Renewable resource facts for kids
A renewable resource is a natural resource that can replace itself over time. This happens through natural processes like reproduction or regrowth. Think of it like a plant that grows new leaves after some are picked, or a forest that regrows trees after some are harvested. These resources are a big part of Earth's natural environment. When we use them carefully, they can last for a very long time.
Renewable resources also include things like the food we grow and the water we drink. Even energy sources like sunlight, wind, and heat from the Earth are considered renewable. These are often called renewable energy resources. Fresh water is a great example of a renewable resource, but only if we manage it wisely.
Contents
What Are Renewable Resources?
Renewable resources are natural materials that can be replenished. This means they can come back or be replaced after we use them. This happens within a human timescale, which means not millions of years. For example, trees can be replanted and grow again. Sunlight and wind are always available.
Some resources are called perpetual resources because they are always there. Sunlight and wind are good examples. They are part of Earth's natural systems. Using these resources in a way that helps them last is called sustainability.
Water: A Precious Renewable Resource
Water is a renewable resource, but we must use it carefully. If we pollute it or take too much too quickly, it can become scarce in certain places. For instance, water deep underground (called groundwater) can take a very long time to refill. If we pump it out faster than it refills, it's like using up a non-renewable resource.
Most of Earth's water is salt water (97.5%). Only 3% is fresh water. A large part of this fresh water is frozen in glaciers and polar ice caps. The rest is mostly underground or in the air.
Water pollution is a big problem for water resources. Industries use a lot of water for things like cooling power plants or in manufacturing. It's important that this water is treated before it goes back into nature. Turning salt water into fresh water (Desalination) is another way to get water. Scientists are working to make this process use less energy from non-renewable sources.
-
Panorama of a natural wetland (Sinclair Wetlands, New Zealand)
Food from Renewable Sources

Food gives our bodies the energy and nutrients we need. Most of our food comes from renewable resources. We get food directly from plants and animals.
Hunting for food is still important for many communities around the world. It's also how wild animals like carnivores get their meals.
Growing Food Wisely: Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture means farming in a way that protects the environment and can continue for a long time. It's about growing plants and raising animals in a balanced system. When we expand farms too much, it can harm biodiversity (the variety of life) and lead to deforestation (cutting down forests).
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations is concerned. They estimate that in the coming years, we will lose more farmland to cities and industries. Forests might also be cleared for farming. This can lead to less biodiversity and more soil erosion.
Crops need healthy soil and enough water. Growing only one type of crop in a field, called monoculture, can harm the land. It can make the soil less fertile or lead to more pests and diseases that target that specific crop. The Great Irish Famine in the 1840s is a sad example of the risks of relying on just one crop.
To keep soil healthy, farmers can use crop rotation. This means growing different crops in the same field over time. For example, planting clover can add nitrogen back into the soil. This helps other crops grow better. Farmers also use green manure (plants grown to be plowed back into the soil) and biochar (a special charcoal) to improve soil.
Farming practices are a major cause of soil erosion. This is when soil is washed or blown away. Experts worry that if erosion continues, crop yields could drop significantly in some areas. The Dust Bowl in the 1930s in the USA was a terrible example. It happened because of severe drought and farming methods that didn't protect the soil.
Modern farming equipment can plow deeply, which makes soil more likely to erode. To fight erosion, farmers can use no-till farming (planting without plowing), plant wind breaks (rows of trees or shrubs), and use compost. Fertilizers and pesticides can also affect soil health. Scientists are concerned about the future supply of phosphate, a key ingredient in many fertilizers.
Moving food from farms to stores also uses energy. Local food, like that sold at a farmers' market, uses less energy for transportation.
The Air We Breathe
Air is a renewable resource that is all around us. All living things need gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon (in different forms) to survive. These gases are constantly recycled through natural processes on Earth.
Renewable Resources Beyond Food

Besides food, plants and animals give us many other useful renewable resources. Wood from forestry is a very important one. People have used wood for building homes and for fuel since ancient times.
