Lake Tahoe facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Lake Tahoe |
|
|---|---|
| dáʔaw (Washo) | |

The south shore of Lake Tahoe in California, as seen from the west shore
|
|

Lake Tahoe from space
|
|
| Location | The Sierra Nevada of the U.S., along the state line of California and Nevada |
| Coordinates | 39°N 120°W / 39°N 120°W |
| Lake type | Ancient lake, Geologic block faulting |
| Primary outflows | Truckee River |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Max. length | 22 mi (35 km) |
| Max. width | 12 mi (19 km) |
| Surface area | 191 sq mi (490 km2): Placer County (41%) El Dorado County (29%) Douglas County (13%) Washoe County (11%) Carson City (6%) |
| Average depth | 1,000 ft (300 m) |
| Max. depth | 1,645 ft (501 m) |
| Water volume | 36 cu mi (150 km3; 120,000,000 acre⋅ft) |
| Residence time | 650 years |
| Shore length1 | 71 mi (114 km) |
| Surface elevation | 6,225 ft (1,897 m) |
| Frozen | Rarely, in Emerald Bay |
| Islands | Fannette Island |
| Settlements | Incline Village, NV South Lake Tahoe, CA Stateline, NV Tahoe City, CA Kings Beach, CA Truckee, CA |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
Lake Tahoe is a large freshwater lake nestled in the Sierra Nevada mountains of the Western United States. It sits right on the border between California and Nevada.
At about 6,225 ft (1,897 m) above sea level, Lake Tahoe is the highest and largest alpine lake in North America. It holds a huge amount of water, making it the second largest by volume in the United States, after the five Great Lakes. The lake is also incredibly deep, reaching 1,645 ft (501 m). This makes it the second deepest lake in the U.S., only surpassed by Crater Lake in Oregon.
Lake Tahoe was formed around two million years ago. Its clear blue water and the stunning mountains all around it are famous. Many people simply call the area "Tahoe." The name "Tahoe" comes from the Washo word dáʔaw, which means 'the lake'. Most of the land around the lake is national forest, managed by the United States Forest Service.
This beautiful lake is a popular spot for tourists in both Nevada and California. People come for winter sports like skiing, summer outdoor fun, and to enjoy the scenery all year long. Ski resorts are a big part of the local economy. The Nevada side also has several casino resorts, and roads make it easy to visit the area any time.
Contents
The Name of Lake Tahoe
The name "Lake Tahoe" comes from the Washo word dáʔaw. This word means 'the lake'. For the Washo people, Lake Tahoe was very important, so they often just called it "the lake" without adding other words.
Exploring Lake Tahoe's Geography
Lake Tahoe is the second deepest lake in the U.S. Its deepest point is 1,645 feet (501 m). It is about 22 mi (35 km) long and 12 mi (19 km) wide. The shoreline stretches for about 72 mi (116 km). The lake is so big that its surface actually looks curved because of the Earth's shape!
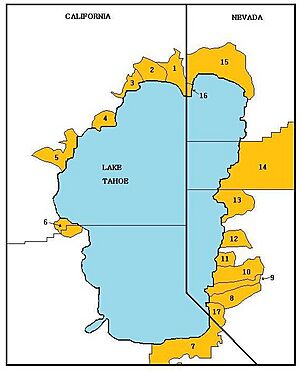
About two-thirds of the lake's shoreline is in California. The biggest city on the lake, South Lake Tahoe, California, is on the south shore. It is next to Stateline, Nevada. On the northwest shore, you'll find Tahoe City, California. Other towns like Kings Beach, California and Incline Village, Nevada are on the north shore. Many parts of the shoreline are protected as state parks or by the United States Forest Service.
The Lake Tahoe Watershed is the land area that drains water into the lake. It covers about 505 sq mi (1,310 km2). Lake Tahoe gets its water from 63 smaller streams and from rain and snow falling directly on its surface.
The Truckee River is the only river that flows out of Lake Tahoe. It travels northeast through Reno, Nevada, and ends in Pyramid Lake. About one-third of the water leaves through the Truckee River, while the rest evaporates from the lake's surface. A dam called Lake Tahoe Dam controls the flow of the Truckee River and the lake's water level.
Lake Tahoe's Natural History
How Lake Tahoe Was Formed
The Lake Tahoe Basin was created by huge movements in the Earth's crust. Blocks of land were pushed up to form the Carson Range mountains to the east and the Sierra Nevada mountains to the west. The land in between dropped down, forming the basin where Lake Tahoe now sits. This process happened over millions of years.
