Morocco facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Kingdom of Morocco
|
|
|---|---|
|
Motto: ٱللَّٰه، ٱلْوَطَن، ٱلْك
"Allāh, al-Waṭan, al-Malik" "God, Country, King" |
|
|
Anthem: ٱلنَّشِيْد ٱلْوَطَنِي
"an-Našīd al-Waṭanīy" "Cherifian Anthem" |
|
Location of Morocco in northwest Africa
Undisputed territory of Morocco Western Sahara, a territory claimed and partly occupied by Morocco |
|
| Capital | Rabat 34°02′N 6°51′W / 34.033°N 6.850°W |
| Largest city | Casablanca 33°32′N 7°35′W / 33.533°N 7.583°W |
| Official languages |
|
| Spoken languages (2024) |
|
| Foreign languages | |
| Ethnic groups | See Ethnic groups |
| Religion
(2020)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Moroccan |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary semi-constitutional monarchy |
|
• King
|
Mohammed VI |
| Aziz Akhannouch | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| House of Councillors | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Establishment | |
| 788 | |
|
• 'Alawi dynasty (current dynasty)
|
1631 |
|
• Protectorate established
|
30 March 1912 |
| 7 April 1956 | |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
446,550 km2 (172,410 sq mi) (57th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
0.056 (250 km2) |
| Population | |
|
• 2024 estimate
|
37,493,183 (38th) |
|
• 2024 census
|
36,828,330 |
|
• Density
|
79.0/km2 (204.6/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2015) | 40.3 medium |
| HDI (2023) | high · 120th |
| Currency | Moroccan dirham (MAD) |
| Time zone | UTC
|
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +212 |
| ISO 3166 code | MA |
| Internet TLD |
|
Morocco, officially known as the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in North Africa. It has coastlines along the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Morocco shares land borders with Algeria to the east and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to the south.
Morocco also claims some Spanish areas like Ceuta, Melilla, and several small islands off its coast. About 37 million people live in Morocco. Islam is the main religion, and Arabic and Berber are the official languages. French and a Moroccan dialect of Arabic are also widely spoken. Moroccan culture is a mix of Arab, Berber, African, and European influences. The capital city is Rabat, and the largest city is Casablanca.
People have lived in the area that is now Morocco for over 300,000 years. The Idrisid dynasty started in 788. After that, different independent rulers controlled Morocco. It was very powerful in the 11th and 12th centuries under the Almoravid and Almohad dynasties. During this time, Morocco controlled much of Spain and North Africa.
In the 15th and 16th centuries, Morocco faced threats from Portugal and the Ottoman Empire. However, Morocco was the only North African country that the Ottomans did not control. The current ruling family, the 'Alawi dynasty, took power in 1631. They expanded trade and relations with Western countries.
Because of its important location near the Mediterranean, European countries became interested in Morocco. In 1912, France and Spain divided the country into protectorates. After many protests and revolts, Morocco became independent and reunited in 1956.
Since gaining independence, Morocco has been quite stable. It has one of the largest economies in Africa and is important in both Africa and the Arab world. Morocco is a constitutional monarchy with an elected parliament. The King and Prime Minister lead the government.
Morocco claims the territory of Western Sahara as its "Southern Provinces." In 1975, Spain left the territory, and Morocco and Mauritania took control. This led to a conflict with some local people. Mauritania later gave up its claim, but the conflict continued. A ceasefire was agreed in 1991, but the issue of who owns the territory is still not settled. Morocco currently controls about two-thirds of Western Sahara.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The English name Morocco comes from the Spanish name Marruecos. This name comes from the city of Marrakesh, which was once a capital city. The ancient Berber name for Marrakesh meant "land of God."
In Arabic, Morocco is called al-Maghrib, which means "the land of the sunset" or "the west." The full official Arabic name means "the kingdom of sunset/the west." In Turkish, Morocco is called Fas, named after the city of Fes.
A Look at Morocco's Past
Early History
People have lived in Morocco for a very long time, possibly as far back as 315,000 years ago. Back then, the area was more like a savanna, not as dry as it is today. Over time, different groups of people moved into the region, including farmers from Europe and herders from the Middle East. The ancient Berber tribes developed from these early communities.
Later, the Phoenicians came and set up trading posts along the coast. One of the earliest independent Moroccan states was the Berber kingdom of Mauretania, which started around 225 BC. This kingdom later became a client state of the Roman Empire.
Christianity arrived in Morocco during Roman times. By the late 3rd century, Roman rule was limited to a few coastal cities. In the 530s, the Eastern Roman Empire took back control of some areas.
Dynasties and Empires
The Muslim conquest of the Maghreb brought Islam and the Arabic language to Morocco in the 7th century. Arab people also began to move into the region. The first independent Muslim state in Morocco was the Kingdom of Nekor, founded in 710.
The Idrisid dynasty was founded in 788 by Idris ibn Abdallah. He made Fes his capital, and Morocco became an important center for Muslim learning.

