Lake County, California facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Lake County, California
|
||
|---|---|---|
| County of Lake | ||

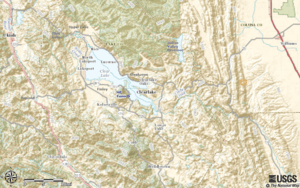
Clear Lake, the dominant geographic feature in Lake County
|
||
|
||
Location in the state of California
|
||
| Country | United States | |
| State | California | |
| Incorporated | May 20, 1861 | |
| Named for | Clear Lake | |
| County seat | Lakeport | |
| Largest city | Clearlake | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | Council–CAO | |
| • Body | Board of Supervisors | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 1,329 sq mi (3,440 km2) | |
| • Land | 1,256 sq mi (3,250 km2) | |
| • Water | 73 sq mi (190 km2) | |
| Highest elevation | 7,059 ft (2,152 m) | |
| Population | ||
| • Total | 68,163 | |
| • Density | 54/sq mi (21/km2) | |
| GDP | ||
| • Total | .274 billion (2022) | |
| Time zone | UTC−8 (Pacific Standard Time) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−7 (Pacific Daylight Time) | |
| Area code | 707 | |
| FIPS code | 06-033 | |
| GNIS feature ID | 277281 | |
| Congressional district | 4th | |
| Website | https://www.lakecountyca.gov/ | |
Lake County is a county in the north-central part of California. In 2020, about 68,163 people lived here. The main town is Lakeport. The county is named after Clear Lake. This lake is the biggest natural lake completely inside California.
Lake County is just north of the San Francisco Bay Area. It is also part of California's famous Wine Country. This area includes Napa, Sonoma, and Mendocino counties. Lake County has many wine-growing areas and about 20 wineries.
Contents
History of Lake County
Lake County was created in 1861. It was formed from parts of Napa and Mendocino counties. People from Europe and America had started settling here in the 1840s. Lake County has always been known for its farming.
In the early 1900s, the main crops were pears and beans. Farmers also grew grain, alfalfa, hay, prunes, peaches, apples, grapes, and walnuts. They also raised goats, hogs, turkeys, and dairy cows.
Some vineyards were planted in the 1870s. The area became famous for its great wines. But in 1920, a law called Prohibition stopped all wine making. Most vineyards were replaced with walnut and pear farms.
Geography and Nature
Lake County covers about 1,329 square miles. Most of this is land, and 73 square miles are water. The county has two main rivers: Cache Creek and Putah Creek. Both flow into the Sacramento River.
Clear Lake is thought to be the oldest lake in North America. This is because of a special geological feature. The lake sits on a large rock block that slowly tilts north. As the lake fills with sediment, it stays at about the same depth.
The land in the county is very interesting. It has many small faults and old volcanoes. The biggest volcano is Cobb Mountain. Other important lakes are Blue Lakes, Lake Pillsbury, and Indian Valley Reservoir.
Lake County is home to many special plants and animals. These include rare herbs and the tule elk. You can also find many waterfowl, bears, and other wildlife around Clear Lake.
Lake County is the only county in California that has never had a railroad line. This is because of its hilly land.
Protected Natural Areas
Lake County has several protected natural areas. These help keep the environment safe.
National Protected Areas
- Mendocino National Forest (part of it)
- Cow Mountain Recreation Area
- Cache Creek Wilderness and Cache Creek Wildlife Area
In 2015, President Barack Obama created the Berryessa Snow Mountain National Monument. This monument includes these and other areas.
State Protected Areas
- Boggs Mountain Demonstration State Forest
- Anderson Marsh State Historic Park
- Loch Lomond Vernal Pool Ecological Reserve
- Boggs Lake Ecological Reserve
- Clear Lake State Park
- Rodman Slough Preserve
Mineral Springs and Resorts
In the late 1800s, mineral water became very popular. People believed it could help with many health problems. Because of this, mineral resorts grew around Clear Lake.
- Bartlett hot springs were found in 1870. They became a resort and bottled mineral water.
- Harbin Hot Springs was built in the 1860s. Sadly, it burned down in the Valley Fire of 2015.
- Highland Springs opened in 1891. It had a nice dining room and a large hotel. It was destroyed by fire in 1945.
- Saratoga Springs Resort opened in 1873. It grew to hold 350 guests.
- Witter Springs Resort opened in 1873 with a hotel and cottages.
Climate and Weather
Lake County has a mediterranean climate. This means it has hot summers. Daytime temperatures in lower areas can be very warm. But nighttime temperatures stay cool all year. This helps to make the summer heat more bearable.
