Hemp facts for kids
Hemp, also known as industrial hemp, is a special type of Cannabis sativa plant. It's grown specifically to be used in many different products. Hemp is one of the fastest-growing plants on Earth, similar to bamboo. It was also one of the very first plants used by humans to make fibers for clothes and ropes, starting about 50,000 years ago!
Hemp can be turned into a huge variety of useful things. These include paper, rope, textiles, clothing, biodegradable plastics (plastics that break down naturally), paint, insulation for houses, biofuel, food, and even animal feed.
Contents
What Hemp is Used For
Hemp is super versatile! People use it to make many different products for homes and industries. These include ropes, fabrics, clothes, shoes, food, paper, and even materials for building.
The strong outer fibers of the hemp plant, called bast fibers, can be used to make fabrics that are 100% hemp. But often, they are mixed with other fibers like flax, cotton, or silk. They can also be blended with recycled polyester to create fabrics for clothes and furniture. The inner, woodier parts of the plant are used for things like mulch, bedding for animals, or litter.
Hemp oil comes from the seeds. When it's exposed to air, it becomes solid. This oil can be used to make oil-based paints, moisturizing creams, cooking oil, and even plastics. Hemp seeds are also a common ingredient in bird feed mixes.
Hemp for Food
Hemp seeds are healthy and can be eaten in many ways. You can eat them raw, grind them into a meal, or sprout them. They can also be made into a liquid mix for baking or for drinks like hemp milk and herbal teas. Hemp oil is pressed from the seeds and is full of healthy fats.
In some places, like the UK and the US, hemp seeds are allowed in food products. They are often sold in health food stores. For hemp to be used in food, it must have very low levels of a substance called THC (less than 0.3%).
Hemp Seed Nutrition
A small serving of hulled hemp seeds (about 100 grams) gives you a lot of food energy. They are packed with protein (64% of what you need daily!), healthy fats, and some carbohydrates.
Hemp seeds are also a great source of dietary fiber, B vitamins, and important dietary minerals. These include manganese, phosphorus, magnesium, zinc, and iron. About 73% of the energy in hemp seeds comes from healthy fats, especially polyunsaturated fatty acids. These include important fats like omega-3 and omega-6.
The amino acids in hemp seeds are similar to those found in other protein-rich foods like meat, milk, and eggs. However, hemp seeds also contain some natural compounds that can make it harder for your body to absorb all their nutrients.
Storing Hemp Oil
Hemp oil can go bad quickly if it's not stored correctly. It's best to keep it in a dark, airtight container in the refrigerator. Both light and heat can make hemp oil spoil faster.
Hemp Fiber Uses
Hemp fiber has been used for a very long time. It became especially popular when it was brought to the Americas. For centuries, people made ropes, fabrics, and industrial materials from hemp. It was also commonly used to make sails for ships.
Pure hemp fabric feels a lot like linen. Because it's so useful, hemp is now found in many everyday items. These include clothes, shoes, accessories, dog collars, and home goods. Sometimes, hemp is even mixed with other modern fibers like lyocell for clothing.
Hemp as a Building Material
Hemp is becoming a popular material for building houses and other structures. It helps solve many problems with traditional building methods. Hemp products are lightweight, resist mold, and allow buildings to "breathe." This makes them useful for many different building needs.
Studies show that hemp is a more sustainable building material than most others used today. Using hemp in construction can help reduce energy costs and create less pollution.
The use of hemp in building is growing, especially in Europe. One challenge is that hemp's legal status in some places can make it more expensive to import and use. However, universities are researching new ways to use hemp in construction, like hemp-lime panels.
Hemp's Sustainability in Building
Hemp is considered a "green" building material because it's good for the environment. Some of its benefits include stopping weed growth, preventing soil erosion, and even cleaning harmful substances from the soil.
Hemp is gaining popularity alongside other natural materials. It needs very little water to grow and doesn't require pesticides. It's also recyclable, non-toxic, and biodegradable. This makes hemp a great choice for green building.
Hemp fiber is very strong and durable. It can even help protect buildings from pests. Recently, hemp has been used to make building materials like insulation, hempcrete (a type of concrete), and varnishes.
Hemp materials have a low "embodied energy," meaning they don't require much energy to produce. The hemp plant also absorbs a lot of CO2 from the air as it grows. This helps improve air quality and has a positive impact on the environment.
Hemp materials resist mold and are breathable. They can absorb and release moisture without getting damaged. If mixed with lime, hemp can even become non-flammable. Its light weight means it can be used in many parts of a building, like walls and roofs.
Hemp Insulation
Hemp is often used as an insulation material. It's flexible and tough, making it easy to fit into walls and other parts of a building. It can also be cut to different sizes during installation. Hemp insulation doesn't settle over time, which means it needs less maintenance.
Hemp insulation is naturally lightweight and non-toxic. This means it can be used in visible areas like floors, walls, and roofs. It absorbs more heat than mineral insulation and can even be better than some types of wood.
