Dromedary facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Dromedary camel |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: |
C. dromedarius
|
| Binomial name | |
| Camelus dromedarius Linnaeus, 1758
|
|
 |
|
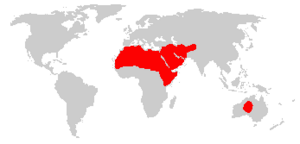
| domestic dromedary range | |
The dromedary camel (Camelus dromedarius), also known as the Arabian camel, is a large animal with one hump on its back. It belongs to the same group as cows and deer, called even-toed ungulates.
Dromedaries are the tallest of all camel types. Adult male dromedaries stand about 1.8 to 2 meters (6 to 6.5 feet) tall at the shoulder. Females are a bit shorter, usually 1.7 to 1.9 meters (5.5 to 6.2 feet) tall. Males typically weigh between 400 and 600 kg (880 to 1,320 lb). Females weigh between 300 and 540 kg (660 to 1,190 lb).
These camels have a long, curved neck and a narrow chest. Their most famous feature is their single hump. This is different from the Bactrian camel, which has two humps. Dromedaries also have long hair on their throat, shoulders, and hump. Their fur is usually brown. The hump is about 20 cm (8 inches) tall or more. It is made of fat, which helps the camel survive in the desert.
Dromedaries are mostly active during the day. They live in groups of about 20 camels. A strong male usually leads these groups.
These camels eat leaves and other plants found in the desert. They have special ways to survive in dry places. For example, they can lose over 30% of their body water and still be okay. This helps them live well in their desert homes.
Female dromedaries give birth to one baby after being pregnant for about 15 months.
Wild dromedaries have not lived in nature for almost 2,000 years. People probably first tamed them in the Arabian Peninsula about 4,000 years ago. Some ancient cave paintings in Somalia suggest they might have been tamed even earlier, 5,000 to 9,000 years ago. In the past, wild dromedaries lived in dry areas like the Sahara Desert. Today, domesticated dromedaries live in dry and semi-dry areas of Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. There is also a large group of wild dromedaries in Australia.
Dromedaries provide many useful things, like meat and milk, for some tribes in northern Arabia. They are also commonly used for riding and carrying heavy loads.
Contents
What is a Dromedary?
The dromedary is part of the Camelus family. This family also includes the two-humped Bactrian camel and the wild Bactrian camel. All camels belong to the Camelidae family.
An ancient Greek thinker named Aristotle was the first to describe camel species. He wrote about the one-humped Arabian camel and the two-humped Bactrian camel. Later, in 1758, a Swedish scientist named Carl Linnaeus gave the dromedary its scientific name: Camelus dromedarius.
How Do Dromedaries Look?
Dromedaries are the tallest of all camel species. Adult males are about 1.8 to 2 meters (6 to 6.5 feet) tall at the shoulder. Females are slightly shorter, from 1.7 to 1.9 meters (5.5 to 6.2 feet). Males usually weigh between 400 and 600 kg (880 to 1,320 lb). Females weigh between 300 and 540 kg (660 to 1,190 lb).
Their special features include a long, curved neck and a narrow chest. They have one hump, unlike the Bactrian camel which has two. Dromedaries also have thick, double-layered eyelashes and bushy eyebrows. These help protect their eyes.
They have excellent eyesight and a good sense of smell.
Male dromedaries have a soft part in their mouth, almost 18 cm (7 inches) long. They can inflate this to make a deep pink sac. This sac hangs from the side of their mouth. It is used to attract females during mating season. People often mistake it for their tongue.
Their fur is usually brown, but it can be black or almost white. The hair is long and grows mostly on their throat, shoulders, and hump.
Their large eyes are protected by strong bones above them. Their ears are small and round.
The hump is at least 20 cm (8 inches) high.
Dromedaries have long, strong legs with two toes on each foot. Their feet are flat and leathery, like pads. Like a giraffe, dromedaries move both legs on one side of their body at the same time when they walk.
Compared to the Bactrian camel, the dromedary is lighter. It has longer legs and shorter hair.
How Do Dromedaries Behave?

Dromedaries are active mainly during the day. Wild groups eat and wander all day. However, they rest during the hottest part of the day, around noon. They spend most of the night resting.
Dromedaries live in groups of about 20 animals. These groups usually have several females led by a strong male. Sometimes, females might take turns leading the group. Some males live alone or form groups with other males. During big events like natural disasters, many herds might come together, forming groups of hundreds of camels.
In Australia, wild dromedaries roam over areas of 50 to 150 square kilometers (19 to 58 square miles) in the short term. Over a year, they can cover thousands of square kilometers.
