Nevada facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Nevada
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Nickname(s):
The Silver State (official);
The Sagebrush State; The Battle Born State |
|||
| Motto(s):
All for Our Country
|
|||
| Anthem: "Home Means Nevada" |
|||
Location of Nevada within the United States
|
|||
| Country | United States | ||
| Before statehood | Nevada Territory, Utah Territory, Arizona Territory | ||
| Admitted to the Union | October 31, 1864 (36th) | ||
| Capital | Carson City | ||
| Largest city | Las Vegas | ||
| Largest county or equivalent | Clark | ||
| Largest metro and urban areas | Las Vegas Valley | ||
| Legislature | Nevada Legislature | ||
| • Upper house | Senate | ||
| • Lower house | Assembly | ||
| Judiciary | Supreme Court of Nevada | ||
| U.S. senators | Catherine Cortez Masto (D) Jacky Rosen (D) |
||
| U.S. House delegation | 3 Democrats 1 Republican (list) |
||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 110,577 sq mi (286,382 km2) | ||
| • Land | 109,781.18 sq mi (284,332 km2) | ||
| • Water | 791 sq mi (2,048 km2) 0.72% | ||
| Area rank | 7th | ||
| Dimensions | |||
| • Length | 492 mi (787 km) | ||
| • Width | 322 mi (519 km) | ||
| Elevation | 5,500 ft (1,680 m) | ||
| Highest elevation | 13,147 ft (4,007.1 m) | ||
| Lowest elevation
(Colorado River at California border)
|
481 ft (147 m) | ||
| Population
(2024)
|
|||
| • Total | |||
| • Rank | 31st | ||
| • Density | 26.8/sq mi (10.3/km2) | ||
| • Density rank | 42nd | ||
| • Median household income | $76,400 (2023) | ||
| • Income rank | 24th | ||
| Demonym(s) | Nevadan | ||
| Language | |||
| • Official language | None | ||
| Time zones | |||
| most of state | UTC−08:00 (Pacific) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−07:00 (PDT) | ||
| West Wendover | UTC−07:00 (Mountain) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−06:00 (MDT) | ||
| USPS abbreviation |
NV
|
||
| ISO 3166 code | US-NV | ||
| Traditional abbreviation | Nev. | ||
| Latitude | 35° N to 42° N | ||
| Longitude | 114° 2′ W to 120° W | ||
| Song | Home Means Nevada |
|---|---|
| Bird | Mountain bluebird (Sialia currucoides) |
| Fish | Lahontan cutthroat trout (Oncorhynchus clarkii henshawi) |
| Flower | Sagebrush (Artemisia tridentata) |
| Tree | Bristlecone pine, Single-leaf Piñon (Pinus monophylla) |
| Insect | Vivid Dancer Damselfly (Argia vivida) |
Nevada is a state located in the Western United States. It shares borders with Oregon, Idaho, California, Arizona, and Utah. Nevada is the seventh largest state by area. It is also the 32nd most populated state.
Most people in Nevada live in Clark County, which includes the Las Vegas area. The state capital is Carson City. Las Vegas is the biggest city in Nevada.
Nevada is often called the "Silver State" because silver mining was very important to its past and economy. It's also known as the "Battle Born State." This is because it became a state during the American Civil War. The words "Battle Born" are even on the state flag! The state's name means "snowy" in Spanish. This refers to the Sierra Nevada mountains. However, most of Nevada is actually a desert or very dry.
Today, tourism is Nevada's biggest job provider. Mining is also a huge part of the economy. Nevada is one of the world's top producers of gold.
Contents
- What's in a Name? The Meaning of Nevada
- Nevada's Past: A Look at History
- Nevada's Landscape: Exploring Geography
- Nature's Playgrounds: Parks and Recreation
- How Nevada is Governed
- Who Lives in Nevada? Population and People
- Nevada's Money: The Economy
- Getting Around: Transportation in Nevada
- Learning in Nevada: Education
- Fun and Games: Culture and Sports
- Nevada's Military Presence
- See also
What's in a Name? The Meaning of Nevada
The name "Nevada" comes from a Spanish word, nevada. This word means "snow-covered" or "snowy." The state was named after the Sierra Nevada mountain range.
