Clear Lake Volcanic Field facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Clear Lake Volcanic Field |
|
|---|---|
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 4,724 ft (1,440 m) |
| Geography | |
| Location | Lake County, California, United States |
| Parent range | North Coast Ranges |
| Topo map | USGS Kelseyville |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | less than 2.1 million years |
| Mountain type | lava domes, cinder cones, maars within volcanic field |
| Last eruption | Holocene |
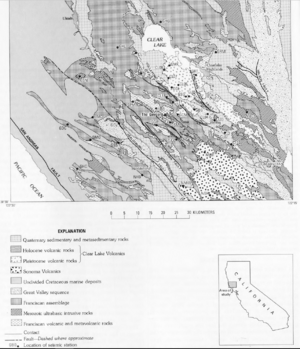
The Clear Lake Volcanic Field is a special area with many volcanoes. It is located next to Clear Lake in California. This field is part of the northern Coast Ranges.
This volcanic area has been active for a very long time. It started about 2.1 million years ago and continued until recently. You can find different types of volcanoes here. These include lava domes, cinder cones, and maars. The rocks that came out of these volcanoes vary. Some are dark, heavy basalt, while others are lighter, glassier rhyolite. The two tallest peaks in this volcanic field are Cobb Mountain (4,724 feet (1,440 m)) and Mount Konocti (4,285 feet (1,306 m)).
Contents
Discover the Clear Lake Volcanic Field
The Clear Lake Volcanic Field is a fascinating place. It shows us how Earth's forces shape our world. This field is a great example of an active volcanic area. It has been forming for millions of years.
What is a Volcanic Field?
A volcanic field is not just one big volcano. Instead, it is a region with many smaller volcanoes. These volcanoes share the same source of magma deep underground. In the Clear Lake field, you can see various volcanic features. These include domes, cones, and craters.
Types of Volcanoes You Can Find
- Lava Domes: These are round, steep-sided mounds. They form when thick, sticky lava slowly oozes out of a vent. It piles up around the opening.
- Cinder Cones: These are cone-shaped hills. They are built from small pieces of volcanic rock and ash. These pieces are called cinders. They erupt explosively and fall around the vent.
- Maars: These are broad, flat-bottomed craters. They form when magma heats groundwater. This creates a huge steam explosion. The explosion blasts a wide hole in the ground.
Power from Deep Inside the Earth
Deep under the Clear Lake Volcanic Field, there is a huge pocket of hot, melted rock. This is called a magma chamber. This intense heat powers a special area known as The Geysers.
The Geysers: A Geothermal Powerhouse
At The Geysers, you will find the biggest group of geothermal power plants in the world. These plants use the Earth's natural heat to make electricity. They tap into hot steam and water from deep underground. This steam spins turbines to create power.
How Much Power Does The Geysers Make?
The Geysers can produce a lot of electricity. It generates about 2,000 megawatts. This is enough power to supply two large cities. Imagine powering places the size of San Francisco just from Earth's heat! This makes the Clear Lake area very important for clean energy.
Minerals and the Volcanic Field
The heat from the Clear Lake volcanoes also played a role in forming valuable minerals. Hot water and steam moved through the rocks. This process is called hydrothermal activity.
Sulphur Bank Mine and Gold
This activity helped create mercury ores at the Sulphur Bank Mine. It also formed gold ore at the McLaughlin Mine. These mines show how volcanic heat can lead to rich mineral deposits.
Images for kids
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |


