Clear Lake (California) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Clear Lake |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
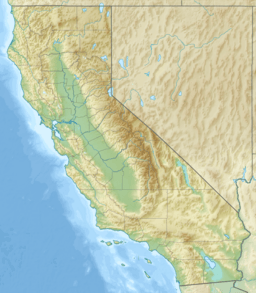
| Location | Lake County, California |
| Coordinates | 39°03′42″N 122°49′38″W / 39.0616°N 122.8272°W |
| Lake type | Eutrophic/hypereutrophic |
| Primary inflows | Scotts Creek Middle Creek Forbes Creek Morrison Creek Seigler Canyon Creek Shindler Creek Kelsey Creek Adobe Creek Manning Creek |
| Primary outflows | Cache Creek |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Max. length | 19 mi (31 km) |
| Max. width | 8 mi (13 km) |
| Surface area | 68 sq mi (180 km2) |
| Average depth | 27 ft (8.2 m) |
| Max. depth | 60 ft (18 m) |
| Water volume | 1,155,000 acre⋅ft (1,425,000 dam3) |
| Shore length1 | 100 mi (160 km) |
| Surface elevation | 1,329 ft (405 m) |
| Islands | Anderson Island Fruit Island Garner Island Indian Island Rattlesnake Island Slater Island Stubbs Island Tule Island Weekend Island |
| Settlements | Clearlake, California Clearlake Oaks, California Finley, California Glenhaven, California Kelseyville, California Lakeport, California Lower Lake, California Lucerne, California Middletown, California Nice, California Upper Lake, California |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
Clear Lake is a large natural freshwater lake in Lake County, California. It's located north of Napa County and San Francisco. This lake is special because it's the biggest natural freshwater lake completely within California. It covers about 68 square miles (180 km2) of water.
Clear Lake is also incredibly old, at about 2.5 million years! This makes it the oldest lake in North America. It has been a lake in this spot for a very long time.
People call Clear Lake the "Bass Capital of the West." It's home to many fish like largemouth bass, crappie, bluegill, carp, and catfish. Most fish caught here are largemouth bass, with some weighing over 17.52 pounds (7.95 kg). Besides fish, many animals live around Clear Lake. You can see ducks, pelicans, eagles, deer, bears, and raccoons.
The lake's large, warm waters are perfect for watersports. Popular activities include swimming, water skiing, wakeboarding, sailing, and jet skiing.
It's important to know that the California Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment has a safety advisory for fish caught in Clear Lake. This is because of higher levels of mercury found in some fish.
Contents
Clear Lake's Amazing History and Geology
Clear Lake is about 19 mi (31 km) long and 8 mi (13 km) wide. Its surface area is about 43,785 acres (17,719 ha). The lake's average depth is 27 ft (8.2 m), but it can get as deep as 60 ft (18 m). The water temperature is usually around 40 °F (4 °C) in winter and 76 °F (24 °C) in summer.
How Clear Lake Stays Deep
Scientists believe Clear Lake is one of the oldest lakes in North America. It sits on a huge rock block that slowly tilts north. As the lake fills with sediment (like dirt and sand), the tilting helps keep the water at about the same depth. Studies of the lake's sediments show it's at least 480,000 years old. Some experts think Mono Lake might be older, but Clear Lake's history is more continuous.
Volcanoes and Lake Changes
Long ago, Clear Lake was even bigger and included the Blue Lakes nearby. But volcano eruptions and landslides changed the land. This separated Clear Lake from the Blue Lakes and stopped its water from flowing into the Russian River.
Clear Lake is part of the Clear Lake Volcanic Field. This area has The Geysers, which uses steam from the earth to make electricity. There are many small faults (cracks in the earth) and volcanoes around the lake. The biggest volcano is Mount Konocti, right in the middle of the lake's south shore. Even though there haven't been eruptions for thousands of years, scientists watch for signs that could mean future activity.
Weather Around Clear Lake
The weather around Clear Lake can change a lot. In summer, temperatures can go over 92 °F (33 °C). In winter, they can drop below freezing, around 32 °F (0 °C).
Sometimes, there are summer thunderstorms, but they are not very common. Snow can fall near the lake, but it usually doesn't stay long. However, snow on the mountains around the lake is common. The wettest months are December and January, with a good amount of rain.
Fun Activities and Recreation
With over 100 miles (160 km) of shoreline, Clear Lake is a great place for water sports. Fishing, swimming, sailing, windsurfing, waterskiing, boating, and riding personal water craft are all popular, especially in summer.