Some of the highest mountains around Lake Tahoe were formed during this time. These include Freel Peak (10,891 ft (3,320 m)), Monument Peak (10,067 ft (3,068 m)), and Mount Tallac (9,735 ft (2,967 m)).
Long ago, a volcano called Mount Pluto erupted and created a natural dam on the north side of the basin. Then, melting snow filled the lowest part of the basin, forming the first version of Lake Tahoe. Over time, more rain and runoff added to its waters.
During the Ice Ages, huge glaciers carved out many of the beautiful canyons and lakes nearby, like Emerald Bay and Fallen Leaf Lake. Lake Tahoe itself was never covered by glaciers, but its water was held in place by ancient volcanic rock.
Scientists believe that strong earthquakes along the faults under Lake Tahoe could cause large tsunamis. These waves could be as high as 10 to 33 ft (3.0 to 10.1 m) and cross the lake in just a few minutes.
Lake Tahoe's Climate
Lake Tahoe has a climate with warm, dry summers and cold winters that get a lot of snow. Most of the rain and snow falls between November and April. Heavy snowmelt in late spring and early summer can cause floods. Sometimes, summer storms from the Great Basin bring strong rainfall, especially to the higher mountains.
August is usually the warmest month, with average high temperatures around 78.7 °F (25.9 °C). January is the coldest, with average high temperatures around 41.0 °F (5.0 °C). It can get very cold, with temperatures sometimes dropping below 0 °F (−18 °C). Freezing temperatures can happen in any month of the year.
| Climate data for Tahoe City, California (Elevation 6,230 ft; 1,900 m) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 59 (15) |
60 (16) |
67 (19) |
74 (23) |
89 (32) |
90 (32) |
99 (37) |
94 (34) |
87 (31) |
80 (27) |
70 (21) |
60 (16) |
99 (37) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 38.6 (3.7) |
40.3 (4.6) |
44.0 (6.7) |
50.4 (10.2) |
59.6 (15.3) |
68.7 (20.4) |
77.9 (25.5) |
77.2 (25.1) |
69.8 (21.0) |
58.8 (14.9) |
46.9 (8.3) |
40.3 (4.6) |
56.0 (13.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 19.1 (−7.2) |
19.9 (−6.7) |
22.8 (−5.1) |
26.9 (−2.8) |
32.8 (0.4) |
38.6 (3.7) |
44.4 (6.9) |
43.7 (6.5) |
39.0 (3.9) |
32.3 (0.2) |
25.8 (−3.4) |
20.8 (−6.2) |
30.5 (−0.8) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −14 (−26) |
−15 (−26) |
−6 (−21) |
5 (−15) |
9 (−13) |
24 (−4) |
22 (−6) |
28 (−2) |
21 (−6) |
9 (−13) |
1 (−17) |
−16 (−27) |
−16 (−27) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 5.97 (152) |
5.29 (134) |
4.12 (105) |
2.14 (54) |
1.20 (30) |
0.65 (17) |
0.26 (6.6) |
0.30 (7.6) |
0.59 (15) |
1.82 (46) |
3.57 (91) |
5.55 (141) |
31.47 (799) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 45.9 (117) |
36.5 (93) |
35.2 (89) |
15.9 (40) |
3.7 (9.4) |
0.2 (0.51) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0.3 (0.76) |
2.4 (6.1) |
15.5 (39) |
35.2 (89) |
190.7 (484) |
| Source: The Western Regional Climate Center | |||||||||||||
Plants and Animals of Lake Tahoe
The forests around Lake Tahoe are mostly made up of different types of pine and fir trees. You can also find wet meadows, brushy areas, and rocky spots, especially higher up. A special plant called Lake Tahoe yellowcress grows only on the wet sandy beaches of Lake Tahoe.

Native fish in the lake include the Lahontan cutthroat trout and mountain whitefish. However, many of these fish populations have decreased because new types of fish, Asian clams, and mysid shrimp were introduced to the lake. These new species competed with the native ones. Efforts to bring back the cutthroat trout began in 2019.
Some of the fish that were introduced to the lake include lake trout, rainbow trout, and sockeye salmon. Every autumn, from late September to mid-October, sockeye salmon turn a bright red color and swim up Taylor Creek to lay their eggs. After laying eggs, they die, providing food for animals like mink, bears, and bald eagles.
North American beavers were brought back to the Tahoe Basin between 1934 and 1949. Today, you can see beavers in places like Taylor Creek and Kings Beach. Beaver dams help keep the water clean by trapping nutrients and sediments.