People from Nevada usually say the name with the "a" sound like in "apple." This is how the state government says it too.
Nevada's Past: A Look at History
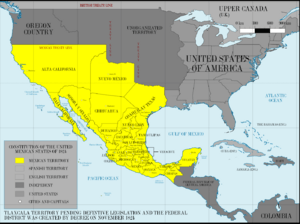
The first Europeans to explore this area were Spanish. They named the region "Nevada" because of the snow on the mountains. This was similar to the Sierra Nevada in Spain.
The land that is now Nevada was once part of New Spain. This was a large area controlled by Spain. In 1821, Mexico became independent from Spain. The Nevada area then became part of Mexico's Alta California territory.
Early Explorers and Settlements
Jedediah Smith explored the Las Vegas Valley in 1827. Peter Skene Ogden traveled along the Humboldt River in 1828. In 1847, a group called the Mormons claimed much of Nevada. They built a fort near Las Vegas in 1855. This was the first lasting building in the valley.
Becoming Part of the United States
After the Mexican–American War in 1848, the United States took control of Alta California. This included the Nevada area. It became part of the Utah Territory in 1850.
A big discovery happened in 1859: silver! The Comstock Lode was found near Virginia City, Nevada. This brought many people to the area. Because of this population boom, the Nevada Territory was created in 1861.
Nevada Becomes a State
Nevada officially became the 36th U.S. state on October 31, 1864. This happened just before the 1864 presidential election. The statehood was rushed to help Abraham Lincoln and the Union during the Civil War. Nevada's silver mines provided a lot of money for the Union.
Nevada is one of only two states that significantly grew its borders after becoming a state. In 1866 and 1867, more land was added to Nevada from the Utah and Arizona territories. This included the area where Las Vegas is today. Officials thought Nevada could better manage the gold discoveries in these new areas.
Mining continued to shape Nevada's economy. After a decline, new silver strikes in the early 1900s brought more people to the state.
Gambling and Growth
Gambling was common in early Nevada mining towns. But it was made illegal in 1909. During the Great Depression, Nevada faced tough economic times. So, in 1931, the state made gambling legal again. This helped the economy, especially with the construction of the Hoover Dam starting around the same time.
Nuclear Testing in Nevada
The Nevada Test Site was created in 1951. It is about 65 miles northwest of Las Vegas. This site was used to test nuclear weapons. The last above-ground test was in 1962. Underground testing continued until 1992.
A large part of Nevada's land (over 80%) is owned by the U.S. federal government. This is because the dry land was not suitable for large farms.
Nevada's Landscape: Exploring Geography




Nevada is mostly part of the Basin and Range Province. This means it has many mountain ranges running north to south. Between these ranges are valleys.
Much of northern Nevada is in the Great Basin. This is a mild desert with hot summers and cold winters. Sometimes, summer thunderstorms happen. Pacific storms can also bring snow.
The Humboldt River flows across northern Nevada. Other rivers like the Walker, Truckee, and Carson rivers flow eastward from the Sierra Nevada. These rivers end in lakes or dry lakebeds within the state. The Colorado River forms much of Nevada's border with Arizona.
Nevada's mountains can be very tall, some over 13,000 feet high. These mountains have forests, which are like "sky islands" for unique plants and animals. The valleys are also quite high in elevation.
The southern part of Nevada, including Las Vegas, is in the Mojave Desert. This area gets less winter rain. It is also lower in elevation, leading to very hot summers and cool winter nights.
Nevada has many mountain peaks. It ranks second in the USA for the number of mountains with significant height. This makes Nevada the most mountainous state in the connected United States.
Nevada's Climate: Weather Patterns
Nevada is the driest state in the U.S. Most of it has a desert or semi-arid climate. This means it gets very little rain. In many parts of the state, summer temperatures can change a lot between day and night.
Northern Nevada has long, cold winters. Southern Nevada has shorter, milder winters. Most of the rain in the state falls on the eastern slopes of the Sierra Nevada mountains.
Nevada's Plants: Vegetation Zones
Nevada's plant life is varied. It changes depending on the area. The state has six main plant zones:
- Alpine (high mountains)
- Sub-alpine (below alpine)
- Ponderosa pine forests
- Pinion-juniper woodlands
- Sagebrush areas
- Creosotebush areas (desert)
Nature's Playgrounds: Parks and Recreation

Nevada has many beautiful natural areas for people to enjoy.