From the 11th century, powerful Berber dynasties rose to power. The Almoravid dynasty and the Almohad dynasty controlled much of North Africa and parts of Spain.
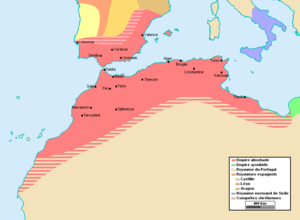
In the 13th and 14th centuries, the Marinids ruled Morocco. After them came the Wattasids. In the 15th century, many Muslims and Jews moved to Morocco after Muslim rule ended in Spain.

In 1549, the Saadi dynasty took over, followed by the Alawi dynasty in the 17th century, who still rule today. Under the Saadis, Morocco defeated Portugal in a major battle in 1578. The reign of Ahmad al-Mansur brought wealth and power, and Morocco even expanded into West Africa.
The 'Alawi dynasty reunited Morocco in the late 1660s. They made the kingdom stable and wealthy. Morocco was the first country to recognize the United States as an independent nation in 1777. The 1786 Moroccan–American Treaty of Friendship is the oldest unbroken friendship treaty for the U.S.
European Influence and Independence

In the 19th century, European countries became interested in Morocco. France was especially interested because of Morocco's location. In 1860, a war with Spain led to Spain gaining more territory. In 1884, Spain created a protectorate in some coastal areas.

In 1912, the Treaty of Fez made Morocco a protectorate of France. Spain also kept its coastal protectorate. Many European settlers moved to Morocco, buying land and developing mines and ports. Moroccan soldiers also served in the French army during World War I and World War II. Slavery was ended in Morocco in 1925.
Between 1921 and 1926, there was an uprising in the Rif Mountains led by Abd el-Krim. This led to the short-lived Republic of the Rif. Spanish and French forces eventually stopped the uprising.
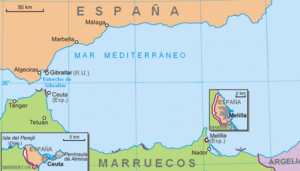
In 1943, the Istiqlal Party was formed to push for independence. In 1953, France sent Sultan Mohammed V away, which caused strong opposition. France allowed him to return in 1955, and Morocco gained independence from France in March 1956. A month later, Spain also gave up its protectorate in Northern Morocco. However, Spain kept its two coastal cities, Ceuta and Melilla, which Morocco still claims.
Modern Morocco

Sultan Mohammed became King in 1957. After his death, Hassan II became King in 1961. Morocco held its first general elections in 1963.
In 1963, Morocco and Algeria fought a short conflict over border claims. The Spanish area of Ifni was returned to Morocco in 1969.
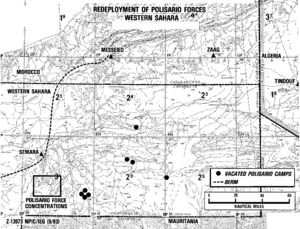
The Polisario movement was formed in 1973 to create an independent state in the Spanish Sahara. In 1975, King Hassan organized the "Green March," where 350,000 civilians walked into the Spanish Sahara. Spain then agreed to leave the territory, which became Western Sahara, and transfer it to Morocco and Mauritania. Moroccan forces occupied the area.
Moroccan and Algerian troops clashed in Western Sahara. Mauritania later gave up its claim, but fighting between the Moroccan military and Polisario forces continued for many years. A ceasefire began in 1991, but the status of the territory is still undecided. Morocco proposed an autonomy plan for Western Sahara in 2007.
Political changes in the 1990s led to a parliament with two chambers. King Hassan II passed away in 1999, and his son, Mohammed VI, became king. He has introduced some economic and social changes.

