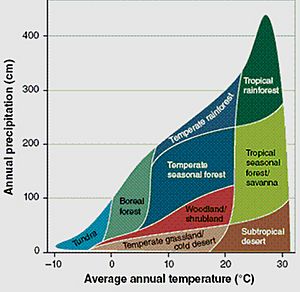
The climate is the biggest factor that decides where different land biomes are found. Important climate factors include:
- latitude: This is how far north or south a place is from the equator. It affects how warm or cold it is. Examples are arctic (very cold) or tropical (very warm).
- humidity: This means how much moisture or water is in the air. Places can be humid (lots of moisture) or arid (very dry).
- Seasonal changes: Some places get rain all year, while others have wet and dry seasons.
- Dry summer, wet winter: Most places get rain in summer. But places with a Mediterranean climate get most of their rain in winter.
- elevation: This is how high a place is above sea level. Going higher up a mountain can be like going further from the equator. The types of habitats change in a similar way.
Generally, you'll find more different kinds of plants and animals closer to the equator. Also, places with more moisture tend to have more biodiversity.
How Scientists Classify Land Biomes
Scientists use different ways to group biomes. Most systems look at a place's latitude (which affects temperature) and how much moisture it gets.
WWF System
The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) created a system that identifies 14 main types of land biomes. They call these "major habitat types." This system helps decide which areas are most important to protect. Here are some of the main types:
- Forests (areas with lots of trees)
- Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests: These are warm, very wet forests, like rainforests.
- Tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests: These are warm forests with wet and dry seasons.
- Tropical and subtropical coniferous forests: These are warm forests with cone-bearing trees.
- Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests: These are forests in cooler areas with trees that lose their leaves in winter, mixed with evergreens.
- Temperate coniferous forests: These are cooler forests with cone-bearing trees, like pine forests.
- Boreal forests/taiga: These are cold, wet forests found in northern regions.
- Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub: These are warm areas with dry summers and wet winters.
- Grasslands (areas mostly covered by grasses)
- Tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands: These are warm areas with tall grasses and scattered trees.
- Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands: These are cooler grasslands, like prairies.
- Flooded grasslands and savannas: These areas are often underwater, either with fresh or salty water.
- Montane grasslands and shrublands: These are grasslands found on mountains.
- Tundra (very cold, treeless areas)
- Deserts and xeric shrublands (very dry areas)
- Mangrove (forests that grow in salty water along coastlines in warm areas)
Water Biomes: Life in Oceans and Rivers
Water biomes are found in oceans, lakes, rivers, and other watery places. Here are some examples:
- continental shelf: The shallow part of the ocean floor near land.
- littoral/intertidal zone: The area along the coast that is covered by water at high tide and exposed at low tide.
- riparian: The areas along rivers and streams.
- pond: Small bodies of still water.
- coral reef: Underwater structures made by tiny animals, full of colorful life.
- kelp forest: Underwater forests made of giant seaweed.
- Drift ice: Floating ice in polar regions.
- hydrothermal vents: Hot springs on the ocean floor.
- cold seeps: Areas on the ocean floor where cold, chemical-rich water seeps out.
- benthic zone: The very bottom of a body of water.
- pelagic zone: The open water part of the ocean, away from the bottom or shore.
Hidden Biomes
Scientists have recently found a new type of biome called the Endolithic biome. This biome is made up of tiny microscopic life forms that live inside rocks. They can be found kilometers beneath the Earth's surface! This biome is so unique that it doesn't fit into the usual ways we classify biomes.
See also
 In Spanish: Bioma para niños
In Spanish: Bioma para niños
 | Georgia Louise Harris Brown |
 | Julian Abele |
 | Norma Merrick Sklarek |
 | William Sidney Pittman |