Pampas facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Pampas Plain
|
|
|---|---|

Landscape in the Pampas at eye level in Brazil
|
|
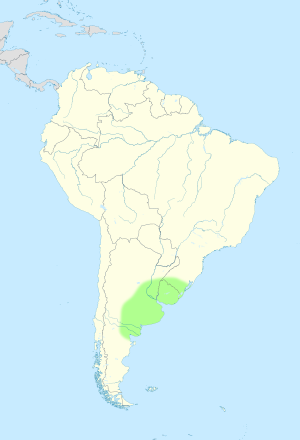
Approximate location and borders of the Pampas encompassing the southeastern area of South America bordering the Atlantic Ocean
|
|
| Countries | |
| Provinces of Argentina | |
| States of Brazil | |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,200,000 km2 (500,000 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 160 m (520 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 44,399,835 |
| • Density | 37.0/km2 (96/sq mi) |
The Pampas (which means 'plain' in the Quechua language) are huge, fertile grasslands in South America. They cover more than 1,200,000 square kilometers (about 463,000 square miles). You can find the Pampas in parts of Argentina, all of Uruguay, and the southernmost state of Brazil, Rio Grande do Sul.
These vast plains are a special natural area. Only a few low hills, like the Ventana and Tandil hills in Argentina, break up the flat landscape. Over time, people have changed this area, especially by bringing in animals like cattle, pigs, and sheep to graze.
The climate here is generally mild. Rain falls throughout the year, making the soil great for agriculture (farming). This region is also part of the larger Paraná–Paraguay plain. The Pampas connect to the Atlantic Forest and Gran Chaco to the north, the Sierras Pampeanas and Cuyo Region to the west, and Patagonia to the south.
Contents
Exploring the Pampas Landscape
The Pampas region generally has low elevations. Most areas are less than 600 meters (about 2,000 feet) high. Coastal areas and much of Buenos Aires Province are mostly flat plains, sometimes with wetlands (areas where the land is covered by water).
Further inland, especially in southern Brazil and Uruguay, you'll find low ranges of hills. These are called coxilhas in Portuguese and cuchillas in Spanish. These grassy hills are a common sight in the northern Pampas countryside. The highest points in the Pampas are in the Sierra de la Ventana mountains in southern Buenos Aires Province. Here, Cerro Tres Picos reaches 1,239 meters (about 4,065 feet) high.