In 2002, Morocco and Spain had a disagreement over the small island of Perejil. In 2005, there were tensions as migrants tried to cross into the Spanish cities of Melilla and Ceuta.
During the 2011–2012 Moroccan protests, people called for political reform. In July 2011, the King proposed a new constitution, which was approved. In the elections that followed, the Justice and Development Party won the most seats.
In August 2021, Algeria ended diplomatic relations with Morocco, accusing Morocco of supporting a separatist group. Morocco called this decision unfair.
On September 8, 2023, a strong earthquake hit Morocco, causing many deaths and injuries. The earthquake's center was southwest of Marrakech.
In December 2020, Morocco announced it would restart diplomatic relations with Israel. This agreement was met with some criticism due to later events in the region.
Morocco's Landscape

Morocco has a coastline on the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. It is bordered by Spain to the north, Algeria to the east, and Western Sahara to the south. Since Morocco controls most of Western Sahara, its southern border is with Mauritania.
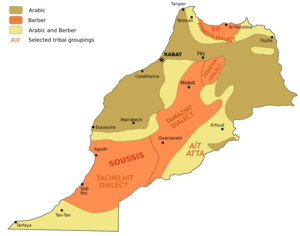
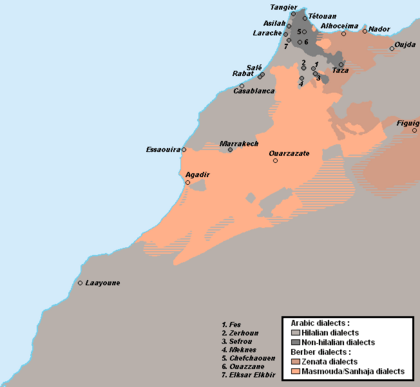
Much of Morocco is mountainous. The Atlas Mountains are in the center and south, and the Rif Mountains are in the north. These mountains are mainly home to the Berber people. Morocco's total area is about 446,300 square kilometers (172,317 square miles). The capital is Rabat, and the largest city is Casablanca. Other big cities include Fes, Marrakesh, and Tangier.
Most of the country's southeast is part of the Sahara Desert, which is dry and has few people. Most Moroccans live north of the mountains, where the land is more fertile.
Spain has five small areas on the Mediterranean coast near Morocco: Ceuta, Melilla, Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, Peñón de Alhucemas, and the Chafarinas islands. Morocco is also near the Strait of Gibraltar, a busy shipping route between the Atlantic and Mediterranean.
Morocco's Climate
Morocco's climate is mostly "hot summer Mediterranean" and "hot desert." The central mountains and the cold Canary Current off the Atlantic coast create different climate zones. These range from green forests in the mountains to dry desert areas in the south. Coastal areas have moderate temperatures, even in summer.
In the Rif and Atlas Mountains, the climate varies. Coastal lowlands have a Mediterranean climate. Higher up, it's more humid, allowing forests to grow. In the highest parts, the climate is alpine, with snow and ski resorts.
Southeast of the Atlas mountains, the climate is very dry with long, hot summers. This is because the mountains block rain. The southernmost parts of Morocco are very hot and include parts of the Sahara Desert, with sand dunes and rocky plains dotted with green oases.
The coastal plains in central and northern Morocco are fertile. This is where most of the country's farming happens, and 95% of the population lives there. Morocco's climate in the northern half is similar to southern Europe. About 12% of the country is covered by forests, and 18% is farmland.
Morocco's climate zones include:
- Mediterranean: Found along the Mediterranean coast and parts of the Atlantic coast. Summers are hot and dry, and winters are mild and wet.
- Sub-Mediterranean: Influenced by the ocean or elevation.
- Oceanic: Cooler summers and mild, wet winters. Cities like Rabat and Casablanca are in this zone.
- Continental: Hotter summers and colder winters, with more temperature changes between day and night. Cities like Fès and Meknès are here.
- Continental: Dominates mountainous regions. Summers are hot, and winters are cold with snow.
- Alpine: Found in parts of the Middle and High Atlas Mountains. Summers are warm, and winters are long, cold, and snowy. There are ski resorts here.
- Semi-arid: In the south and east, with less rainfall. Cities like Agadir and Marrakesh are in this zone.
South of Agadir and east of Jerada, the climate becomes arid and desert-like.
Morocco's closeness to the Sahara and the Atlantic Ocean means temperatures can change quickly. Hot winds from the east can cause heatwaves, while cold air from the northwest can bring cold spells. These usually last only a few days.
Climate change is expected to affect Morocco significantly. As a coastal country with dry climates, it faces many environmental challenges. Morocco is ranked highly for its efforts to prepare for climate change.
Wildlife and Nature