Wilderness Areas
There are 68 special wilderness areas in Nevada. These areas protect over 6.5 million acres of land. They are managed by different U.S. government agencies.
State Parks
Nevada has 24 state park units. These include state parks, historic sites, and recreation areas. They are managed by the state of Nevada. One park, Van Sickle Bi-State Park, is shared with California.
How Nevada is Governed
Nevada's government is split into three main parts:
- Executive Branch: Led by the governor of Nevada. This branch carries out laws.
- Legislative Branch: The Nevada Legislature makes laws. It has two parts: the Assembly and the Senate.
- Judicial Branch: The Supreme Court of Nevada and other courts interpret laws.
The governor is the state's chief leader. Other elected officials, like the lieutenant governor and secretary of state, also work in the executive branch.
Members of the Assembly serve for two years. Senators serve for four years. Since 2010, there are limits on how many years a person can serve in the legislature. The legislature meets for 120 days every two years.
In 2018, Nevada became the first U.S. state to have more women than men in its legislature.
Cities in Nevada can make their own laws, as long as they don't go against state law.
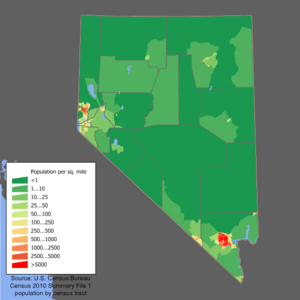
Who Lives in Nevada? Population and People
In 2020, Nevada had a population of over 3.1 million people. It was one of the fastest-growing states for many years. Most of the population lives in the Las Vegas area.
Since 1950, Nevada has had the lowest percentage of people born in the state. This means many people move to Nevada from other states.
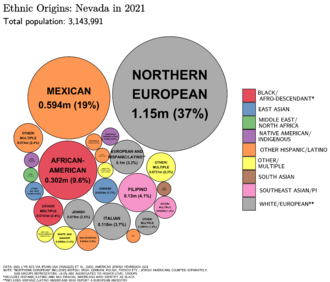
Diverse Backgrounds: Race and Ethnicity
Nevada is a very diverse state. Many different groups of people live here.
- Hispanic or Latino: This is the fastest-growing group. Many come from Mexico, Guatemala, and El Salvador.
- White (European ancestry): This is the largest group overall. Many have German, English, Irish, or Italian roots.
- Asian Americans: Filipinos are the largest Asian group in Nevada. There are also many Chinese, Japanese, and Korean Americans.
- African Americans: Most African Americans live in the Las Vegas and Reno areas.
- Native Americans: Tribes like the Paiute, Shoshone, and Washoe people live on reservations in the state.
Nevada is the third most diverse state in the country. Only Hawaii and California are more diverse.
A small number of people in Nevada live in rural areas. Life in these areas is different from the big cities. People in rural areas are more likely to have been born in Nevada. Mining and ranching are very important to their economies.
Beliefs and Religions
Nevada has one of the lowest rates of church attendance in the U.S. The main religious groups in Nevada are:
- Protestant
- People with no religious affiliation
- Roman Catholic
- Latter-day Saints (Mormons)
- Jewish
Parts of eastern Nevada are in the "Mormon Corridor," where many Latter-day Saints live.
Languages Spoken in Nevada
Besides English, the most common languages spoken in Nevada are Spanish, Tagalog, and Chinese. Native American languages like Northern Paiute and Shoshone are also spoken.
Nevada's Money: The Economy


Nevada's economy relies on tourism, entertainment, mining, and cattle ranching. The state makes money from things like machinery, printing, food processing, and electrical equipment.
Mining for Riches
Mining is a huge part of the economy outside of Las Vegas and Reno. Gold is the most important mineral mined. In 2022, Nevada mined gold worth over $7 billion! Other minerals found in Nevada include copper, gypsum, and lithium.
Cattle Ranching
Raising cattle is a big business in rural Nevada. Farmers also grow hay, alfalfa, onions, and potatoes. Most cattle eat grass on open land in the summer. Then they are sent to other states to be prepared for market. Over 90% of Nevada's farmland is used to grow hay for these animals.
