California facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
California
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Nickname(s):
The Golden State
|
|||
| Motto(s):
"Eureka"
|
|||
| Anthem: "I Love You, California" | |||
Location of California within the United States
|
|||
| Country | United States | ||
| Before statehood | Mexican Cession unorganized territory | ||
| Admitted to the Union | September 9, 1850 (31st) | ||
| Capital | Sacramento | ||
| Largest city | Los Angeles | ||
| Largest metro and urban areas | Greater Los Angeles | ||
| Legislature | State Legislature | ||
| • Upper house | State Senate | ||
| • Lower house | State Assembly | ||
| Judiciary | Supreme Court of California | ||
| U.S. senators | Alex Padilla (D) Adam Schiff (D) |
||
| U.S. House delegation |
|
||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 163,696 sq mi (423,970 km2) | ||
| • Land | 155,959 sq mi (403,932 km2) | ||
| • Water | 7,737 sq mi (20,047 km2) 4.7% | ||
| Area rank | 3rd | ||
| Dimensions | |||
| • Length | 760 mi (1,220 km) | ||
| • Width | 250 mi (400 km) | ||
| Elevation | 2,900 ft (880 m) | ||
| Highest elevation | 14,505 ft (4,421.0 m) | ||
| Lowest elevation | −279 ft (−85.0 m) | ||
| Population
(2024)
|
|||
| • Total | |||
| • Rank | 1st | ||
| • Density | 251.3/sq mi (97/km2) | ||
| • Density rank | 11th | ||
| • Median household income | $95,500 (2023) | ||
| • Income rank | 5th | ||
| Demonym(s) | Californian Californio (archaic Spanish) Californiano (Spanish) |
||
| Language | |||
| • Official language | English | ||
| • Spoken language |
|
||
| Time zone | UTC−08:00 (PST) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−07:00 (PDT) | ||
| USPS abbreviation |
CA
|
||
| ISO 3166 code | US-CA | ||
| Traditional abbreviation | Calif., Cal., Cali. | ||
| Latitude | 32°32′ N to 42° N | ||
| Longitude | 114°8′ W to 124°26′ W | ||
| Dance | West Coast Swing |
|---|---|
| Bird | California quail |
| Fish |
|
| Flower | California poppy |
| Fruit | Avocado |
| Tree | Coast redwood & giant sequoia |
| Insect | California dogface butterfly |
| Vegetable | Artichoke |
| Sport | Surfing |
| Color | Blue & Gold |
California is a large state located in the Western United States. It shares borders with Oregon to the north and Nevada and Arizona to the east. To the south, it borders the Mexican state of Baja California. The state also has a long coastline along the Pacific Ocean to the west.
California is the most populous state in the U.S. with over 39.5 million people. It is also the third-largest state by area, covering about 163,696 square miles (423,970 square kilometers).
Sacramento is the state's capital city. Los Angeles is the largest city in California. It is also the second most populous city in the entire country, after New York City.
California's History
Early California and European Arrival
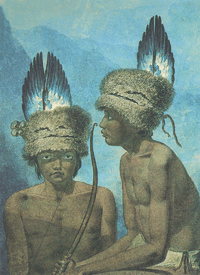
Long ago, more than 70 different groups of Native Americans lived in the area we now call California.
The name "California" used to describe a much larger area. This included parts of today's Mexico, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, and Wyoming. Early maps sometimes even showed California as an island.
The first European to visit parts of the California coast was Juan Rodriguez Cabrillo from Portugal in 1542. Later, in 1579, Sir Francis Drake from Great Britain explored the entire coast.
In the late 1700s, Spanish religious leaders, called missionaries, built towns and villages. These are known as the famous California Missions. After Mexico gained independence from Spain, the Mexican government took over these villages.
Becoming Part of the United States

