Houthi movement facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Houthis |
|
|---|---|
| الحوثيون Participant in
* Houthi–Saudi Arabian conflict
|
|

The Sarkha
|
|
| Active | 1994–present |
| Ideology |
|
| Groups | Houthi tribe and Zaidi Shias |
| Leaders | Abdul-Malik al-Houthi (since 2004) Hussein al-Houthi † (1994–2004) † |
| Spokesman | Mohammed Abdul Salam |
| Headquarters | Saada, Yemen (since 1994) Sanaa, Yemen (since 2014) |
| Area of operations | Yemen, including Saudi Arabia–Yemen border |
| Allies | State allies:
|
| Opponents | State opponents:
|
| Designated as a terrorist organisation by | |
|
|
The Houthi movement, also known as Ansar Allah (meaning "Supporters of God"), is a political and military group from Yemen. It started in the 1990s. Most of its members are Zaidi Shias, a branch of Shia Islam found mainly in Yemen. The group's leaders come from the Houthi tribe.
The Houthis first opposed Yemen's President Ali Abdullah Saleh. They accused him of being corrupt and supported by Saudi Arabia and the United States. In 2003, they adopted a slogan against the United States, Israel, and Jewish people. This was influenced by Hezbollah, a group in Lebanon.
In 2004, the Yemeni military killed the Houthi leader, Hussein al-Houthi, in Saada. This event started the Houthi insurgency. Since then, his brother, Abdul-Malik al-Houthi, has mostly led the movement.
Contents
What Are the Houthis?
The Houthi movement is a powerful group in Yemen. They have both political and military goals. Their main aim is to govern all of Yemen. They also support groups that oppose the United States, Israel, and Saudi Arabia.
How the Movement Began
The Houthi movement started as an opposition group. They were against the government of President Ali Abdullah Saleh. They believed his government was corrupt. They also felt it was too influenced by outside countries.
Joining the Yemeni Revolution
In 2011, the Houthis joined the Yemeni Revolution. They took part in protests and worked with other groups. They joined talks about peace but later rejected a peace deal.
Taking Control of the Capital
In late 2014, the Houthis worked with former President Saleh. With his help, they took control of Yemen's capital city, Sanaa. This led to a military response by Saudi Arabia and its allies. They wanted to bring back the recognized government. This started an ongoing civil war.
Recent Actions in the Red Sea
After the 2023 Israel–Hamas war started, the Houthis began to fire missiles at Israel. They also started attacking ships in the Red Sea. They say these actions are to support Palestinians. They also want to help humanitarian aid reach the Gaza Strip.
What Do the Houthis Believe?
The Houthis attract followers by saying they fight for economic development. They also say they want to end the political neglect of Zaidi Shias. They promote their ideas through media.
Their Main Ideas
The Houthi movement has a mix of beliefs. These include religious ideas, Yemeni nationalism, and popular support. They often say they are defending all Yemenis. They claim to fight against corruption and extremism. They also say they represent marginalized tribal groups and the Zaidi sect.
The group has used public anger about corruption to gain support. They also gained support when the government reduced financial help for people.
Religion and the Houthis
The Houthi movement's beliefs are based on the Zaidi branch of Islam. This branch is mostly found in Yemen. About 25% of Yemen's people are Zaidi. For 1,000 years, Zaidi leaders ruled Yemen until 1962. The Houthi movement often works to bring back Zaidi traditions in Yemen.
Women's Rights and Expression
The Houthis' views on women's rights and freedom of expression are complex. They say they support women's right to vote and hold public office. Some women have moved to Houthi-controlled areas. The Houthis also have their own women's security force. However, there have been reports that Houthis restrict women's freedoms.
The Houthis use media, social media, and poetry to spread their views. They also try to teach their values in schools. This is called "Houthification." They want to encourage young people to join their fight. Sometimes, they allow music and Western content on radio. Other times, they ban songs and bother artists. Their rules can change depending on the local area.
Who Leads the Houthis?
The Houthi movement has several important leaders.
- Hussein Badreddin al-Houthi – He was the first leader. He died in 2004.
- Abdul-Malik Badreddin al-Houthi – He is the current leader.
- Yahia Badreddin al-Houthi – A senior leader in the movement.
- Abdul-Karim Badreddin al-Houthi – A high-ranking commander.
- Badr Eddin al-Houthi – He was a spiritual leader. He died in 2010.
- Abdullah al-Ruzami – A former military commander.
- Abu Ali Abdullah al-Hakem al-Houthi – A military commander.
- Saleh Habra – A political leader.
- Fares Mana'a – He was appointed governor of Sa'dah by the Houthis.
How the Houthis Act
The Houthis use different ways to achieve their goals.
Political Actions
The Houthis have used peaceful protests against governments. In 2014, they organized large protests in Sanaa. They were protesting higher fuel prices. They also demanded the government resign due to corruption. These protests grew into a larger conflict.
After Saudi-led airstrikes in 2015, many Yemenis protested. They were angry about civilian deaths. The Houthi leader called for these protests.
The movement wants to fight economic problems in Yemen. They also want more self-rule for areas where Houthis live. A Houthi spokesperson said in 2018 that they support a democratic republic in Yemen. Fighting corruption is a key part of their political plan.
Cultural Gatherings
The Houthis have held many large public events. In 2013 and 2014, thousands gathered to celebrate the birth of Mohammed. These events were very organized. Men and women were kept separate.
Images for kids
-
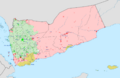
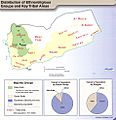
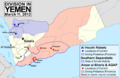
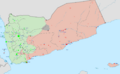
A map showing who controls what in the Yemeni Civil War (2014–present) in September 2023.
-
Yemen's former president Ali Abdullah Saleh worked with the Houthis from 2014 until his death in 2017.
See also
 In Spanish: Hutíes para niños
In Spanish: Hutíes para niños