Fishing in the "Bass Capital"
Clear Lake is famous as the "Bass Capital of the West." The California Department of Fish and Wildlife helps keep the lake stocked with fish like largemouth bass, crappie, catfish, bluegill, and rainbow trout. You can rent Fishing boats and find many stores selling fishing gear. Lots of fishing tournaments happen here all year. Bassmaster Magazine even ranked Clear Lake as the #3 best bass lake in the U.S. and #1 on the West Coast in 2016!
Other Fun Things to Do
There are 11 free boat launch ramps around the lake for public use. You can also rent boats and jet skis from local businesses. The area also has many wineries where adults can taste wine.
Protecting the Lake
Boaters coming to Lake County are warned about tiny creatures called quagga and zebra mussels. These invasive mussels can harm Clear Lake. Boats must be inspected before launching to prevent their spread. Signs also warn boaters not to spread a plant called hydrilla in the county's waters. Efforts have largely controlled hydrilla in Clear Lake.
The lake also hosts an annual "splash-in," which is the oldest and largest gathering of seaplanes in the Western U.S.
Wildlife and Plants Around Clear Lake
The Clear Lake area is a home for many different animals and plants.
Amazing Animals
You can see lots of waterfowl here, like mallards, western grebes, geese, ospreys, and mergansers. On land, there are Wild turkeys, blacktail deer, gray squirrels, raccoons, and river otters. Sometimes, you might even spot a mountain lion or a ringtail. Many different birds, reptiles, and amphibians also live here, including red-tailed hawks, garter snakes, and bullfrogs.
The endangered northern spotted owl is occasionally seen. A special type of deer called tule elk has also been brought back to the area. A large group of bald eagles lives in the Cache Creek canyon.
Fish and Plants in the Lake
The lake has native fish like the Clear Lake hitch. It also has fish like channel catfish and Florida strain largemouth bass that were put there for fishing. Along the shore, you'll find plants like tule, cattail, willow, and cottonwood.
The streams that flow into Clear Lake have fish like Sacramento pikeminnow and rainbow trout. Pacific lamprey are also found in Kelsey Creek.
The Clear Lake Gnat
Clear Lake is known for a tiny insect called the Clear Lake gnat. It's a "phantom midge" because its larvae are clear and hard to see. It looks like a tiny mosquito but doesn't bite. Before pesticides were used in the 1940s, there were so many gnats that they formed huge piles under streetlights. People even had to clean their car windshields every 1⁄4 mile (0.40 km) because of the gnats!
Now, the gnat population is much lower. This is thanks to two types of fish, the threadfin shad and the inland silverside, which eat the same food as the gnats.
Forests Around the Lake
The mountains around Clear Lake are covered with thick forests. You'll see trees like blue oak, valley oak, pacific madrone, and chaparral shrubs. Some areas have Douglas fir trees. These rugged forests have helped keep the area natural and undeveloped.
Clear Lake's Past
Archaeologists believe that Native Americans have lived around Clear Lake for at least 11,000 years. The lake provided plenty of fish, game, and birds, making it a great place to live. The native Clear Lake Hitch fish were once so many that millions would fill the streams. When Spanish missionaries arrived, thousands of Native Americans, mainly Pomo, Yuki, and Wappo people, lived here.
Early Settlers and Challenges
European settlers began arriving around 1845. Sadly, they often treated the native Pomo people unfairly. One sad event was the Bloody Island massacre in 1850. After some Pomo people were mistreated, they fought back. A United States Army group then attacked a Pomo group on an island in Clear Lake. Many Pomo people, including women and children, lost their lives. Today, a historical marker for Bloody Island is on Highway 20.
Later, the Pomo people were forced to live on small "rancherias" (reservations) and faced poverty for many years. Today, some of the fastest-growing businesses in Lake County are the casinos run by four Pomo rancherias.
Clear Lake in World War II
During World War II and the early Cold War, Clear Lake was used as a seaplane base. Large Flying boats could land on Clear Lake when it was too dangerous to land in San Francisco Bay.
Learning About History
You can learn more about the region's history and culture at Clear Lake State Park and Anderson Marsh State Historic Park. Lake County also has two museums: the Lake County Museum in Lakeport and the Lower Lake Historical Schoolhouse Museum in Lower Lake.
How Clear Lake's Water is Managed
The Clear Lake area, called a drainage basin, is quite large. It covers about 458 square miles (1,190 km2). The lake itself has three main parts: the Upper Arm, the Oaks Arm, and the Lower Arm. Cache Creek is the only river that flows out of the lake.
Water Levels and Flooding
The lake's water level is carefully watched. Long ago, a rocky spot in Cache Creek, called the "Grigsby Riffle," controlled the water flow. In 1872, a man named DeWitt Clinton Rumsey set up a gauge to record the water level. "Zero feet Rumsey" is the level when water stops flowing over the riffle. The lake level can go below zero due to evaporation and water being pumped out. The highest recorded level was 13.66 feet (4.16 m) in 1890, and the lowest was −3.50 feet (−107 cm) in 1920.