In 1846, during the Mexican–American War, some Americans in California wanted to create their own country. They called it the California Republic and flew a "Bear flag." However, this republic quickly ended when the United States Navy claimed California.
After the war, California was divided between Mexico and the United States. The part given to the U.S. became today's state of California.
In 1848, gold was discovered in California. This led to the California Gold Rush, and many people moved to the area very quickly. In 1850, California officially became a state in the United States.
During the American Civil War (1861-1865), California supported the North (the Union). It sent many troops to help fight in the war.
Growth and Development
Traveling between California and the eastern U.S. was difficult at first. It was a long and dangerous journey by land or by boat around South America. But in 1869, the first railroad across the continent was completed. This made travel much faster and safer.
People also realized that California's land was great for growing fruits and other crops. This led to California becoming a huge farming state.
In the early 1900s, more people moved to California. Major highways like the Lincoln Highway and Route 66 were built. The state's population grew from less than one million in 1900 to become the most populous state by 1965.
Filmmakers were attracted to California's mild weather and diverse landscapes. They built the studio system in Hollywood in the 1920s. This made California a world center for entertainment.

After World War II, California's economy grew even more. Industries like aerospace and defense became very strong. Stanford University also encouraged people to develop new technologies. This led to the creation of Silicon Valley, a global hub for technology and engineering.
California has faced natural disasters. The 1906 San Francisco earthquake and the 1928 St. Francis Dam flood were two of the deadliest in U.S. history.
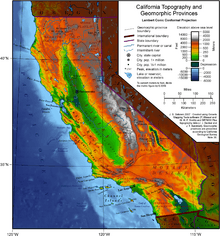
California's Geography
Regions and Landscapes
California is often divided into two main parts: Southern California and Northern California.
In the middle of the state is the California Central Valley. This valley is surrounded by mountains: the Sierra Nevada to the east and coastal mountains to the west. It is California's most important farming area.
The Central Valley is split by the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta. The northern part is the Sacramento Valley, and the southern part is the San Joaquin Valley. These valleys are named after the rivers that flow through them.
The Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta is very important for water supply. Water from the delta provides drinking water for almost two-thirds of California's population. It also supplies water for farms.
The Channel Islands are a group of islands located off the Southern California coast.
Mountains and Deserts
The Sierra Nevada mountain range is in the east. It includes Mount Whitney, which is the highest peak in the contiguous United States at 14,505 feet (4,421 meters). This range is home to Yosemite Valley, famous for its beautiful rock formations. It also has Sequoia National Park, where you can find giant sequoia trees. These are some of the largest living things on Earth.
East of the Sierra Nevada are Owens Valley and Mono Lake. Mono Lake is an important place for migratory birds. In the western part of the state is Clear Lake, the largest freshwater lake entirely within California.
About 45 percent of California is covered by forests. Many trees in the California White Mountains are among the oldest in the world. Some bristlecone pine trees are over 5,000 years old.
In the south, there is a large salt lake called the Salton Sea. The south-central part of the state is the Mojave Desert. Death Valley, located in the Mojave, is the lowest and hottest place in North America. It is 279 feet (85 meters) below sea level. The distance from the bottom of Death Valley to the top of Mount Whitney is less than 90 miles (145 km). Much of southeastern California is hot, dry desert.
California has both the highest point (Mount Whitney) and the lowest point (Death Valley) in the contiguous United States.
Cities and Natural Hazards
Most of California's big cities are located along the coast or in major valleys. These include the San Francisco Bay Area, the Sacramento metropolitan area, the Los Angeles area, and the San Diego metropolitan area.
California is part of the Pacific Ring of Fire. This means it can experience tsunamis, floods, droughts, wildfires, and landslides. The state also has many earthquakes because of several fault lines, especially the San Andreas Fault. About 37,000 earthquakes are recorded each year, but most are too small to feel.
California's Climate
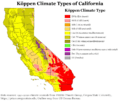
California has a very diverse climate because of its large size. While most of the state has a Mediterranean climate, it can range from very cold (subarctic) to very warm (subtropical).
Near the coast, the cool California Current often creates summer fog. Farther inland, winters are colder and summers are hotter. Northern California generally receives more rain than the southern parts of the state.
California's mountains create "rain shadows" on their eastern side. This leads to large deserts in those areas.
California's Ecology
Plants and Animals
California is known for its rich and diverse natural environments. It has many unique species of plants and animals found nowhere else. Some of these species are now endangered due to human development and the introduction of new species.
California is home to some amazing trees. It has the largest trees (giant sequoias), the tallest trees (coast redwoods), and the oldest trees (bristlecone pines) in the world. Some giant sequoias are thought to be at least 4,000 years old.
The state has six main "life zones" based on climate and terrain. These zones include deserts, foothills, coastal areas, and high mountain elevations.
In the deserts, you can find animals like jackrabbits, kangaroo rats, and opossums. Birds like owls and roadrunners are common. Reptiles include the sidewinder viper and desert tortoise.
In the foothills and coastal areas, you might see antelopes, ring-tailed cats, and the California Condor. Forests are home to black-tailed deer, black bears, gray foxes, cougars, and bobcats. You can also find garter snakes and rattlesnakes.
Higher in the mountains, animals like the mountain weasel, snowshoe hare, and bighorn sheep live. Birds like the blue-fronted jay and water ouzel are also found here.
California's waters are full of life. Mountain lakes and streams have many types of trout, including rainbow and golden trout. Salmon also migrate through these waters. In the Pacific Ocean, you can find sea bass, yellowfin tuna, and various types of whale. Seals, sea lions, and many shorebirds live along the northern California cliffs.
California's Rivers
Most of California's rivers have dams. These dams are part of two huge water projects: the Central Valley Project and the California State Water Project. These projects move water from northern to southern California, mainly for farming and drinking water.
The two most important rivers in California are the Sacramento River and the San Joaquin River.
California's Government
State Government Structure
The capital city of California is Sacramento.
California's government is divided into three main parts, like the U.S. federal government:
- The executive branch includes the governor and other elected officials.
- The legislative branch makes laws and has two parts: the Assembly and the Senate.
- The judicial branch includes the Supreme Court of California and other courts.
Citizens in California can also directly vote on "ballot propositions." These are laws or changes to the state constitution that people propose.
Executive Branch Leaders