Morocco has many different kinds of plants and animals. It is part of the Mediterranean basin, an area with many unique species that are losing their habitats. This makes it an important area for conservation.
Morocco is home to 454 bird species. The Barbary lion, which used to live in Morocco, is now extinct in the wild. The last one was seen in the Atlas Mountains in 1922. The Atlas bear is also extinct, and the Barbary leopard is critically endangered. The Barbary macaque, a type of monkey found only in Morocco and Algeria, is also facing extinction. This is due to human activity, city growth, and loss of forests.
Trading animals and plants for food, pets, or medicine is common in Morocco, even though many of these activities are illegal. This trade is harming wild populations.
How Morocco is Governed
Morocco is a hybrid regime, meaning it has elements of both democracy and authoritarian rule. It ranks well in the Middle East and North Africa for democracy.
After elections in March 1998, a government led by Abderrahmane Youssoufi was formed. This was the first time an opposition group led the government in the modern Arab world. The current government is led by Aziz Akhannouch.
Morocco's constitution sets up a monarchy with a Parliament and independent courts. With changes made in 2011, the King has fewer executive powers, and the Prime Minister has more. The King is the country's leader and also the "Commander of the Faithful" because he is a descendant of the Prophet Mohammed. He leads the Council of Ministers and appoints the Prime Minister.
The King is also the commander-in-chief of the armed forces. He can issue decrees that have the force of law.
Lawmaking in Morocco
Morocco's parliament has two chambers. The Assembly of Representatives of Morocco has 395 members, elected for five-year terms. The Assembly of Councillors has 120 members, elected for six-year terms.
The Parliament's powers have grown over time. They include approving the budget, passing laws, questioning ministers, and investigating government actions. The lower chamber can even dissolve the government.
The most recent parliamentary elections were held on September 8, 2021. About 50.35% of registered voters participated.
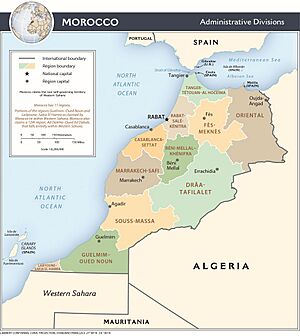
Regions and Divisions
Morocco is divided into 12 regions. These regions are then divided into 62 provinces and 13 prefectures.
Regions
- Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceima
- Oriental
- Fès-Meknès
- Rabat-Salé-Kénitra
- Béni Mellal-Khénifra
- Casablanca-Settat
- Marrakesh-Safi
- Drâa-Tafilalet
- Souss-Massa
- Guelmim-Oued Noun
- Laâyoune-Sakia El Hamra
- Dakhla-Oued Ed-Dahab
International Relations
Morocco is a member of the United Nations and other important organizations like the African Union and the Arab League. Morocco has strong ties with Western countries for economic and political reasons. France and Spain are its main trading partners.
In 2004, the United States gave Morocco the status of a major non-NATO ally. Morocco was the first country to recognize U.S. independence in 1777. This long-standing relationship has continued, with the U.S. being a top ally. Morocco is also part of the European Union's Neighborhood Policy.
Morocco left the African Union in 1984 after it recognized the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic. However, Morocco rejoined the AU in 2017. In November 2020, the Polisario Front ended a ceasefire agreement with Morocco. In December 2020, Morocco began military cooperation with Israel. In August 2021, Algeria cut diplomatic ties with Morocco.
Western Sahara: A Disputed Territory
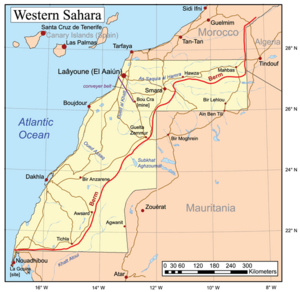
The status of the Western Sahara region is still debated. The Western Sahara War was fought between the Polisario Front and Morocco and Mauritania from 1976 to 1991. The Moroccan government calls its claimed area of Western Sahara the "Southern Provinces."
The United Nations has a mission, MINURSO, to organize a vote on whether the territory should be independent or part of Morocco. No UN member state has recognized Morocco's control over Western Sahara. In 2006, Morocco suggested an autonomous status for the region.
In 2020, the United States supported Morocco's claim over Western Sahara, in exchange for Morocco normalizing relations with Israel. This led to more clashes between Morocco and the Polisario.
Morocco's Military
Morocco's military includes the Royal Armed Forces, which has the Army, Navy, Air Force, Royal Guard, Royal Gendarmerie, and Auxiliary Forces. Internal security is generally good. The UN has a small observer force in Western Sahara, where many Moroccan troops are stationed.
Morocco's Economy
Morocco has a relatively liberal economy based on supply and demand. Since 1993, the government has privatized some economic sectors. Morocco is a major economic player in Africa and has one of the largest economies on the continent.
Government changes and steady growth of 4–5% each year from 2000 to 2007 helped Morocco's economy become stronger. The World Bank predicted 4% growth for Morocco in 2012. Between 2000 and 2019, fewer Moroccans worked in agriculture, and more worked in industry.
Tourism in Morocco

