Western United States facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Western United States
American West, Far West, the West
|
|
|---|---|
|
Left-right from top: Los Angeles skyline, the Grand Canyon, Yellowstone National Park, Boise skyline, Angel's Landing, Mt. Rainier, Seattle skyline
|
|
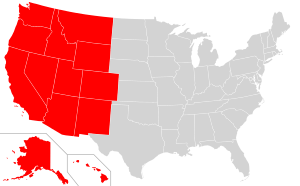
This map reflects the Western United States as defined by the Census Bureau. This region is divided into Mountain and Pacific areas.
|
|
| Subregions |
|
| Country | |
| States |
|
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,873,251.63 sq mi (4,851,699.4 km2) |
| • Land | 1,751,053.31 sq mi (4,535,207.3 km2) |
| Population
(2020)
|
|
| • Total | 78,588,572 |
| • Density | 41.9530248/sq mi (16.19815341/km2) |
| Demonym(s) | Westerner |
| GDP (nominal) | |
| • Total | $5.619 trillion (2019) |
| • per capita | $71,719 (2019) |
The Western United States is a large region in the United States. It is also known as the American West or the West. The United States Census Bureau defines it as one of the four main regions of the country.
Over time, the idea of "the West" has changed. Before the 1800s, the Appalachian Mountains were considered the western edge. As Americans moved further west, the land west of the Mississippi River became known as "the West."
Today, the U.S. Census Bureau includes 13 states in the Western region. These states stretch from the Rocky Mountains and the Great Basin all the way to the Pacific Coast. The state of Hawaii, located in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, is also part of this region. To the east, the West borders the Midwestern United States and the Southern United States. Canada is to the north, and Mexico is to the south.
The West has many different natural environments, called biomes. These include dry plateaus and plains, especially in the American Southwest. There are also forested mountains, like the Sierra Nevada, the Cascades, and the Rocky Mountains. The long coastline of the American Pacific Coast and the rainforests of the Pacific Northwest are also found here.
Contents
What is the Western United States?
The Western United States is the largest region in the country. It covers almost half of the land in the main part of the United States. It also has the most varied geography. You can find temperate rainforests in the Northwest, and the highest mountain ranges, including the Rocky Mountains, the Sierra Nevada, and the Cascade Range. There are also many glaciers and the western edge of the Great Plains.
The West also contains most of the desert areas in the United States. The Mojave and the Great Basin deserts are entirely within the West. Parts of the Sonoran and Chihuahuan deserts are also here. Because of its huge and varied geography, it's hard to define the region exactly.
Subregions of the West
The U.S. Census Bureau divides the Western region into two smaller parts:
- Mountain states: These include Montana, Wyoming, Colorado, New Mexico, Idaho, Utah, Arizona, and Nevada.
- Pacific states: These are Washington, Oregon, California, Alaska, and Hawaii.
Other ways to divide the West include the Southwest and Northwest. Arizona, New Mexico, and parts of Texas are usually seen as the Southwest. Montana, Idaho, Oregon, and Washington are often considered part of the Northwest.
The term West Coast usually refers to California, Oregon, Washington, and Alaska. Hawaii is geographically separate from the main U.S. landmass.
| State | 2020 Census | 2010 Census | Change | Area |
Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7,151,502 | 6,392,017 | +11.88% | 113,594.08 sq mi (294,207.3 km2) | 63/sq mi (24/km2) | |
| 5,773,714 | 5,029,196 | +14.80% | 103,641.89 sq mi (268,431.3 km2) | 56/sq mi (22/km2) | |
| 3,271,616 | 2,763,885 | +18.37% | 82,169.62 sq mi (212,818.3 km2) | 40/sq mi (15/km2) | |
| 3,104,614 | 2,700,551 | +14.96% | 109,781.18 sq mi (284,332.0 km2) | 28/sq mi (11/km2) | |
| 2,117,522 | 2,059,179 | +2.83% | 121,298.15 sq mi (314,160.8 km2) | 17/sq mi (6.6/km2) | |
| 1,839,106 | 1,567,582 | +17.32% | 82,643.12 sq mi (214,044.7 km2) | 22/sq mi (8.5/km2) | |
| 1,084,225 | 989,415 | +9.58% | 145,545.80 sq mi (376,961.9 km2) | 7/sq mi (2.7/km2) | |
| 576,851 | 563,626 | +2.35% | 97,093.14 sq mi (251,470.1 km2) | 6/sq mi (2.3/km2) | |
| Mountain | 24,919,150 | 22,065,451 | +12.93% | 855,766.98 sq mi (2,216,426.3 km2) | 29/sq mi (11/km2) |
| 39,538,223 | 37,254,523 | +6.13% | 155,779.22 sq mi (403,466.3 km2) | 254/sq mi (98/km2) | |
| 7,705,281 | 6,724,540 | +14.58% | 66,455.52 sq mi (172,119.0 km2) | 116/sq mi (45/km2) | |
| 4,237,256 | 3,831,074 | +10.60% | 95,988.01 sq mi (248,607.8 km2) | 44/sq mi (17/km2) | |
| 1,455,271 | 1,360,301 | +6.98% | 6,422.63 sq mi (16,634.5 km2) | 227/sq mi (88/km2) | |
| 733,391 | 710,231 | +3.26% | 570,640.95 sq mi (1,477,953.3 km2) | 1/sq mi (0.39/km2) | |
| Pacific | 53,669,422 | 49,880,669 | +7.60% | 895,286.33 sq mi (2,318,781.0 km2) | 60/sq mi (23/km2) |
| West | 78,588,572 | 71,946,120 | +9.23% | 1,751,053.31 sq mi (4,535,207.3 km2) | 45/sq mi (17/km2) |
Outlying Areas of the West
Some Pacific U.S. territories are sometimes considered part of the Western United States. These include American Samoa, Guam, and the Northern Mariana Islands. These islands are far from the main U.S. land. However, they are linked to the West by some government agencies.