Understanding the Pampas Climate
The Pampas generally have a mild climate. It becomes more humid and subtropical in the north. The southern and western edges have a cold semi-arid climate, meaning they are drier. The southeastern part, near the coast, has an oceanic climate, which is influenced by the ocean.
Seasonal Weather Patterns
Summer temperatures are quite steady, usually between 28 to 33 degrees Celsius (82 to 91 degrees Fahrenheit) during the day. Sometimes, temperatures can reach 38 degrees Celsius (100 degrees Fahrenheit) when warm, dry winds blow from the north.
Autumn arrives in March, April, and May. In April, daytime highs are around 20 to 25 degrees Celsius (68 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit). Nighttime lows are about 9 to 13 degrees Celsius (48 to 55 degrees Fahrenheit). The first frosts can happen in mid-April in the south and later in May or June in the north.
Winters are usually mild. Daytime temperatures are typically 12 to 19 degrees Celsius (54 to 66 degrees Fahrenheit). Nights are cooler, from 1 to 6 degrees Celsius (34 to 43 degrees Fahrenheit). Frosts happen everywhere in the Pampas, but they are more common in the southwest. Snow is very rare, especially in the northern parts.
Spring weather can change a lot. It's often warmer than autumn, especially in the west. However, it can be much colder along the Atlantic coast. Strong storms are common, and temperatures can vary widely. For example, a day of 35 degrees Celsius (95 degrees Fahrenheit) might be followed by a night below 5 degrees Celsius (41 degrees Fahrenheit) or even frost, all within a few days.
Rainfall and Storms
Rainfall varies across the Pampas. The northeast receives about 1400 mm (55 inches) of rain each year. The southern and western edges get much less, around 400 mm (16 inches) or less. In the west, most rain falls in the summer. Eastern areas have more rain in autumn and spring, with slightly drier winters.
Very intense thunderstorms are common in spring and summer. The Pampas is known for having frequent lightning and very tall storm clouds. These severe thunderstorms can bring heavy hailstorms, floods, and flash floods. It is also one of the most active tornado regions outside of the central and southeastern United States.
Amazing Animals of the Pampas
Human activities have greatly changed the wildlife in the Pampas. Many large and medium-sized animals have lost their homes. This is mainly due to the growth of farming and ranching. Animals like the puma, rhea, Capybara, plains viscacha, maned wolf, marsh deer, and Pampas deer are now found in only a few remaining natural spots. Other animals, such as the Jaguar and the Guanaco, have completely disappeared from this area.
Animals Living Today
Some mammals still live in the Pampas. These include the Brazilian guinea pig, southern mountain cavy, coypu, Pampas fox, Geoffroy's cat, lesser grison, white-eared opossum, Molina's hog-nosed skunk, big lutrine opossum, big hairy armadillo, and southern long-nosed armadillo.
Many bird species also call the Pampas home. You might see the ruddy-headed goose, pampas meadowlark, hudsonian godwit, maguari stork, white-faced ibis, white-winged coot, southern screamer, dot-winged crake, curve-billed reedhaunter, burrowing owl, and the rhea. Some animals, like the European hare, wild boar, and house sparrow, were brought here by humans and are now common.
Ancient Animals of the Pampas
Around 12,000 years ago, many giant mammals that lived in the Pampas became extinct. Imagine huge, elephant-sized ground sloths called Megatherium americanum roaming the plains! There were also smaller, but still large, ground sloths like Mylodon.
Other amazing ancient animals included the rhinoceros-like Toxodon, the camel-like Macrauchenia, and elephant relatives called Notiomastodon. There were also ancient horses like Equus neogeus and Hippidion. Giant, car-sized relatives of armadillos, known as glyptodonts (like Glyptodon and Doedicurus), also lived here. The fearsome Smilodon populator, a saber-tooth cat larger than any living big cat, was the top predator of this ancient ecosystem.
-
The skeleton of Doedicurus.
-
A life restoration of Macrauchenia, a camel-sized animal.
Plants and Grasses of the Pampas
The main types of plants in the Pampas are grassy prairie and grass steppe. Many species of Stipa grass are very common here. "Pampas grass" (Cortaderia selloana) is a famous plant of the region. The vegetation usually includes perennial grasses and herbs. Different layers of grasses grow depending on how much water is available.
Why are the Pampas Treeless?
Scientists have long wondered why the original Pampas had no trees. One idea is that seasonal dry periods made it hard for trees to grow. Another thought is that grass roots compete strongly for water, preventing tree seedlings from surviving. Heavy, clay soils might also make it difficult for tree roots to grow deep.
Other ideas include fires started by indigenous peoples to clear land. Large plant-eating animals might also have played a role. Some believe the Pampas are remnants of drier climates from the past. It's likely that a combination of these factors, like low seed dispersal, tough environmental conditions, and competition from other plants, all worked together to slow down tree growth.
Pampas Ecoregions
The World Wildlife Fund divides the Pampas into three main ecoregions:
- The Uruguayan Savanna is east of the Paraná River. It includes all of Uruguay, most of Entre Ríos and Corrientes provinces in Argentina, and southern Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil.
- The Humid Pampas covers eastern Buenos Aires Province and southern Entre Ríos Province.
- The Semiarid Pampas includes western Buenos Aires Province and nearby parts of Santa Fe, Córdoba, and La Pampa provinces.
The Pampas are surrounded by the drier Argentine Espinal grasslands.
Farming and Ranching
Central Argentina is a very successful farming area. Crops are grown on the Pampas, especially south and west of Buenos Aires. Much of the land is also used for raising cattle. More recently, vineyards have been planted in the Buenos Aires wine region. The area is also used for making honey with European honeybees. These farming regions can sometimes experience flooding during thunderstorms. The average temperature in the Pampas is about 16 degrees Celsius (60 degrees Fahrenheit) year-round.
A Glimpse into Pampas History

When Spanish colonists arrived on the shores of the Río de la Plata and founded Buenos Aires in the 16th century, they met local indigenous tribes, mainly the Querandí. By the end of the 18th century, the Salado River marked a boundary between the Spanish settlements and the indigenous territories.
As European settlers created new communities, conflicts arose over resources and land with indigenous groups like the Mapuche. The Mapuche sometimes took cattle from settlements and moved them to Chile through mountain passes. A main route for this was called Camino de los chilenos. In the 1870s, to manage these conflicts and establish clearer boundaries, Argentina built a deep trench called Zanja de Alsina. This trench aimed to prevent cattle from being moved west and to define the territories of the indigenous tribes in the Pampas.
A leader named lonco Calfucurá traveled from Chile to the Pampas around 1830. In 1859, Calfucurá and 3,000 warriors approached Bahía Blanca in Argentina. In 1872, Calfucurá and 6,000 warriors moved across the Pampas, reaching cities like General Alvear, Veinticinco de Mayo, and Nueve de Julio. After these events, Argentina organized its forces to secure the land, in what was known as the Conquest of the Desert.

European Immigration
Starting in the 1840s and increasing after the 1880s, many European immigrants came to the Pampas. Some were part of government plans to settle the land. Others became tenant farmers, working for landowners to earn a living.
However, after the 1930s, as industries grew, many immigrants moved to cities for more stable jobs. Because of this, the history of immigration in Buenos Aires Province is often linked to city life. In contrast, in Entre Ríos Province and Santa Fe Province, European immigration had a stronger connection to rural areas and farming.
See also
 In Spanish: Pampa (geobotánica) para niños
In Spanish: Pampa (geobotánica) para niños
- Dry Pampa
- Humid Pampas
- Estancia
- Federal University of Pampa
- Gaucho
- José Froilán González – the "Pampas Bull"
- Luis Ángel Firpo – the "Wild Bull of Las Pampas"
- Médanos (dunes)
- Médanos wines
- Riograndense Republic
- Southern Cone
- South American jaguar



