Tourism is a very important part of Morocco's economy. It focuses on the country's coast, culture, and history. In 2023, Morocco had a record 14.5 million international tourists.

Many tourists visit Morocco for its culture, ancient cities, and Islamic sites. Agadir is a popular coastal resort. The government has launched campaigns to attract tourists, showing Morocco as an affordable, exciting, and safe place. Most visitors are from Europe, especially France.
Casablanca is a major port for cruise ships. The Majorelle botanical garden in Marrakech is a popular spot. Adventure tourism in the Atlas and Rif Mountains is growing fast, with opportunities for walking and trekking. The government is also developing desert tourism.
Infrastructure and Transport
Morocco has some of the best infrastructure in Africa. It ranks highly for roads, sea transport, air travel, and railways. The government invested over $15 billion from 2010 to 2015 to improve its infrastructure.
Morocco has the largest port in Africa and the Mediterranean, Tanger-Med. It can handle over 9 million containers and is a key logistics hub.
In 2014, Morocco began building Africa's first high-speed railway system, connecting Tangier and Casablanca. It opened in 2018. This is the first part of a planned 1,500-kilometer (930-mile) high-speed rail network.
Energy Sources

In 2008, about 56% of Morocco's electricity came from coal. However, Morocco's energy needs are growing. A new law encourages the country to use more renewable resources. Morocco is building large solar energy farms to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and to export electricity to Europe. In April 2022, the first phase of the Nor II solar energy plant, a large multi-site project, was launched.
Water Supply
Morocco has made big improvements in providing water and sanitation over the last 15 years. However, challenges remain, such as treating wastewater and connecting homes in poorer areas. In 2005, a National Sanitation Programme was approved to treat more wastewater and connect more homes to sewers.
Between 1960 and 2020, the amount of available fresh water per person decreased significantly. The World Bank has supported Morocco's solar power project to help with water scarcity and its effects on farming.
Science and Technology
The Moroccan government is working to improve education and research. In 2009, Morocco's prime minister announced a big increase in investment for science and technology. Morocco was ranked 66th in the Global Innovation Index in 2024.
The Moroccan Innovation Strategy was launched in 2009. It aimed to produce 1,000 Moroccan patents and create 200 new innovative companies by 2014. In 2011, a Moroccan Club of Innovation was created to help develop new projects.
The Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research supports research in advanced technologies. The Moroccan Phosphate Office has invested in a "smart city" project around Mohammed VI University. In 2012, the Hassan II Academy of Sciences and Technologies identified key areas for Morocco, like mining, fisheries, and renewable energy.
In 2015, a report suggested increasing spending on research and development. As of 2015, Morocco had three technoparks that support new companies in technology and green industries. Patent filings in Morocco grew by 167% between 2015 and 2019.
In 2024, Morocco was among the top four most internet-connected countries in Africa. In January 2024, Morocco had about 34.5 million internet users, with a high internet use rate of about 90.7%.
