Acid rain facts for kids

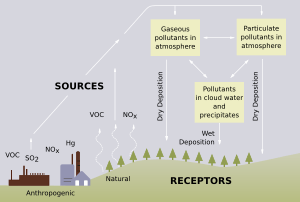
Acid rain is rain that is much more acidic than normal. This happens when certain gases go high into the sky and mix with the water in the air.
Acid rain can harm plants, animals, and even humans.
A scientist named Robert Angus Smith first used the term "acid rain." In 1852, he showed how acid rain was connected to air pollution in Manchester.
Contents
What is Acid Rain?
"Acid rain" is a common way to talk about different types of acidic stuff falling from the sky. This can be wet, like rain, snow, or fog, or dry, like tiny acidic bits and gases.
Normal, clean rain is a little bit acidic, but usually not below a pH of 5.7. This is because carbon dioxide in the air mixes with water to form a weak acid called carbonic acid.
- H
2O (l) + CO
2 (g) ⇌ H
2CO
3 (aq)
However, acid rain is much more acidic. Sometimes, in busy industrial areas, the pH of rain and fog can be as low as 2.4! This is like the acidity of lemon juice.
The main causes of the pollution that leads to acid rain are:
- Burning fossil fuels to make electricity.
- Powering cars and trucks.
- Making products in factories.
These activities release gases like sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into the air.
Why Does Acid Rain Happen?
While some natural things like carbon dioxide and gases from volcanoes can cause a little acid rain, most of it comes from human activities.
When people started building many factories and power stations, they burned coal or oil. These fuels contain sulfur. When burned, the sulfur goes into the air, mixes with other chemicals, and creates acid rain.
Since the 1970s, governments have tried to clean the smoke from factories and power stations. This helps stop too much sulfur from going into the air. It has worked well, but it costs a lot of money.
For example, in 2001, Great Britain still released about five million tonnes of these gases each year. China produced 18 million tonnes. The United States used to produce over 20 million tonnes, but by 2010, that number dropped to 8.1 million.
How Acid Rain Harms Nature
Effects on Lakes and Rivers

The pH level in lakes and rivers is very important for fish and other water animals to live. Acid rain can change this pH level. If the water becomes too acidic, several bad things can happen:
- Fish larvae (baby fish) might not hatch because the special chemicals (called enzymes) they need won't be made.
- Aluminium can move more easily through acidic water. This makes fish produce more mucus around their gills, making it hard for them to breathe.
- Tiny water plants called phytoplankton won't grow well. Animals that eat these plants will then suffer from lack of food.
Effects on Soil and Plants
Acid rain can hurt soil by killing tiny living things called microbes that are important for healthy soil. The acid also allows harmful chemicals (called toxins) to move around in the soil. It also washes away important nutrients that plants need.
Forests often have special fungi that help trees get water and minerals. The trees, in return, give the fungi food. This helpful relationship, called mycorriza, can be destroyed by acid rain. This makes it harder for trees to grow.
Other Harmful Effects

Acid rain harms both living things and non-living things.
- The leaves and roots of trees get damaged. This makes it harder for them to make food (photosynthesis) and take in nutrients.
- Harmful chemicals released by acid rain can be dangerous to humans.
- Old statues and buildings can also be damaged by acid rain, causing them to wear away over time.
Stopping Acid Rain
In the U.S., one way to stop sulfur from escaping into the air from factory smokestacks is called Flue gas desulfurization (FGD). A common method is using a wet scrubber. This machine pulls gases from the smokestack into a tower and cleans them using lime or limestone. This changes the harmful chemicals into a different form, like calcium sulfate, which can then be removed. Sometimes, these sulfates are sold to other companies. Other times, they are put into a special landfill.
Some people believe that pollution is a natural part of factories and power stations. They think that if pollution is not handled carefully, it could be dangerous. Others install pollution controls because they see the benefits for the environment and people's health.
Cool Facts About Acid Rain
- Acid rain happens when gases mix with water high up in the air.
- Sulfur dioxide is a main chemical that causes acid rain. It comes from machines, homes, and vehicles.
- Acid rain makes it harder for aquatic animals (animals living in water) to survive.
- It can also damage the soil and the plants that grow in it.
- There are ways to stop so much sulfur dioxide from getting into the air. Many companies use special machines in their factories to control pollution.
Images for kids
-
Since 1998, Harvard University wraps some of its statues with waterproof covers every winter. This protects them from damage caused by acid rain and snow.
See also
 In Spanish: Lluvia ácida para niños
In Spanish: Lluvia ácida para niños
 | Laphonza Butler |
 | Daisy Bates |
 | Elizabeth Piper Ensley |