Top Employers in Nevada
Many people in Nevada work for large companies and organizations. Some of the biggest employers include:
- Clark County School District
- Washoe County School District
- Clark County (the local government)
- Large hotels and casinos like Wynn Las Vegas, Bellagio, and MGM Grand
- Las Vegas Metropolitan Police Department
- Universities like UNLV and UNR
Getting Around: Transportation in Nevada
Trains, buses, and cars are all ways to travel in Nevada.
- Trains: The California Zephyr train stops in northern Nevada cities like Elko and Winnemucca. Las Vegas does not have passenger train service.
- Buses: Greyhound Lines offers bus service across the state.
- Highways: Interstate 15 goes through southern Nevada, serving Las Vegas. Interstate 80 crosses northern Nevada. Many U.S. highways and state routes also connect different parts of the state. Nevada is one of the few states where its two biggest cities (Las Vegas and Reno) are not connected by a single interstate highway.
- Public Transit: RTC Transit runs buses in the Las Vegas area. RTC RIDE operates buses in the Reno-Sparks area.
- Monorail: Las Vegas has a monorail system. It connects several casinos and the convention center.
- Airports: Harry Reid International Airport in Las Vegas is the busiest airport. Reno-Tahoe International Airport is the other main airport.
Nevada is one of the few states that allows large trucks with three trailers.
Powering Nevada: Energy
Nevada has a growing solar energy industry. However, changes in state policy have affected the use of rooftop solar panels.
Yucca Mountain in Nevada was chosen as a possible site for storing the nation's nuclear waste.
Finding a Home: Affordable Housing
Nevada faces challenges with affordable housing. There are not enough affordable homes for people with lower incomes. Housing prices have gone up, but salaries have not kept pace. This means many renters pay a large part of their income for housing. Solutions are being explored to help more people find affordable places to live.
Learning in Nevada: Education
Education in Nevada happens through public and private schools. These include elementary, middle, and high schools. There are also many colleges and universities.
A law passed in 2015 helps families pay for private schools or tutoring. This gives more choices for education. About 86.9% of Nevadans have a high school degree.
Public Schools
Nevada has many public school districts. The Clark County School District is the fifth largest in the United States.
Colleges and Universities
Nevada has several colleges and universities, including:
- University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV)
- University of Nevada, Reno (UNR)
- Nevada State University (NSU)
- Community colleges like Truckee Meadows Community College and College of Southern Nevada
Fun and Games: Culture and Sports
Entertainment and Tourism
Nevada is famous for its resort areas. Las Vegas, Reno, Lake Tahoe, and Laughlin attract visitors from all over the world. In 2022, Nevada casinos made billions of dollars from gaming and other activities.
Nevada has more hotel rooms per person than any other U.S. state. It has one hotel room for every 14 residents!
Sports in Nevada
Nevada is home to several professional sports teams:
- Vegas Golden Knights (Ice Hockey - NHL)
- Las Vegas Raiders (Football - NFL)
- Las Vegas Aces (Women's Basketball - WNBA)
The Oakland Athletics baseball team also plans to move to Las Vegas.
College sports are also popular. The Nevada Wolf Pack (UNR) and UNLV Rebels (UNLV) are the state's main college teams. UNLV's men's basketball team was very famous in the late 1980s and early 1990s. They even won a national championship in 1990!
Las Vegas often hosts major boxing matches and mixed martial arts (MMA) events. The Las Vegas Motor Speedway hosts NASCAR races. Rodeo events are also popular, with the National Finals Rodeo held in Las Vegas.
Famous athletes from Nevada include tennis player Andre Agassi and baseball star Bryce Harper.
Nevada's Military Presence
Several U.S. Navy ships have been named USS Nevada to honor the state.
Area 51, a well-known U.S. Air Force facility, is located in Nevada. The state also has many military bases. These bases are used for training, including for unmanned aircraft and fighter pilots. The United States Air Force Thunderbirds flight demonstration team is based in Nevada.
See also
 In Spanish: Nevada para niños
In Spanish: Nevada para niños
 | Precious Adams |
 | Lauren Anderson |
 | Janet Collins |