Hemp insulation allows air and moisture to pass through it. It can absorb a lot of moisture without losing its ability to insulate. It also helps air circulate, bringing in fresh air and removing old air. When used on the outside of a building, it helps remove moisture from the walls.
Plus, hemp insulation also works as a sound barrier, making rooms quieter.
Hemp Concrete (Hempcrete)
Hemp is often used to make a special type of concrete called hempcrete. This material is much lighter than regular concrete, about seven times lighter! Hempcrete is made from hemp hurds (the woody inner parts of the stem), hydraulic lime, and water. The mix can be changed depending on how the concrete will be used. For example, flooring needs to be stronger, while walls and roofs can be lighter.
Hempcrete blocks are not strong enough for the main structure of a building. They need to be supported by wood, brick, or steel frames. The first use of hempcrete in building was in France in the late 20th century. Later, in the 2000s, it was used for test homes in the UK. These homes were studied and found to be very advanced. This helped hemp become more popular in UK construction.
Hemp Oils and Varnishes
Cannabis seeds have a lot of fat, about 30-35% fatty acids. The oil extracted from them is useful for building. This biodegradable hemp oil can be used as a wood varnish. It protects floors from mold, pests, and wear. It stops water from getting into the wood but still lets air pass through. It's often used indoors on wood floors and panels.
Hemp Plaster
Hemp-based insulating plaster is made by mixing hemp fibers with calcium lime and sand. This plaster can be applied to inner walls, ceilings, and floors, up to ten centimeters thick. It helps control the humidity in the air and spreads it evenly. The way it slowly absorbs and releases water prevents it from cracking. Hemp plaster can also come in different colors.
Hemp Ropes and Strands
Hemp ropes can be made in different thicknesses and are very strong. This makes them useful for many building tasks, like installing frames or connecting parts. They are also used in building bridges, tunnels, and traditional homes. Some of the earliest uses of hemp rope date back to 1500 BC in Egypt.
Hemp rope was very important during the age of sailing ships. However, it had to be treated with tar to prevent it from rotting. This was a lot of work. Later, manila rope became available, which didn't need tarring, and hemp rope was used less.
Hemp Plastics
Hemp-based bioplastic is a biodegradable option that can replace regular plastics. It could even replace materials like polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which is used for plumbing pipes.
Hemp Wood
Hemp grows very quickly, reaching maturity in about 100 days. This is much faster than trees used for construction. When dry, hemp fibers can be pressed into strong wood alternatives. These can be used for wood-frame construction, wall and ceiling panels, and flooring. Hemp wood is also flexible and can be used in more ways than traditional wood. It can even be made from recycled hemp paper.
Hemp in Composite Materials
Since 2002, a mix of fiberglass, hemp fiber, and other plant fibers has been used to make composite panels for cars. Car makers like Audi, BMW, Ford, and Mercedes are starting to use hemp in their vehicles. For example, some cars can contain up to 20 kg of hemp!
Hemp Paper
Hemp paper is made mostly or entirely from the fibers of industrial hemp. It's often used for special papers like cigarette paper, banknotes, and technical filter papers.
Compared to wood pulp, hemp fibers are much longer (four to five times longer!). They also have less of a substance called lignin and are stronger. However, making hemp paper is currently about four times more expensive than wood paper. This is because the equipment and systems for using hemp are not as developed yet.
If the paper industry switched from wood to hemp, there would be many benefits:
- Hemp produces three to four times more usable fiber per acre each year than forests.
- Hemp doesn't need pesticides or herbicides to grow.
- Hemp grows very fast, maturing in about 3–4 months, while trees can take 20 to 80 years.
- Hemp paper doesn't need harsh, toxic chemicals like chlorine for bleaching. It can be whitened with hydrogen peroxide, which is much better for the environment.
- Hemp paper can be recycled up to 8 times, while wood paper can only be recycled about 3 times.
- Hemp paper lasts a long time and doesn't turn yellow or brown with age. It's one of the strongest natural fibers.
Using hemp instead of wood for paper can help protect forests and the environment. However, it's still hard for hemp paper to compete with cheaper wood paper. This is because it's still difficult to efficiently separate the useful fibers from the less useful ones in hemp stems.
Hemp Jewelry
Hemp jewelry is made by knotting hemp twine using a technique called macramé. You can find hemp bracelets, necklaces, anklets, rings, and other decorations. Some pieces include beads made from crystals, glass, stone, wood, and bones. The hemp twine comes in different thicknesses and colors.
Hemp for Animal Bedding
The inner woody parts of the hemp stem, called shives or hurds, are used for animal bedding (like for horses) or as mulch in gardens. Growing industrial hemp is more profitable when both the fibers and the shives (or even the seeds) can be used.
Hemp for Water and Soil Purification
Hemp can act like a "mop crop" to clean up dirty water. It can remove impurities from sewage or extra phosphorus from animal waste. Hemp is even being used to clean up contaminated soil at the Chernobyl nuclear disaster site. This process is called phytoremediation, where plants help remove harmful substances like radioactive materials and other toxins from soil, water, and air.