Because water flows into the lake quickly but flows out slowly, low-lying areas like downtown Clearlake often experience flooding.
Water Rights and Use
Yolo County has rights to use water from Cache Creek. In 1912, they built the Cache Creek dam. Water companies that use the lake's water pay Yolo County for it. Rules are in place to keep the lake level from getting too high or too low. For example, Yolo County can draw a certain amount of water if the lake is "full" on May 1st. To help with water needs, the Indian Valley Reservoir was built in 1975 and is controlled by Yolo County.
Some areas at the north end of Clear Lake were blocked off with levees (walls) between 1900 and 1940 to create farmland. Now, there's a project to remove these levees and bring back about 1,650 acres (670 ha) of lake and wetlands. This will make Bloody Island an island again! It will also provide more water for local towns.
The goal of managing the lake's water level is to prevent flooding, provide water for Yolo County and local towns, and keep enough water for fun activities. Also, sewage from many Lake County towns is now pumped away from the lake to a geothermal plant.
In 2014, the lake level dropped to −0.31 feet (−9.4 cm) on the Rumsey gauge, which was the lowest since a drought in 1977. When full, the lake is at 7.56 feet (230 cm).
Environmental Challenges and Solutions
Clear Lake faces several environmental challenges, but many groups are working to protect it.
Farming and Wetlands
The Clear Lake area has both freshwater marshes and vernal pools (seasonal ponds). These wetlands are important habitats for fish and wildlife. They also help filter out dirt and pollution from streams before they reach the lake. Sadly, about 79% of Clear Lake's historic wetlands have been lost due to farming and city growth.
Farming has been a big part of the area since the mid-1800s. It can lead to more sedimentation (dirt filling the lake) and pollution from fertilizers and pesticides. For example, high levels of nitrate have been found in the Big Valley area. Farming also uses a lot of water, which can cause streams to dry up early.
Pesticides and Their Impact
In the past, chemicals were used to control the Clear Lake gnats. In the 1940s, a pesticide called DDD was used. It helped with the gnats but had terrible effects on wildlife, especially western grebes, which died from high levels of DDD. Later, other pesticides were used more carefully. Now, the gnat population is controlled by certain fish species that eat the gnats' food.
Invasive Species
Invasive species are plants and animals that are not native to the lake and can cause problems. Hydrilla is an invasive water plant that can take over and harm fish and boating. The California Department of Food and Agriculture has a program to remove hydrilla and prevent its spread, and it has been very successful. The lake is also watched for quagga and zebra mussels, which are also harmful invasive species.
Harmful Algal Blooms
Clear Lake is naturally rich in nutrients, which can lead to Cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) blooms. These blooms often start in spring and last through fall. They can create thick mats of scum and cause bad smells. Studies show that too many nutrients, especially phosphorus from fertilizers, can make these blooms worse. These blooms can produce toxins that might affect health. Scientists are studying what causes these blooms.
Mercury Contamination
The lake has a lot of mercury from the nearby Sulphur Bank Mine. This abandoned mine was declared a Superfund site in the 1990s and is still being cleaned up. Because of methylmercury in the lake sediments, the California Department of Fish and Wildlife suggests that women of child-bearing age and children should not eat certain fish from Clear Lake.
Monitoring and Restoration Efforts
Clear Lake is listed as an "impaired water body" under the Clean Water Act. This means it doesn't meet water quality standards. Because of this, strategies like Total Maximum Daily Loads (TMDLs) are used to manage pollution. Many groups, including government agencies and local communities, are working together to reduce pollution from various sources.
The Middle Creek Project started in 1995 to bring back native wetlands around Clear Lake. The goal is to double the size of the wetlands. Lake County also has rules to prevent the loss of wetland plants on private property.
In 2009, a law called Assembly Bill 74 was signed. It provides money to remove levees and restore 1,650 acres (670 ha) of lake and wetlands. This project also aims to reduce phosphorus entering the lake by 40%.
A special Blue Ribbon Committee for the Rehabilitation of Clear Lake was created. It includes members from tribes, universities, and government groups. They give scientific advice on how to manage the lake's "economy, ecosystem, and heritage."
A Cyanobacteria Task Force was formed in 2014. It includes local tribes and government agencies. They focus on monitoring the lake and testing for toxins. Local rules also help protect the lake from land use practices in nearby towns.
Lake County is also part of the State Department of Water Resources' Integrated Regional Water Management programs. They work with other counties to manage water long-term. The Lake County Watershed Protection District helps with clean water programs and managing stormwater to prevent pollution. They also manage aquatic plants in the lake using special permits. All these efforts help protect Clear Lake's natural resources.
Images for kids