Habitat fragmentation facts for kids
Habitat fragmentation happens when big natural areas, called habitats, get broken up into smaller pieces. This splits up the animals and plants that live there and rely on each other to survive. It's like a big puzzle that gets shattered into many tiny, separate parts.
Contents
What Causes Habitat Fragmentation?
Habitat fragmentation is a big problem because it always involves destroying some of these natural homes. When habitats are broken up, it's often because of human activities.
Human Activities
- Building roads and cities: When new roads, towns, or cities are built, they cut through forests, grasslands, or wetlands. This divides the land into smaller sections.
- Farming: Large areas of land are cleared to create farms. This removes natural habitats and leaves only small patches of original land.
- Logging: Cutting down trees for wood can break up large forests into smaller, isolated woodlands.
- Mining: Digging for minerals can destroy habitats and create barriers for wildlife.
When these things happen, plants and other living things in these areas are often destroyed. Animals that can move, like deer or birds, try to escape and find new homes. This can lead to too many animals in one small area, causing them to fight for food and space.
Why is Fragmentation a Problem?
Habitat fragmentation causes many issues for wildlife and the environment.
Smaller Populations
When a large habitat is broken into smaller pieces, the animal and plant populations living there also get split up.
- Less space: Animals have less room to find food, water, and mates.
- Isolation: Small groups of animals become isolated. They can't easily move to other areas to find new mates, which can lead to less healthy populations over time.
- Increased danger: Animals might have to cross dangerous areas like roads to find resources, putting them at risk.
Edge Effects
The edges of fragmented habitats are different from the inside.
- Changes in environment: Edges are often windier, drier, and have more sunlight. This can harm plants and animals that need the stable conditions of a deep forest or wetland.
- More predators: Predators like foxes or raccoons often thrive near edges, making it harder for some species to survive there.
- Human disturbance: Edges are closer to human activities, which can bring more noise, pollution, and disturbance to wildlife.
What Can We Do?
Protecting habitats is very important for the health of our planet.
Conservation Efforts
- Protecting existing habitats: Keeping large areas of natural land untouched is the best way to prevent fragmentation.
- Creating wildlife corridors: These are strips of land that connect fragmented habitats, allowing animals to move safely between them. This could be a tunnel under a road or a bridge over a river.
- Restoring habitats: Planting trees or restoring wetlands can help bring back lost habitats and connect existing ones.
- Sustainable practices: Using farming and logging methods that are less harmful to the environment can help reduce habitat destruction.
By understanding habitat fragmentation, we can work towards better ways to share our planet with all living things.
Images for kids
-
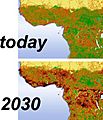
This map shows how the homes of Great Apes in Central Africa have been broken up. The black and red areas show where a lot of their habitat has been lost.
-
This picture shows deforestation (cutting down forests) in Europe. France has lost a lot of its native forests.
-
This image from 2016 shows deforestation happening in Bolivia, likely for growing sugarcane.
See also
 In Spanish: Fragmentación de hábitat para niños
In Spanish: Fragmentación de hábitat para niños