Bronchitis facts for kids
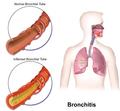
Bronchitis is when the tubes that carry air to your lungs get swollen and irritated. These tubes are called bronchial tubes. When they are inflamed, they make more mucus than usual. This can make it hard to breathe and cause you to cough a lot.
Bronchitis can be caused by an infection, like a cold or the flu. It can also happen if you breathe in things that irritate your lungs, such as cigarette smoke or air pollution.
Contents
What is Bronchitis?
Your lungs have many air passages, like branches of a tree. The main branches are the bronchial tubes. When you have bronchitis, the lining of these tubes gets red and swollen. This swelling makes the tubes narrower. Also, your body produces extra mucus, which can block the tubes even more. This is why a cough is the main symptom of bronchitis.
Types of Bronchitis
There are two main types of bronchitis:
Acute Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is very common. It often happens after you've had a cold or the flu. It's sometimes called a "chest cold."
- Causes: Most often, viruses cause acute bronchitis. The same viruses that cause the common cold or flu can lead to it.
- Symptoms: You might have a cough that lasts for a few weeks. This cough can bring up mucus. Other symptoms include a sore throat, tiredness, and a mild fever.
- Duration: Acute bronchitis usually gets better on its own within a few weeks. The cough might linger for a bit longer.
- Treatment: Doctors usually suggest rest, drinking plenty of fluids, and using over-the-counter medicines to help with symptoms. Antibiotics don't work for viruses.
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is a more serious, long-term condition. It means you have a cough that brings up mucus almost every day for at least three months a year, for two years in a row.
- Causes: The most common cause of chronic bronchitis is long-term exposure to irritants. Smoking cigarettes is the biggest risk factor. Breathing in secondhand smoke, air pollution, or dust can also cause it.
- Symptoms: A persistent cough with mucus is the main sign. You might also feel short of breath, especially when you are active.
- Severity: Chronic bronchitis is a type of COPD. COPD is a group of lung diseases that block airflow and make it hard to breathe.
- Treatment: The most important step is to stop being exposed to the irritant, especially smoking. Doctors may also prescribe medicines to help open your airways and clear mucus.
Causes of Bronchitis
Bronchitis happens when your bronchial tubes get irritated. Here are the main causes:
- Viruses: These are the most common cause of acute bronchitis. The same viruses that cause the common cold and flu can infect your bronchial tubes.
- Bacteria: Less often, bacteria can cause bronchitis.
- Irritants: Breathing in certain things can irritate your airways.
- Cigarette Smoke: This is the leading cause of chronic bronchitis. Both smoking yourself and being around secondhand smoke can damage your lungs.
- Air Pollution: Breathing in polluted air can also irritate your bronchial tubes.
- Dust and Fumes: Exposure to dust, chemical fumes, or other irritants at work can also cause bronchitis.
Symptoms to Look For
The symptoms of bronchitis can vary, but here are the most common ones:
- Cough: This is the main symptom. It can be dry or produce mucus. The mucus might be clear, white, yellowish-gray, or green.
- Tiredness: You might feel very tired or run down.
- Shortness of Breath: You might feel like you can't get enough air, especially with chronic bronchitis.
- Wheezing: This is a whistling sound when you breathe.
- Mild Fever and Chills: These are more common with acute bronchitis.
- Chest Discomfort: You might feel pain or tightness in your chest.
How Doctors Diagnose Bronchitis
If you have symptoms of bronchitis, a doctor will usually:
- Ask About Your Symptoms: They will want to know about your cough, how long it's lasted, and what kind of mucus you're producing.
- Do a Physical Exam: The doctor will listen to your lungs with a stethoscope to check for unusual sounds.
- Chest X-ray: Sometimes, a chest X-ray is done to make sure you don't have Pneumonia, which is a more serious lung infection.
- Sputum Test: If you have chronic bronchitis, the doctor might take a sample of your mucus (sputum) to check for bacteria.
Treatment and Prevention
The treatment for bronchitis depends on whether it's acute or chronic.
Treating Acute Bronchitis
- Rest: Get plenty of rest to help your body fight the infection.
- Fluids: Drink lots of water, juice, or broth. This helps thin the mucus, making it easier to cough up.
- Humidifier: A cool-mist humidifier can help loosen mucus and ease your cough.
- Over-the-Counter Medicines: Pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help with fever and body aches. Cough medicines might help, but always ask an adult before taking them.
- Avoid Irritants: Stay away from smoke, dust, and strong fumes.
Treating Chronic Bronchitis
- Stop Smoking: If you smoke, quitting is the most important step.
- Avoid Irritants: Try to avoid secondhand smoke, air pollution, and other lung irritants.
- Medicines: Doctors might prescribe inhalers to open your airways or steroids to reduce inflammation.
- Oxygen Therapy: In severe cases, some people might need extra oxygen.
Preventing Bronchitis
- Wash Your Hands: Wash your hands often with soap and water to prevent the spread of viruses.
- Get Vaccinated: Get your annual flu shot. This can help prevent the flu, which often leads to bronchitis.
- Avoid Smoke: Stay away from cigarette smoke, both first-hand and secondhand.
- Wear a Mask: If you're in a dusty or polluted area, wearing a mask can help protect your lungs.
When to See a Doctor
Most cases of acute bronchitis get better on their own. However, you should see a doctor if:
- Your cough lasts longer than three weeks.
- You have a high fever.
- You are coughing up blood.
- You have trouble breathing or wheezing.
- You get bronchitis often.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Bronquitis para niños
In Spanish: Bronquitis para niños