People and Culture
Population and Groups
Morocco has a population of around 37.5 million people. In 2024, about 49.7% of the population is female and 50.3% is male. In 2014, there were about 84,000 immigrants in Morocco, mostly from France and other West African countries. Before independence, many Europeans lived in Morocco.
Morocco has a large number of its people living abroad, especially in France, Spain, the Netherlands, and Belgium. There are also communities in Italy, Canada, the United States, and Israel. Morocco has the largest Berber population in the world, making up between 40-60% of the population.
Ethnic Groups
In Morocco, identity is linked to language and culture. The main groups are Arabs and Berbers. Arabs are the largest group, making up 65% to 80% of the population. Berbers, also called Amazigh, make up 30% to 35%. They live in mountain areas and speak different dialects.
Over centuries, Arab migrants from the Arabian Peninsula have shaped Morocco's population and culture. The population also includes people of West African descent and descendants of European Muslims who were expelled from Spain and Portugal.
Religions in Morocco
Almost all Moroccans are Muslim, mostly Sunni. Other religious groups make up less than 1% of the population. A 2018 survey found that nearly 15% of Moroccans describe themselves as non-religious, but almost all still identify as Muslim.
Before Morocco became independent in 1956, there was a large Christian community, mainly of Spanish and French origin. Many of these Christians left after independence. Today, there are about 40,000 practicing foreign resident Christians.
Before 1948, Morocco had about 265,000 Jews, the largest Jewish community in the Muslim world. Today, there are about 2,500 Jews in Casablanca and smaller numbers elsewhere. The Baháʼí Faith community has 350 to 400 people.
Languages Spoken
Morocco's official languages are Arabic and Berber. The local Arabic dialects are called Darija. About 92.7% of the population can speak Arabic. Berber languages are spoken by 24.8% of the population in three main dialects.
After independence in 1956, French and Arabic became the main languages for government and education. French is widely used in government, media, and business. It is taught in all schools. English is becoming more popular among young people.
About 1.5 million people in Morocco speak Spanish, mostly in northern Morocco and the former Spanish Sahara. This is because Spain used to control those areas.
Education System
| Literate population of Morocco (2024) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| percent | ||||
| Can read and write in Arabic | 99.2% | |||
| Can read and write in French | 57.7% | |||
| Can read and write in English | 20.5% | |||
| Can read and write in Berber languages | 1.5% | |||
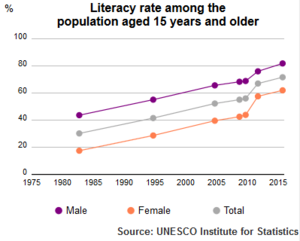
Education in Morocco is free and required through primary school. The literacy rate in 2012 was 72%. In 2006, UNESCO recognized Morocco for its efforts in literacy.
Morocco has many universities and higher learning institutes. Some of the main ones include Mohammed V University in Rabat and Al-Akhawayn University in Ifrane, which is the first English-language university in Northwest Africa.
The al-Qarawiyin University in Fes, founded in 859, is considered by some to be the "oldest university in the world." Morocco also has several respected postgraduate schools.
Health and Well-being