Plants provide many non-food items. These include energy crops (grown for fuel) and non-food crops (grown for other uses). For example, plants give us vegetable oils for lubricants, fibers for textiles like cotton and hemp, and paper from wood or grasses. They also provide materials for bioplastics, latex, ethanol, and resin.
Animals also provide renewable resources. These include fur, leather, and fats for lubricants. Historically, people used animal parts for things like animal glue and even for making strong composite bows. Today, feathers from poultry farming are used as filler, and chitin from crustaceans can be used to make chitosan. Even human hair is traded worldwide for artificial hair integrations.
Some medicines have also come from natural sources. For example, certain plant extracts and even venoms from snakes or insects have been used to create important pharmaceutical ingredients. Before modern methods, some important medicines like insulin came from animal sources.
How We Used Renewables in the Past

In the past, people relied heavily on renewable resources like firewood, charcoal, and plant dyes. However, in early modern times, people sometimes used these resources too much. This led to problems like deforestation (cutting down too many trees), overgrazing (too many animals eating plants in one area), and overfishing.
Farmers in the past also used animal products beyond food. They used tendons, horns, and bones. Animals like oxen and horses were vital for transportation and powering machines.
A big change in farming, called the British Agricultural Revolution, happened because of new ways to rotate crops. Farmers learned to plant different crops like wheat, turnips, barley, and clover. Clover is special because it can take nitrogen from the air and put it into the soil, making it more fertile. This allowed farmers to grow more food and keep livestock year-round.
Over time, new technologies and the use of fossil fuels and minerals changed how we used resources. But today, there's a renewed interest in renewable products. This is thanks to modern agriculture, scientific research, and new ways to extract materials. People are looking for renewable options to replace fossil fuels and other non-renewable resources.
Innovation with Local Resources
Scientists have always looked for ways to use local resources to create new materials. For example, in the past, researchers explored using plants like hemp, flax, and rapeseed for various industrial purposes. These plants are still important today.
During World War 2, German scientists tried to use certain types of Taraxacum (dandelion) to make natural rubber. Today, scientists are still interested in rubber dandelions. In 2013, researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute announced they had developed a type of dandelion that could be used to produce natural rubber commercially. This shows how scientific research continues to find new uses for renewable resources.
Renewable Energy: Powering Our Future
Renewable energy comes from resources that naturally replenish themselves as quickly as they are used. These include sunlight, wind, biomass, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat. Renewable energy can power our homes, heat our water, and even fuel our vehicles.
Energy from Biomass
Biomass refers to biological material from living or recently living organisms, usually plants. Humans have used biomass for energy since they first burned wood for fire. Wood is still the biggest source of biomass energy today.
Using biomass sustainably means making sure we don't use it faster than it can regrow. This helps reduce air pollution and land degradation. Biomass energy can come from garbage, wood, plants, waste, landfill gases, and alcohol fuels.
In some parts of the world, simple ways of burning biomass indoors can cause unhealthy air. Modern biomass power plants, however, use advanced technologies to generate electricity cleanly. For example, in the United States, biomass power plants produce about 1.4% of the country's electricity. They often use wood residues from forests. In other regions, agricultural waste like sugarcane residue or rice husks are used.
Biofuels for Transportation

Biofuels are a type of fuel made from biological materials. They get their energy from plants that have captured carbon from the air. Biofuels can be solid, liquid, or gas.
Bioethanol is an alcohol made by fermenting plant sugars or starches. Crops like corn, sugarcane, or switchgrass are often used.
Biodiesel is made from vegetable oils and animal fats. It's produced through a process called transesterification. Biodiesel is a common biofuel, especially in Europe.
Biogas: Energy from Waste
Biogas is a mixture of gases produced when organic materials break down without oxygen. This process is called anaerobic digestion. It happens with things like manure, sewage, municipal waste, and plant material. Biogas is mainly methane and carbon dioxide. It's a renewable source of energy that can be used for heating or electricity.