Because Lake Tahoe is so cold and deep, things that sink to the bottom break down very slowly. For example, a diver's body was found almost perfectly preserved 300 ft (91 m) deep, 17 years after he disappeared.
Lake Tahoe's Human History
Native Peoples and Early Explorers
The Washoe Native Americans lived around Lake Tahoe for thousands of years. The lake was the heart of their territory. Cave Rock, a large rock formation on the southeastern shore, is a sacred site for the Washoe. They called it deʔek wadapush, meaning 'Standing Gray Rock'.
The first European-American to see Lake Tahoe was Lt. John C. Frémont in 1844. He named it "Lake Bonpland," but that name didn't stick. Over the years, it was called "Lake Bigler" after California's governor. However, during the American Civil War, many people didn't like the governor's name on the lake because of his political views.
In 1862, a mapmaker named William Henry Knight and a colleague suggested the name "Tahoe." They believed it meant "water in a high place" in the local tribal language. Even though some people, like Mark Twain, didn't like the new name at first, "Lake Tahoe" eventually became the official name in 1945.
Mining and Transportation
When gold was discovered in California in 1848, many gold seekers passed near Lake Tahoe. Later, in 1858, silver was found nearby in Nevada. For many years, trees from the Tahoe basin were cut down to support the underground mines. This logging was so extensive that almost all the native forests were cut.
Lake Tahoe became a busy place for transportation. Steamboats carried mail and supplies around the lake. The famous steamboat Tahoe, launched in 1896, was a fast and important vessel for passengers and mail. As cars became more common, many of the steamboats were retired.
Modern Development and Protection
In the early 1900s, Lake Tahoe was mostly a place for a few vacation homes. After World War II, more people moved to the area. Gambling casinos were built on the Nevada side in the 1950s, and new highways were built for the 1960 Winter Olympics held nearby. This led to a big increase in buildings and people around the lake.
To protect the lake, the U.S. Congress and the California and Nevada governments created the Tahoe Regional Planning Agency (TRPA) in 1969. This agency helps manage land use to protect the environment of the Lake Tahoe Basin.
Environmental Challenges
Keeping Lake Tahoe's Water Clear

Lake Tahoe is known for its incredibly clear water. However, over the years, the water has become less clear. This is mainly due to tiny particles and algae from things like urban stormwater runoff. Scientists are working to reduce these pollutants to bring back the lake's historic clarity.
Lake Tahoe never completely freezes over because it is so deep and large. The water temperature has been slowly rising over the years, which might affect how the lake mixes and its clarity.
Changes in the Lake's Ecosystem
Since the 1960s, the types of plants and animals in Lake Tahoe have changed. For example, opossum shrimp were introduced to feed salmon, but they also ate tiny creatures called cladocerans, which are important food for young fish.
Recently, goldfish have been seen growing to large sizes in the lake. These are an invasive species, likely from pets that were released into the water.
The Lake Tahoe area also faces the risk of wildfires. In 2007, the Angora Fire burned a large area near South Lake Tahoe. Scientists are studying how these fires and the ash they produce might affect the lake's ecosystem.
To protect Lake Tahoe, organizations like the League to Save Lake Tahoe (Keep Tahoe Blue) work to monitor the lake and oppose harmful development projects. Researchers at the UC Davis Tahoe Environmental Research Center also study the lake and share information to help protect it. In 2019, tiny pieces of plastic, called Microplastics, were found in Lake Tahoe. This pollution is a growing concern for the lake's health.
Fun Things to Do at Lake Tahoe

Lake Tahoe is a huge tourist spot with many restaurants, ski slopes, golf courses, and casinos. The Nevada side of the lake offers more casinos because gambling is legal there.
Winter Sports Fun
In winter, thousands of people come to Lake Tahoe for downhill skiing. The area is known for its beautiful scenery and heavy snowfalls.
Lake Tahoe has 15 ski areas! Some of the most popular include:
- Heavenly Mountain Resort: A big resort near Stateline.
- Palisades Tahoe: A large resort that hosted the 1960 Winter Olympics.
- Northstar California: Known for its great terrain park.
- Kirkwood Mountain Resort: Often gets the most snow in the region.
You can also find places for sledding, snow tubing, cross-country skiing, snowmobile riding, and snowshoeing around Tahoe.
Summer Water Sports
From late spring to early fall, the lake is perfect for water sports and beach activities. Popular towns for tourists include South Lake Tahoe and Stateline, as well as Tahoe City and Kings Beach.