Hemp for Weed Control
Hemp plants grow tall and have thick leaves. They can be planted close together to act as a "smother crop" that kills tough weeds. This method helps farmers avoid using herbicides, get organic certification, and benefit from crop rotation. However, because hemp grows so quickly and densely, some places consider it a weed itself.
-
The dense growth of hemp helps kill weeds, even thistle.
Hemp for Biofuels
Biodiesel can be made from the oils found in hemp seeds and stalks. This product is sometimes called "hempoline." Also, alcohol fuel (like ethanol) can be made by fermenting the entire hemp plant.
Filtered hemp oil can even be used directly in diesel engines. In 1892, Rudolf Diesel invented the diesel engine, intending it to run on various fuels, including vegetable and seed oils.
However, very little vehicle fuel is currently made from hemp. Most commercial biodiesel and biogas come from other sources like cereals, coconuts, palm seeds, or even cheaper materials like garbage and animal waste.
How Hemp is Processed
Separating the inner woody part (hurd) from the outer fibers (bast fiber) is called decortication. In the past, hemp stalks were soaked in water first. Then, the fibers were beaten off by hand.
Today, machines are used to separate the fibers. These machines use rollers to crush the hemp or mechanical hammers to beat it. Recently, new high-speed machines have been developed that can separate hemp into three parts: bast fiber, hurd, and green microfiber.
Growing Hemp
Hemp is usually planted in spring (March to May) in the northern half of the world, and in autumn (September to November) in the southern half. It takes about three to four months to grow fully.
Over thousands of years, people have used selective breeding to create different types of hemp. These types are suited for different climates and produce different amounts of useful substances. Hemp grown for fiber is planted close together. This makes the plants grow tall and thin with long fibers.
Hemp seeds are planted about 13 to 25 millimeters deep using regular farm equipment. The soil needs to have enough nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Using natural fertilizers like manure can also help control weeds.
Hemp Varieties
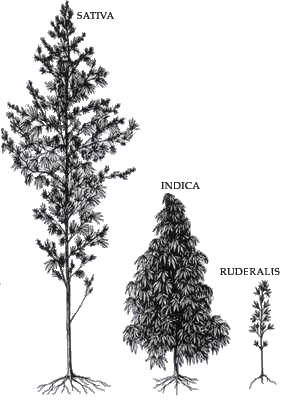
Cannabis sativa L. subsp. sativa var. sativa is the type grown for industrial use. Another type, C. sativa subsp. indica, usually doesn't have good fiber quality. The main differences between these types are how they look and how much THC they produce. Industrial hemp has very low levels of THC.
-
Cannabis sativa stem
Harvesting Hemp
On small farms, hemp is usually harvested by hand. The plants are cut close to the ground and left to dry. On larger farms, machines are used to cut the hemp.
After cutting, the hemp is left in rows to dry for up to four days. Traditionally, this was followed by "retting." This is a process where the hemp is soaked in water or left on the ground to be affected by dew, molds, and bacteria. This helps separate the fibers.
-
Industrial hempseed harvesting machine in France
Hemp Pests
Several insects can harm hemp plants. The most serious ones are caterpillars that bore into the stems, like the European corn borer. Other pests, like aphids and mites, feed on the plant's sap, making it weaker. Root feeders, like beetle grubs, can also damage the roots and are hard to spot.
Farmers use strategies like Integrated pest management to control these pests. This means focusing on preventing problems and finding pests early. They also use natural controls, and only use chemicals as a last resort.
Hemp Diseases
Hemp plants can get sick from various pathogens, including bacteria, fungi, nematodes, and viruses. These diseases can reduce the quality of the fiber, stop the plant from growing, or even kill it. However, these diseases rarely affect the overall amount of hemp harvested from a field. So, farmers usually don't need to use pesticides to grow hemp.
Hemp's Environmental Impact
Hemp is considered environmentally friendly. It uses less land and has fewer negative impacts on the environment compared to some other crops. Some studies suggest it can help reduce our ecological footprint.
Hemp is also said to need few pesticides and no herbicides. It's even called a carbon negative raw material because it absorbs a lot of CO2 from the air as it grows.
Where Hemp is Produced

China is the world's biggest producer of hemp, growing over 70% of the world's supply. France is second, producing about a quarter of the world's hemp. Smaller amounts are grown in other parts of Europe, Chile, and North Korea. More than 30 countries grow industrial hemp, including Canada, Australia, Germany, and the United Kingdom.
The UK and Germany started growing hemp again for commercial use in the 1990s. In the UK, most hemp is used for animal bedding. Companies in many countries process hemp seeds into a growing range of food products and cosmetics. Many traditional hemp-growing countries continue to produce fiber for textiles.
The amount of dry hemp stalks harvested per hectare (about 2.5 acres) can vary. In Europe, the average yield of dry hemp stalks was about 6 tons per hectare in 2001 and 2002. From this, about one tonne of strong fiber and 2–3 tonnes of core material can be separated. The FAO says that a good yield of hemp fiber is more than 2 tonnes per hectare.
See also
 In Spanish: Cáñamo para niños
In Spanish: Cáñamo para niños