Climate facts for kids
The climate of a place is like its long-term weather story. It's the typical weather patterns, averaged over many years, usually 30. Think of it as what you expect the weather to be like in a certain season or month.
Scientists measure things like temperature, humidity (how much moisture is in the air), wind, and precipitation (rain, snow). These measurements help us understand a region's climate. Climate is also about how the atmosphere (air), oceans, ice, land, and living things on Earth all interact.
Many things affect a place's climate. These include how far it is from the equator (its latitude), how high up it is (its altitude), and if it's near large water bodies or mountains. Even how people use the land can play a role.
We can group climates into different types, often based on their average temperature and precipitation. One popular way to do this is called the Köppen climate classification system.
Scientists who study ancient climates are called paleoclimatologists. They look at clues like tree rings and ice cores to learn about Earth's climate from long ago. Today, climate models are like computer programs that help us understand past, present, and future climates. Sometimes, climate changes, and recent warming is often called global warming. This can cause plants and animals to move to new areas.
Contents
What is Climate?
Climate is often called the "average weather" of a place over a long time. This usually means looking at weather data for 30 years. It's not just the average, but also how much the weather changes from day to day or year to year.
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) helps define these averages. They call them "climate normals." These normals are like a baseline to see how current weather patterns compare to the past. A 30-year period is chosen because it's long enough to smooth out yearly ups and downs, but short enough to show bigger changes over time.
The easiest way to remember the difference between climate and weather is: "Climate is what you expect, weather is what you get!" For example, you expect winters in Canada to be cold (that's climate). But on a specific day, it might be unusually warm (that's weather).
Many things affect a region's climate. These include its latitude (how far north or south it is), its altitude (how high above sea level), and how close it is to large oceans or mountains. Even the types of plants growing in an area can influence its climate.
Things like ocean currents also move heat around the Earth. The amount of greenhouse gases in the air, like carbon dioxide, affects how much heat our planet keeps. This can lead to the Earth getting warmer or cooler over long periods.
How Do We Classify Climates?
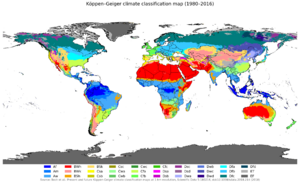
We classify climates to help us understand and compare different regions around the world. These systems group places with similar weather patterns together. Often, a climate classification matches closely with the types of plants and animals (called a biome) that live there. This is because climate has a huge effect on life.
The most famous system is the Köppen climate classification. It was created over a hundred years ago. This system mainly uses temperature and precipitation to define different climate zones.
Some ways to classify climates look at why a climate is the way it is. Other ways look at the effects of the climate, like what kinds of plants can grow there. It's important to remember that in real life, climate zones don't have sharp lines. Instead, they usually blend into each other gradually.
Studying Climate History
Learning About Past Climates (Paleoclimatology)
Paleoclimatology is the study of Earth's climate from long, long ago. Since we didn't have thermometers thousands of years ago, scientists look for clues. They study things like:
- Ice cores: These are long tubes of ice drilled from glaciers. The layers of ice hold tiny bubbles of ancient air and dust, telling us about past temperatures and atmospheres.
- Tree rings: The width and density of tree rings can show how much rain fell and how warm it was each year.
- Sediments from lake beds: Layers of mud and dirt at the bottom of lakes can contain pollen and other materials that reveal past plant life and climate.
By studying these clues, scientists can figure out if past climates were stable or if they changed a lot. They can also see if these changes happened in regular patterns.
Measuring Today's Climate
For the last few hundred years, we've been able to measure climate directly. We use tools like thermometers for temperature, barometers for air pressure, and anemometers for wind speed.
In the past, most of these measurements were taken in cities or richer countries. But since the 1960s, satellites have been launched into space. These satellites can collect climate data from all over the world, even from remote places like the Arctic and the middle of the oceans. This gives us a much better picture of Earth's climate.
Why Climate Changes Naturally
Climate variability describes how climate changes naturally over time. These changes can happen over different periods and in different places. Some changes seem random, while others follow regular patterns.
Many natural factors can cause Earth's climate to change. These include:
- Changes in the Sun's energy.
- Large volcanic eruptions that can block sunlight.
- How heat moves between the oceans and the atmosphere.
Sometimes, these natural changes can be hidden or made stronger by human activities. For example, the release of greenhouse gases by people can affect these natural patterns.
Understanding Climate Change
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in global or regional climates. These changes can be caused by natural processes within Earth, outside forces like changes in sunlight, or human activities.
In recent times, especially when we talk about the environment, "climate change" often means the warming of our planet. This warming is mostly due to human activities. The United Nations uses the term "climate variability" for natural changes and "climate change" for human-caused changes.
Earth has experienced many climate shifts in its long history. There have been several major ice ages, which were very cold periods. These were separated by warmer times called interglacial periods. For example, when there's a lot of snow and ice, it reflects more of the Sun's energy back into space, keeping the Earth cooler.
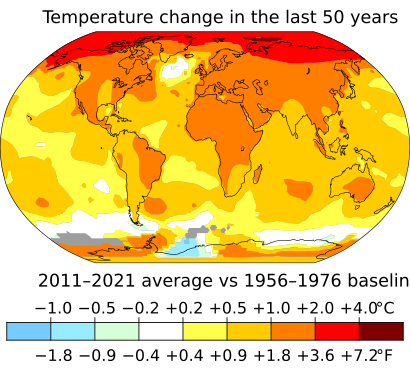
Increases in greenhouse gases, like from volcanic activity, can make the Earth warmer. However, these natural climate changes happen very slowly, over thousands or millions of years. The current rate of change, largely caused by human activities releasing greenhouse gases, is happening much faster.
According to the EU's Copernicus Climate Change Service, the average global air temperature passed 1.5°C of warming during the period from February 2023 to January 2024. This shows how quickly our planet is warming.
How Climate Models Work
Climate models are like powerful computer programs. They use math and physics to simulate how the atmosphere, oceans, land, and ice interact. Scientists use these models for many reasons. They help us understand how weather and climate systems work. They also help us predict what future climates might be like.
All climate models try to balance the energy coming into Earth from the Sun with the energy leaving Earth. If there's an imbalance, the Earth's average temperature will change.
These models can be very detailed, showing climate changes over small areas. The most important use of these models recently has been to predict what will happen as more greenhouse gases, especially carbon dioxide, are added to the atmosphere. These models predict that the average global temperature will continue to rise, especially in the northern parts of the world.
Models can be simple or very complex. Simple models might treat the Earth as a single point. More complex models use detailed equations to simulate how mass, energy, and radiation move around the planet.
See also
 In Spanish: Clima para niños
In Spanish: Clima para niños
- Climate Prediction Center
- Climatic map
- Climograph
- Ecosystem
- Greenhouse effect
- List of weather records
- Microclimate
- National Climatic Data Center
- Outline of meteorology
 | Stephanie Wilson |
 | Charles Bolden |
 | Ronald McNair |
 | Frederick D. Gregory |