| Climate data for Clearlake, California (1981–2010 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 76 (24) |
81 (27) |
84 (29) |
94 (34) |
101 (38) |
114 (46) |
113 (45) |
112 (44) |
111 (44) |
104 (40) |
92 (33) |
78 (26) |
114 (46) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 55 (13) |
58 (14) |
62 (17) |
67 (19) |
75 (24) |
84 (29) |
92 (33) |
90 (32) |
85 (29) |
75 (24) |
62 (17) |
55 (13) |
72 (22) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 32 (0) |
34 (1) |
36 (2) |
39 (4) |
45 (7) |
51 (11) |
55 (13) |
53 (12) |
49 (9) |
42 (6) |
35 (2) |
32 (0) |
42 (6) |
| Record low °F (°C) | 8 (−13) |
16 (−9) |
17 (−8) |
23 (−5) |
28 (−2) |
34 (1) |
39 (4) |
40 (4) |
30 (−1) |
21 (−6) |
19 (−7) |
6 (−14) |
6 (−14) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 6.45 (164) |
5.91 (150) |
4.53 (115) |
1.73 (44) |
1.13 (29) |
.22 (5.6) |
.02 (0.51) |
.10 (2.5) |
.43 (11) |
1.44 (37) |
3.51 (89) |
5.95 (151) |
31.42 (798.61) |
People and Population
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1870 | 2,969 | — | |
| 1880 | 6,596 | 122.2% | |
| 1890 | 7,101 | 7.7% | |
| 1900 | 6,017 | −15.3% | |
| 1910 | 5,526 | −8.2% | |
| 1920 | 5,402 | −2.2% | |
| 1930 | 7,166 | 32.7% | |
| 1940 | 8,069 | 12.6% | |
| 1950 | 11,481 | 42.3% | |
| 1960 | 13,786 | 20.1% | |
| 1970 | 19,548 | 41.8% | |
| 1980 | 36,366 | 86.0% | |
| 1990 | 50,631 | 39.2% | |
| 2000 | 58,309 | 15.2% | |
| 2010 | 64,665 | 10.9% | |
| 2020 | 68,163 | 5.4% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 67,878 | 5.0% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790–1960 1900–1990 1990–2000 2010 2020 |
|||
In 2020, Lake County had a population of 68,163 people. Most people were White (64.85%). About 22.65% of the population was Hispanic or Latino.
The population is spread out. About 24.1% are under 18 years old. About 19.5% are 65 years or older. The average age in the county is 43 years.
The median income for a family in 2005 was about $55,818. About 4.6% of the population lived below the poverty line. This included 22.8% of those under 18.
Lake County has two main cities: Lakeport (the county seat) and Clearlake (the largest city). There are also many smaller communities.
Economy and Jobs
The biggest employers in Lake County are the healthcare industry and Native American casinos. Grocery stores, school districts, and the electricity company Calpine also provide many jobs. Calpine works at the Geysers geothermal field.
The county's economy mostly depends on agriculture. Farmers grow many crops.
Main Crops in Lake County
The main crops grown in Lake County in 2022 were:
| Crop | Production (tons) | Value | Bearing acres |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grapes (wine) | 45,637 | $84,756,086 | 10,987 |
| Pears | 16,371 | $16,286,443 | 1,375.5 |
| Walnuts | 262 | $239,959 | 3,485 |
| Nursery production | $624,085 | 16 | |
| Vegetables (misc.) | $287,078 | 9 | |
| ... (mixed light) | unknown | 7.6 | |
| ... (outdoor) | unknown | 178 |
Wine Industry
The first vineyards in Lake County were planted in the late 1800s. But Prohibition and the county being far away hurt the wine industry. The wine industry started to grow again in the 1970s.
Most of the grapes grown here are still sent to nearby Napa, Sonoma, and Mendocino counties. There, they are made into wine. The amount of land used for vineyards grew a lot. It went from less than 100 acres in 1965 to over 11,000 acres in 2023.
The region has nine special wine-growing areas. These include Guenoc Valley, High Valley, and the Red Hills. There are also about 20 wineries.
Transportation and Travel
Lake County has several main highways. These roads help people travel around the county and to other areas.
Major Highways
 State Route 20
State Route 20 State Route 29
State Route 29 State Route 53
State Route 53 State Route 175
State Route 175 State Route 281
State Route 281
There are also several numbered county roads.
Public Transportation
Lake Transit provides bus service around Clear Lake. Local buses serve Lakeport, Clearlake, and Lower Lake. You can also take buses to St. Helena and Ukiah. Some routes only run on weekdays. There is no service on Sundays or public holidays.
Airports
Lampson Field is the county's public airport. There is also a 4,000-foot airstrip in Gravelly Valley. This is north of Lake Pillsbury. The county also has some private airstrips.
Communities in Lake County
Lake County has two cities and many smaller communities.
Cities
Census-designated places (CDPs)
These are areas that are like towns but are not officially cities.
- Clearlake Oaks
- Clearlake Riviera
- Cobb
- Hidden Valley Lake
- Kelseyville
- Lower Lake
- Lucerne
- Middletown
- Nice
- North Lakeport
- Soda Bay
- Spring Valley
- Upper Lake
Unincorporated Communities
These are smaller places that are not part of any city or CDP.
Famous People from Lake County
- Michael Berryman, an American actor.
- Benjamin Dewell, an early settler and rancher.
- Ellis O. Knox, the first African American to earn a Ph.D. on the West Coast.
- Lillie Langtry, a British actress.
See also
 In Spanish: Condado de Lake (California) para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Lake (California) para niños
 | Percy Lavon Julian |
 | Katherine Johnson |
 | George Washington Carver |
 | Annie Easley |