Morocco has worked hard to improve health for its citizens. In 2005, the government approved reforms to expand health insurance coverage. This helped more people get access to good healthcare.
Infant mortality rates have greatly improved, from 144 deaths per 1,000 births in 1960 to 15 per 1,000 births in 2022. The number of children under five who died also dropped by 60% between 1990 and 2011. The maternal mortality rate also fell by 67% between 1990 and 2010.
In 2014, Morocco spent 5.9% of its GDP on healthcare. Life expectancy in Morocco in 2024 is 74.2 years.
Moroccan Culture
Morocco has a very rich culture and history. It has been influenced by many different people over time. Moroccan culture mixes Arabic, Berber, and Jewish traditions with French, Spanish, and Anglo-American styles. Since independence, painting, sculpture, music, theater, and filmmaking have grown. Many art and music festivals happen in the summer.
Moroccan Literature
Moroccan literature is written mainly in Arabic, Berber, Hebrew, and French. In the past, Moroccan literature was closely linked to the literature of Spain under Muslim rule. The University of al-Qarawiyyin in Fes was an important center for learning, attracting scholars from other countries.
Modern Moroccan literature began in the 1930s. Writers like Mohamed Choukri, Driss Chraïbi, and Tahar Ben Jelloun became well-known. Oral storytelling is also a very important part of Moroccan culture.
Music of Morocco
Moroccan music has roots in Arabic, Berber, and sub-Saharan African traditions. Rock-influenced chaabi bands are popular, as is trance music. Berber people play music using instruments like the lotar, a type of lute. Traditional poetry is also sung with instruments.
Aita is a traditional musical style sung in the countryside. Chaabi ("popular") music comes from many forms of Moroccan folk music. Morocco is also home to Andalusian classical music, which developed under the Moors in Spain. Modern artists mix traditional styles with new influences. Western music like hip hop, rock, and fusion is also popular.
Media and Film
Cinema in Morocco has a long history, starting in 1897. Many foreign movies have been filmed in Morocco. In 1944, the Moroccan Cinematographic Centre (CCM) was created to regulate films. Studios were also opened in Rabat.
In 1952, Orson Welles' Othello won an award at the Cannes Film Festival under the Moroccan flag. In 1958, Mohammed Ousfour made the first Moroccan movie. Film festivals are held in Tangier and Marrakech. Some Moroccan TV channels include 2M and Al Aoula.
Delicious Moroccan Food

Moroccan food is known for being very diverse. It's a mix of Moorish, European, and Mediterranean cooking. Spices are used a lot. Many ingredients, like saffron, mint, olives, and citrus fruits, are grown in Morocco.
Chicken is the most common meat eaten. Beef is also popular, often cooked in a tagine with vegetables. Lamb is eaten but is more expensive. Seafood is becoming more common.
Some of the most famous Moroccan dishes are Couscous, Pastilla, Tajine, Tanjia, and Harira (a soup). Eating pork is not allowed in Islam.
Bread is a big part of daily meals. Moroccan bread is usually made from durum wheat semolina. Bakeries are common, and fresh bread is a staple. The most popular drink is "atai," which is green tea with mint leaves.
Sports in Morocco
Football (soccer) is the most popular sport in Morocco, especially among young people in cities. In 1986, Morocco was the first Arab and African country to reach the second round of the FIFA World Cup. Morocco will host the Africa Cup of Nations again in 2025.
Morocco has tried to host the FIFA World Cup six times. It will finally co-host the 2030 FIFA World Cup with Portugal and Spain. In the 2022 FIFA World Cup, Morocco made history by becoming the first African and Arab team to reach the semifinals, finishing 4th.
At the 1984 Summer Olympics, two Moroccans won gold medals in track and field. Nawal El Moutawakel was the first woman from an Arab or Islamic country to win an Olympic gold medal. Saïd Aouita also won gold. Hicham El Guerrouj won two gold medals at the 2004 Summer Olympics and holds several world records in running.
Traditional sports in Morocco used to focus on horsemanship. But European sports like football, polo, swimming, and tennis became popular in the late 1800s. Tennis and golf are now widely played. Morocco also has one of Africa's first competitive basketball leagues. Kickboxing is also popular, with famous Moroccan fighters like Badr Hari.
See also
 In Spanish: Marruecos para niños
In Spanish: Marruecos para niños
 | Frances Mary Albrier |
 | Whitney Young |
 | Muhammad Ali |