You can go parasailing, rent jet skis, or try eco-friendly paddle sports like kayaking and stand-up paddleboarding. Boating is also very popular, and the lake hosts a famous wooden boat show every August. The United States Coast Guard even has a station on Lake Tahoe!
SCUBA diving is also popular, but it's considered advanced because of the high altitude, which means divers need to be careful about decompression sickness.
Motorcycling Adventures
The roads around Lake Tahoe are great for motorcyclists. A popular route goes all the way around the lake, offering amazing views. Some scenic stops include Emerald Bay, Zephyr Cove, and Sand Harbor.
Hiking and Biking Trails
There are many trails for hiking and mountain biking around the lake. The most famous is the Tahoe Rim Trail, a 165 miles (266 km) path that circles the entire lake. You can also explore the Granite Chief Wilderness and the Desolation Wilderness for hiking and camping. The Flume Trail is a favorite for mountain bikers. There are also paved paths for bicycling in many communities.
Gambling Fun

Gambling is legal on the Nevada side of Lake Tahoe. You can find casinos with slot machines and table games in Stateline, Nevada, Crystal Bay, and Incline Village. The first casino at the lake, the Cal-Neva, opened in 1926. Famous singer Frank Sinatra even owned it in the 1960s!
Getting to Lake Tahoe
You can reach Lake Tahoe by car or bus. The closest train station is in Truckee, served by Amtrak's California Zephyr train. There are also bus connections from Sacramento. The nearest major airport is Reno-Tahoe International Airport (RNO).
Highways Around the Lake
It takes about two hours to drive to Lake Tahoe from Sacramento, one hour from Reno, or thirty minutes from Carson City. In winter, you often need snow tires or chains on your car.
California State Route 89 follows the western shore, connecting parks and towns like Emerald Bay State Park and Tahoe City. California State Route 28 and Nevada State Route 28 complete the loop around the northern and eastern shores.
Major Airports Nearby
- Reno-Tahoe International Airport (Reno, Nevada)
- Sacramento International Airport (Sacramento, California)
- Lake Tahoe Airport (South Lake Tahoe, California)
- Truckee-Tahoe Airport (Truckee, California)
Communities Around Lake Tahoe
California
|
Nevada
|
Lake Tahoe's Legends and Stories
Lake Tahoe is home to many interesting legends. These stories have been passed down by the local Native American tribes and other people.
Water Babies
In Washoe tradition, Water Babies are powerful spirits that live in bodies of water, including Lake Tahoe. They were believed to be able to cause harm. Washoe healers would visit sacred places like Cave Rock to ask the Water Babies for help, bringing gifts to gain their favor.
The Ong
The Ong is a creature from Washoe legend, described as a huge bird that lived in Lake Tahoe. It was said to hunt animals and even people. One story tells how a young man named Tahoe escaped the Ong by feeding it poisoned arrowheads. The bird was believed to have died and sunk into the lake.
Tahoe Tessie
Tahoe Tessie is a mysterious creature said to live in Lake Tahoe. Descriptions of Tessie are similar to other lake monsters, like the Loch Ness Monster. Many people think it might be a very large aquatic animal, possibly a type of sturgeon.
Ghosts of Fannette Island
Fannette Island in Emerald Bay is rumored to be haunted by the ghost of Captain Richard Barter. He lived on the island in the late 1800s and passed away while returning to the island in 1873. Some local stories say his ghost can still be seen wandering the island.
Lake Tahoe in Movies and Music
The TV show Bonanza used to film its opening scenes on the Nevada side of Lake Tahoe, with Mount Tallac in the background.
The 1974 movie The Godfather Part II filmed several scenes at a lakeside estate called Fleur de Lac. This estate was once owned by Henry Kaiser and is now a private community.
The 2014 movie Last Weekend was filmed at a lakefront home on the west shore. This house was also used for the exteriors in the 1951 movie A Place in the Sun, starring Elizabeth Taylor.
The British rock band A has a song called "Here We Go Again (I Love Lake Tahoe)" about their love for the lake. The band Pavement also mentions the lake in their song "Unfair."
Singer Kate Bush has a song called "Lake Tahoe" where a woman who drowned in the lake is reunited with her dog.
See also
 In Spanish: Lago Tahoe para niños
In Spanish: Lago Tahoe para niños
 | Shirley Ann Jackson |
 | Garett Morgan |
 | J. Ernest Wilkins Jr. |
 | Elijah McCoy |