Renewable Materials for Industry
Renewable resources are also used to create many industrial products.
Bioplastics: Eco-Friendly Materials
Bioplastics are plastics made from renewable sources like vegetable fats and oils, corn starch, or pea starch. The most common type is thermoplastic starch. Other bioplastics include those made from cellulose or Polylactic acid.
Using bioplastics is generally seen as more sustainable than using plastics made from petroleum. However, making bioplastics can still require energy from non-renewable sources. The market for bioplastics is growing as people look for greener alternatives.
Bioasphalt: Roads of the Future
Bioasphalt is an alternative to traditional asphalt. It's made from renewable resources instead of petroleum. Sources for bioasphalt include sugar, molasses, rice, corn, potato starches, and waste from vegetable oils. In 2004, a company in France even patented asphalt made with vegetable oil-based binders.
Natural Fibers: From Plants and Animals
Natural fibres are hair-like materials that come from plants or animals. They can be long, continuous strands or shorter pieces. These fibers are used to make many products. They can be woven into thread for clothing or pressed into sheets for paper or felt. Examples include cotton from plants and wool from animals.
Protecting Our Renewable Resources
Renewable resources are amazing, but they are not limitless if we don't manage them well. Uncontrolled industrial growth and overuse can put them at risk. We must manage them carefully so that nature can keep replenishing them. This is all about sustainability and protecting our natural world.
The Dangers of Overfishing
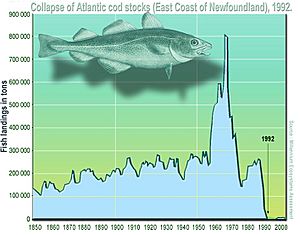
Overfishing means taking too many fish from the sea, too quickly. When this happens, the fish species can't reproduce fast enough to replace those that are caught. This can lead to a big drop in fish populations.
For example, some types of Tuna are in danger because of overfishing. Organizations around the world are working to regulate fishing. They want to protect species and prevent them from disappearing. The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea has rules to help manage fishing.
Overfishing has caused problems in places like the North Sea in Europe and the Grand Banks of Newfoundland in North America. It can also affect other animals, like penguins, who rely on the same fish for food.
Why Forests Matter: Understanding Deforestation
Forests are vital renewable resources. Besides providing wood for fuel and building, trees are crucial for our environment. They absorb carbon dioxide (a gas that contributes to climate change) and release oxygen (which we breathe).
When large areas of forest are cut down (Deforestation), especially rain forests, it causes more carbon dioxide to stay in the atmosphere. This traps heat and leads to global warming, also known as the greenhouse effect.
Deforestation also harms the water cycle. It reduces the amount of water in the soil and air. Without trees, soil is more likely to erode, leading to flooding and landslides. Forests are home to countless species of plants and animals. Losing forests means losing this amazing biodiversity.
Saving Endangered Species
Endangered species are plants and animals that are at a very high risk of disappearing forever. This risk is often caused by a growing human population and using too many resources. Scientists estimate that over 40% of all living species on Earth could be at risk of extinction.
Many countries have laws to protect hunted species and limit hunting. Other ways to help include protecting natural habitats or creating special preserves. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species is a well-known system that tracks the conservation status of species worldwide. Many nations have agreed to create plans to protect endangered species.
Some traditional practices have unfortunately put certain species at risk. For example, the demand for rhinoceros horn has severely reduced rhino populations. It's important to find sustainable ways to use resources and protect all living creatures.
Images for kids
-
A historical image showing a pile of American bison skulls, illustrating past over-hunting.
See also
 In Spanish: Recurso renovable para niños
In Spanish: Recurso renovable para niños
- Exploitation of natural resources
- Habitat conservation
- Natural capital
- Natural resource
- Non-renewable resource
- Recycling
- Resource
- Sustainable development
- Scarcity