Sulfur dioxide facts for kids
Sulfur dioxide (also spelled sulphur dioxide) is a special chemical compound with the formula SO2. It's a colorless gas that smells strong and a bit like burnt matches. It can also feel suffocating if you breathe in too much.
Sulfur dioxide is made naturally by volcanoes. It's also created during many industrial activities. People use it for different things, like protecting wine from going bad and making other important chemicals. When sulfur dioxide dissolves in water, it forms sulfurous acid. It can also be changed into sulfur trioxide, which is then used to make sulfuric acid, a very strong acid.
Contents
Where is Sulfur Dioxide Found?
Sulfur dioxide is present on Earth, but only in very small amounts in our atmosphere.
On other planets, like Venus, sulfur dioxide is much more common. It's the third most abundant gas there! On Venus, it mixes with water to create clouds of sulfuric acid. It plays a big part in Venus's weather and even adds to its global warming. Scientists also think it helped warm up early Mars. On both Venus and Mars, just like on Earth, volcanoes are believed to be the main source of this gas.
In colder places, like the Galilean moons (Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto), sulfur dioxide might exist as ice. On Io, it can be found as frost. On Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto, it might be in the crust and deep inside, possibly even as a liquid that reacts with water.
How is Sulfur Dioxide Used?
The most important use for sulfur dioxide is in making sulfuric acid.
Protecting Food
Sulfur dioxide is sometimes used to keep dried fruits, like apricots and figs, fresh. It stops tiny living things (like bacteria) from growing and prevents the fruit from turning brown. This helps the fruit keep its bright color and stops it from rotting. In Europe, when used this way, it's called E220.
In Winemaking
The ancient Romans were the first to use sulfur dioxide in winemaking. They found that burning sulfur candles inside empty wine containers kept the wine fresh and stopped it from turning into vinegar.
Even today, sulfur dioxide is very important in winemaking. It acts like an antibiotic and an antioxidant. This means it protects wine from bacteria and from reacting with oxygen, which can make the wine turn brown and lose its flavor. It also helps control how sour the wine gets. Wines that contain sulfur dioxide usually have a label saying "contains sulfites."
The amount of sulfur dioxide in wine is carefully measured. It can be in different forms, but the "molecular" form is the most active. This form helps kill germs and stops oxidation. If there's too much, you might smell a strong odor. Rules in the US and EU set limits on how much total sulfur dioxide can be in wine.
Sulfur dioxide is also used to clean and sanitize equipment in wineries. This helps keep everything germ-free so the wine stays good.
As a Cleaning Agent
Sulfur dioxide can act as a "reducing agent." This means it can take away oxygen from other substances. When mixed with water, it can remove color from things. It's used as a bleach for paper and delicate materials like clothes. However, this bleaching effect doesn't usually last long because oxygen in the air can bring the color back.
In places that treat wastewater, sulfur dioxide is used to clean water that has been treated with chlorine before it's released. It changes the chlorine into a harmless form called chloride.
As a Fumigant
In the early 1900s, sulfur dioxide was used in cities like Buenos Aires to kill rats that carried the bacteria causing bubonic plague. This method worked well and was used in other places too, like Rio de Janeiro and New Orleans. Special machines that released sulfur dioxide were brought into the streets for large-scale cleaning efforts.
Safety and the Environment

Breathing Sulfur Dioxide
We often come across sulfur dioxide in small amounts, for example, from burning matches or fuels like coal. In small amounts, it's not very harmful. However, because it's so common, it's a major air pollutant that can affect our health.
Breathing in too much sulfur dioxide can cause problems for your heart and lungs, including conditions like asthma and bronchitis. It's also been linked to babies being born too early or with low birth weight. For example, a study in Beijing found that higher levels of sulfur dioxide in the air were connected to lower birth weights in babies.
Air Pollution
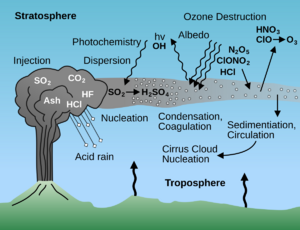
Large volcanic eruptions can release huge amounts of sulfur dioxide into the air. This gas then reacts to form tiny particles called sulfate aerosols. Before the Industrial Revolution, natural sources like volcanoes were the main contributors to these particles.
However, after the Industrial Revolution, human activities started releasing much more sulfur into the atmosphere. By the 1980s, human-made sulfur emissions were even greater than all natural emissions combined! In industrialized areas like Europe and North America, human pollution became the main source.
This increase in sulfate aerosols caused many problems. One of the most noticeable was acid rain. This happens when clouds carry high amounts of sulfate particles, making the rain acidic.
Acid rain has harmed lakes and streams, killing fish and insects in some areas. It also damages soil, making it harder for plants to grow and causing important nutrients to wash away. Plants that can't handle low pH levels die, especially forests in mountains that are often exposed to sulfate-filled fog.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Dióxido de azufre para niños
In Spanish: Dióxido de azufre para niños