Sediment facts for kids


Sediment is tiny bits of material that settle at the bottom of a liquid. Think of it like dirt or sand that falls to the bottom of a glass of water. In nature, sediment is found in oceans, lakes, and rivers.
Over a very long time, these tiny pieces can get pressed together. They can even turn into sedimentary rocks. Sediment can also be carried by wind or water and dropped on land. This material might also become rock later on. The study of how these rocks form is called sedimentology.
Contents
What is Sediment?
Sediment is made of small pieces of natural stuff. It can be bits of rocks, minerals, or even parts of dead plants and animals. These pieces are moved around by wind, water, or ice. When the wind or water slows down, the sediment settles. This settling process is called deposition.
How Sediment Forms Rocks
When layers of sediment pile up, they get squeezed. The weight from the top layers presses down on the bottom ones. Over millions of years, this pressure and natural "glue" (minerals in the water) turn the loose sediment into solid rock. This is how many common rocks like sandstone and limestone are made.
Types of Sediment
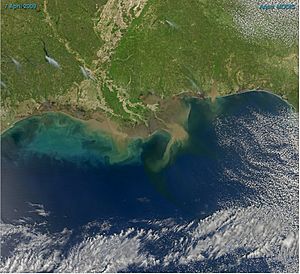

Scientists classify sediment in different ways. One way is by the size of its pieces. Another way is by what it's made of.
Sediment Size: From Clay to Boulders
Sediment pieces come in many sizes. They can be as tiny as dust or as big as a car! Scientists use a special scale to measure these sizes. It helps them understand how sediment moves and settles.
Here are some common sediment sizes:
| Size Name | How Big It Is |
|---|---|
| Boulder | Bigger than 256 millimeters (about 10 inches) |
| Cobble | 64 to 256 millimeters (about 2.5 to 10 inches) |
| Gravel | 2 to 64 millimeters (about 0.08 to 2.5 inches) |
| Sand | 0.0625 to 2 millimeters (about 0.0025 to 0.08 inches) |
| Silt | 0.0039 to 0.0625 millimeters (about 0.00015 to 0.0025 inches) |
| Clay | Smaller than 0.0039 millimeters (about 0.00015 inches) |
You can see that clay is the smallest, and boulders are the biggest!
What Sediment is Made Of
Sediment can be made of different things. It depends on where it came from.
- Rock type: It can be tiny pieces of the original rock it broke off from.
- Minerals: It might be made of specific minerals, like quartz or feldspar.
- Chemicals: Sometimes, sediment forms when chemicals in water combine.
For example, clay can mean two things. It can be a very small size of sediment. But it can also mean sediment made of special clay minerals.
Images for kids
-
Holocene eolianite and a carbonate beach on Long Island, Bahamas
See also
 In Spanish: Sedimento para niños
In Spanish: Sedimento para niños
 | Laphonza Butler |
 | Daisy Bates |
 | Elizabeth Piper Ensley |