The executive branch is led by the governor. There are also seven other elected officials, such as the lieutenant governor and the attorney general. They all serve four-year terms and can be re-elected once.
Legislative Branch (Lawmakers)
The California State Legislature has 40 members in the Senate and 80 members in the Assembly. Senators serve four-year terms, and Assembly members serve two-year terms. There are limits on how many terms they can serve.
Judicial Branch (Courts)
California's court system is the largest in the United States. It has about 1,600 judges. The highest court is the seven-member Supreme Court of California. Below that are the Courts of Appeal and the Superior Courts.
Judges for the Supreme Court and Courts of Appeal are chosen by the governor. Voters then decide if they should stay in their positions every 12 years.
Local Government in California
California has many types of local governments. These manage public services across the state.
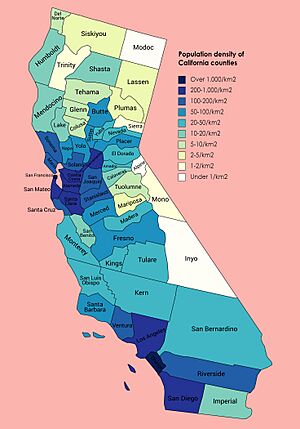
Counties
California is divided into 58 counties. Counties provide services like law enforcement, elections, public health, and libraries. They also act as the local government for areas that are not part of a city. Each county is run by an elected board of supervisors.
Cities and Towns