Dromedaries show they are unhappy by stamping their feet. They might also snap at others without actually biting. Generally, they are not aggressive animals.
Camels scratch themselves with their legs or their lower teeth. They also rub against tree bark and roll in the sand.
Wild dromedaries can face large predators in their areas. These include wolves, lions, and tigers.
What Do Dromedaries Eat?
Dromedaries mainly eat leaves, dry grasses, and desert plants. They especially like thorny plants. Studies show their diet often includes small shrubs, trees, and grasses. Dromedaries prefer to browse, meaning they eat leaves and twigs from plants. In summer, shrubs make up 70% of their diet, and in winter, it's 90%. They might also eat tall, young, juicy grasses.
In the Sahara Desert, over 300 types of plants have been recorded as food for dromedaries.
Dromedaries keep their mouths open while chewing thorny food. They use their lips to grab the food. They chew each bite 40 to 50 times.
They spend 8 to 12 hours a day eating. They also spend the same amount of time chewing their cud, just like cows.
Dromedaries are perfectly suited for their desert homes. They have special ways to save water and control their body temperature.
Their bushy eyebrows and double row of eyelashes stop sand and dust from getting into their eyes during strong winds. They also protect their eyes from the bright sun.
Dromedaries can close their nostrils whenever they want. This helps them save water.
They can save water by changing their body temperature throughout the day. This reduces how much they sweat. In the hottest weather, a dromedary drinks water every four to seven days. This camel can drink water very quickly, about 10 to 20 liters (2.6 to 5.3 US gallons) per minute.
The hump stores up to 80 pounds (36 kg) of fat. The camel can use this fat for energy when food is scarce. The hump also helps the camel get rid of body heat.
Their padded feet help them walk on sand. However, they are not good for walking on slippery or muddy ground.
How Do Dromedaries Reproduce?
A single baby camel is born after the mother has been pregnant for 15 months. Baby camels can walk freely by the end of their first day. The mother cares for and nurses her calf for one to two years.
Where Do Dromedaries Live Today?

In the early 2000s, domesticated dromedaries were found in dry and semi-dry parts of the Old World (Africa, Asia, and Europe).
Africa
Africa has over 80% of all dromedaries in the world. They live in almost every desert area in the northern part of the continent.
Asia
In Asia, nearly 70% of the dromedary population lives in India and Pakistan.
Wild Dromedaries
Wild dromedary populations live in Australia. They were first brought there in 1840 from the Canary Islands (Spain). In 2005, there were about 500,000 dromedaries in Australia.
Almost all of these camels are wild, and their numbers grow by 10% each year. Most of the Australian feral camels are dromedaries. There are only a few Bactrian camels.
Most dromedaries live in Western Australia. Smaller groups are found in the Northern Territory, Western Queensland, and northern South Australia.
How Do Humans Use Dromedaries?
Dromedaries are strong and gentle, which makes them popular as tamed animals. They can be used for many things: riding, transport, plowing fields, and trading. They also provide milk, meat, wool, and leather. For people living in the desert, dromedaries offer many important resources needed for survival. They are very important for several nomadic tribes in northern Arabia.
Riding Camels
Dromedaries have been used in wars since the 2nd century BC. They are especially good at outrunning horses in the desert.
Dromedary racing is also very popular, especially in the Arab world.
Camels for Carrying and Pulling
Camels used for carrying loads should be strong and heavy. They are trained in similar ways to riding camels.
Camels that pull things are used for many jobs. These include plowing fields, working in oil mills, and pulling carts.
Camel Milk Products
Camel milk is a main food for nomadic tribes in deserts.
Dromedaries in Somalia might be milked two to four times a day. In Afar, Ethiopia, they can be milked up to seven times a day.
Cheese and other dairy products can be made from camel milk.
Camel Meat
Camel meat is often eaten by camel herders in Africa. They usually eat it during times of severe food shortage or for special events. Camel meat can be made into foods like burgers, patties, sausages, and shawarma. Dromedaries can be used for meat when they are between four and ten years old. As the animal gets older, the meat becomes tougher and tastes worse. In Somalia and Djibouti, dromedary meat is a common food and is used in many dishes.
Camel Hair and Wool
Camels in hot places usually do not grow long coats. Camel hair is light and does not conduct heat well. It is also durable. This makes it good for making warm clothes, blankets, tents, and rugs. The best quality hair usually comes from young or wild camels.
Images for kids
-
"Lion Attacking a Dromedary," a 19th century taxidermy diorama by Jules and Édouard Verreaux.
-
Camel slaughter in Mauritania
See also
 In Spanish: Dromedario para niños
In Spanish: Dromedario para niños