Most urban areas in California are organized as cities or towns. Many cities have a "council-manager" government. In this system, an elected city council hires a city manager to run the city's daily operations. Some larger cities have a directly elected mayor who leads the city government. San Francisco is unique because its city and county governments are combined into one.
School Districts and Special Districts
About 1,102 school districts manage public education in California. These districts are separate from city and county governments.
There are also about 3,400 "special districts." These districts provide specific services, like fire protection or water supply, within a certain area.
Federal Representation
California sends 52 members to the United States House of Representatives. This is the largest group of representatives from any state. Because of this, California also has the most "electoral votes" in presidential elections, with 54 votes.
California's Population and People
Population Size
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1850 | 92,597 | — | |
| 1860 | 379,994 | 310.4% | |
| 1870 | 560,247 | 47.4% | |
| 1880 | 864,694 | 54.3% | |
| 1890 | 1,213,398 | 40.3% | |
| 1900 | 1,485,053 | 22.4% | |
| 1910 | 2,377,549 | 60.1% | |
| 1920 | 3,426,861 | 44.1% | |
| 1930 | 5,677,251 | 65.7% | |
| 1940 | 6,907,387 | 21.7% | |
| 1950 | 10,586,223 | 53.3% | |
| 1960 | 15,717,204 | 48.5% | |
| 1970 | 19,953,134 | 27.0% | |
| 1980 | 23,667,902 | 18.6% | |
| 1990 | 29,760,021 | 25.7% | |
| 2000 | 33,871,648 | 13.8% | |
| 2010 | 37,253,956 | 10.0% | |
| 2020 | 39,538,223 | 6.1% | |
| 2024 (est.) | 39,431,263 | 5.8% | |
| Sources: 1790–1990, 2000, 2010, 2020, 2024 Chart does not include indigenous population figures. Studies indicate that the Native American population in California in 1850 was close to 150,000 before declining to 15,000 by 1900. |
|||
About one out of every nine people in the United States lives in California. In 2020, California's population was about 39.54 million.
The Greater Los Angeles Area is the second-largest metropolitan area in the U.S. Los Angeles itself is the second-largest city in the country.
Different Backgrounds
California is a very diverse state. People from many different racial and ethnic backgrounds live here.
| Race and ethnicity | Alone | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hispanic or Latino | — | 39.4% |
|
|
| White (non-Hispanic) | 34.7% |
|
38.3% |
|
| Asian (non-Hispanic) | 15.1% |
|
17.0% |
|
| African American (non-Hispanic) | 5.4% |
|
6.4% |
|
| Native American (non-Hispanic) | 0.4% |
|
1.3% |
|
| Pacific Islander (non-Hispanic) | 0.3% |
|
0.7% |
|
| Other (non-Hispanic) | 0.6% |
|
1.3% |
|
| Racial composition | 1950 | 1960 | 1970 | 1980 | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 93.7% | 92% | 89% | 76.2% | 69% | 59.6% | 57.6% | 41.2% |
| Black | 4.4% | 5.6% | 7% | 7.7% | 7.4% | 6.7% | 6.2% | 5.6% |
| Asian | 1.7% | 2% | 2.8% | 5.3% | 9.6% | 10.9% | 13% | 15.4% |
| Native | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.5% | 0.9% | 0.8% | 1% | 1% | 1.6% |
| Native Hawaiian and | — | — | — | — | — | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% |
| Other race | — | 0.1% | 0.7% | 10% | 13.2% | 16.8% | 17% | 21.2% |
| Two or more races | — | — | — | — | — | 4.8% | 4.9% | 14.6% |
| Hispanic or Latino | — | — | 13.7% | 19.2% | 25.8% | 32.4% | 37.6% | 39.4% |
| Non-Hispanic white | — | — | 76.3% | 66.6% | 57.2% | 46.7% | 40.2% | 34.7% |
California has the largest multiracial population in the United States. Many people in California have Mexican, English, German, or Irish backgrounds.
Languages Spoken
| Language | Population (as of 2021[update]) |
% |
|---|---|---|
| English | 20,763,638 | 56.08% |
| Spanish | 10,434,308 | 28.18% |
| Chinese | 1,244,445 | 3.36% |
| Tagalog | 757,488 | 2.05% |
| Vietnamese | 544,046 | 1.47% |
| Korean | 356,901 | 0.96% |
| Arabic | 231,612 | 0.63% |
| Persian | 221,650 | 0.6% |
| Armenian | 211,614 | 0.57% |
| Hindi | 208,148 | 0.56% |
| Russian | 178,176 | 0.48% |
| Punjabi | 156,763 | 0.42% |
| Japanese | 135,992 | 0.37% |
| French | 126,371 | 0.34% |
English is the official language of California. Spanish is the second most common language spoken.
California has historically been one of the most linguistically diverse places in the world. More than 70 different Native American languages were once spoken here. Today, many of these languages are endangered, but there are efforts to bring them back.
Religion in California
Religious self-identification, per Public Religion Research Institute's 2021 American Values Survey Catholicism (34%) Protestantism (27%) Jehovah's Witness (1%) Unaffiliated (28%) Buddhism (2%) Judaism (1%) Hinduism (1%) Other (5%)
The largest religious groups in California are Catholics and Protestants. Many people in California also do not identify with any religion. Other religions practiced include Buddhism, Judaism, and Hinduism.
California's Economy
California has one of the largest economies in the world. If it were a country, its economy would be among the top five globally. California produces about one-seventh of the entire United States' economic output.

The biggest job sectors in California are trade, transportation, government, business services, education, health services, and hospitality.
California's main trading partner is Mexico. The state exports many goods, especially vehicles, computers, and electronic products. Over 50 car companies operate in California, including Tesla.
Agriculture in California
Farming is a very important part of California's economy. Some of the biggest agricultural products are milk, almonds, and grapes. The agriculture sector makes up a small but important part of the state's economy and employs many people.
California's Infrastructure
Energy Sources

California uses a lot of energy. However, because of its focus on saving energy and its mild weather, the amount of energy used per person is one of the lowest in the U.S. California imports a lot of electricity from other states.

California has strong goals for using renewable energy. There are several solar power plants in the Mojave Desert. The state also has many wind farms, like those at Altamont Pass and Tehachapi Pass. Dams across the state also provide hydro-electric power.
California also has oil and natural gas deposits. Natural gas power plants produce more than half of the state's electricity.
Transportation Systems

California has a huge network of highways and roads. People in California often rely on cars, which can lead to a lot of traffic congestion. The state's growing population puts a strain on its transportation networks.
California has been a leader in road construction. The Golden Gate Bridge was the longest suspension bridge in the world when it opened in 1937. It is famous for its orange color and views of the bay. The San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge is another major bridge, carrying about 280,000 vehicles daily. The Arroyo Seco Parkway in Los Angeles was the first freeway in the Western United States.
Los Angeles International Airport (LAX) and San Francisco International Airport (SFO) are major airports. They handle many flights across the Pacific Ocean and across the U.S.
California also has important seaports. The Port of Los Angeles and the Port of Long Beach together form the largest port complex in the country. They handle about a fourth of all container cargo in the U.S. The Port of Oakland is also a major port for trade from the Pacific Rim.

Inter-city rail travel is provided by Amtrak California. These train services are very busy, especially outside the Northeast U.S. California is also building a high-speed rail system.
Most counties and many cities have their own bus lines. Long-distance bus travel is available through companies like Greyhound.

Interesting Facts About California
- The name 'California' comes from a 16th-century book about an island paradise.
- It is the 3rd largest state in the United States by area, after Alaska and Texas.
- California has more forestland than any other state except Alaska.
- The state's ports handle about one-third of all U.S. imports.
- In 2019, California had more millionaire households than any other state.
- California is the only U.S. state to have hosted both the Summer and Winter Olympics.
- The state is home to the oldest college football game, the annual Rose Bowl.
- As of 2018, California's economy was larger than almost all countries in the world.
Images for kids
-
Mission San Diego de Alcalá drawn as it was in 1848. Established in 1769, it was the first of the California Missions.
-
Map showing Alta California in 1838, when it was a sparsely populated Mexican province
-
The flag used by Juan Bautista Alvarado's 1836 movement for Californian independence
-
The Russians from Alaska established their largest settlement in California, Fort Ross, in 1812.
-
Yokayo, a village of Pomo people in Ukiah (Mendocino County), c. 1916
-
The Hollywood Sign, a symbol of the American film industry
-
Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum hosted the Olympic Games in 1932 and 1984
-
A topographic map of California
-
Big Sur coast, south of Monterey at Bixby Bridge
-
Köppen climate types in California
-
Death Valley, in the Mojave Desert
-
Five of the twenty largest wildfires in California history were part of the 2020 wildfire season.
-
The California Tunnel Tree at Yosemite National Park in May 2022
-
A Joshua Tree (Yucca brevifolia) in Joshua Tree
-
A forest of redwood trees in Redwood National Park
-
Sea otter in Morro Bay, California
-
Sunset at Venice Beach
-
The University of California, Berkeley is the first and oldest campus of the UC system.
-
The Claremont Colleges east of L.A. include some of the most selective liberal arts colleges in the U.S.
See also
 In Spanish: California para niños
In Spanish: California para niños