| Territory | 2020 Population Estimate |
2010 Census population |
Change | Area |
Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 49,437 | 55,519 | −10.95% | 224 km2 (86 sq mi) | 221/km2 (570/sq mi) | |
| 168,485 | 159,358 | +5.73% | 544 km2 (210 sq mi) | 310/km2 (800/sq mi) | |
| 51,433 | 53,833 | −4.46% | 464 km2 (179 sq mi) | 111/km2 (290/sq mi) |
Who Lives in the Western United States?
The Western United States is home to many different groups of people. As of 2020, about 78.6 million people live in the 13 states of the West. It is one of the least crowded areas in the U.S. Only California, Washington, and Texas have more people per square mile than the national average.
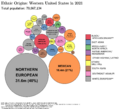
The West has been greatly influenced by people from Europe, Latin America, Asia, and Native American groups. It has the largest number of minority groups in the U.S. In many Western cities, white and Black people make up less than half the population. This is because many Hispanic and Asian people prefer to live in this region.
According to 2022 estimates, the largest ancestry groups in the West are:
- Mexican (24.2%)
- German (10.1%)
- English (9.5%)
- Irish (7.2%)
- Italian (3.5%)
- Filipino (3.4%)
- Chinese (3.3%)
The West also has a large Native American population. Many live on large reservations in the Mountain and Desert States. For example, there are many Navajo, Apache, and Blackfeet people.
Major cities in the West include Los Angeles, San Diego, San Francisco, Seattle, Portland, Denver, Phoenix, and Las Vegas.
What is the Natural Geography of the West?
The Western United States has a very diverse landscape. Along the Pacific Ocean coast are the Coast Ranges. These mountains are not as tall as the Rockies, but they are still impressive. They capture much of the moisture coming from the ocean. East of these ranges are fertile valleys, like the San Joaquin and Sacramento valleys in California. The Willamette Valley in Oregon is also here.
Beyond these valleys are the Sierra Nevada mountains in the south and the Cascade Range in the north. Mount Whitney, the tallest peak in the lower 48 states, is in the Sierra Nevada. The Cascades are volcanic mountains. Mount Rainier in Washington is over 14,000 feet tall. Mount St. Helens, another volcano in the Cascades, famously erupted in 1980. These mountain ranges get a lot of rain and snow. They create a "rain shadow" to their east, which leads to large dry areas. These dry areas cover much of Nevada, Utah, and Arizona. The Mojave Desert and Sonoran Desert are found here.
Beyond the deserts are the Rocky Mountains. In the north, they are very close to the Cascade Range. The Rockies are hundreds of miles wide and stretch from New Mexico to Alaska. The Rocky Mountain Region is the highest area in the United States. Many peaks in the Rockies are over 14,000 feet tall, especially in Colorado. East of the Rockies is the Great Plains, a vast grassy area.
The West has several long rivers that flow into the Pacific Ocean. The Colorado River flows through the Mountain states, forming the Grand Canyon. This river is a major water source for the Southwest. So much water is used for drinking and farming that it often doesn't reach the Gulf of California. The Columbia River, the largest river by volume flowing into the Pacific from North America, and its tributary, the Snake River, provide water to the Pacific Northwest.
Climate and Farming in the West
The climate in most of the West is semi-arid, meaning it's mostly dry. However, some parts get a lot of rain or snow. Other areas are true deserts, receiving less than 5 inches of rain per year. The climate is becoming more unstable, with frequent periods of severe drought.
Temperatures vary greatly. Low areas on the West Coast have warm summers and mild winters with little snow. The desert southwest has very hot summers and mild winters. The mountains in the southwest get a lot of snow. The Inland Northwest has warm to hot summers and cold winters.
Rainfall is higher in the eastern parts of the West and decreases towards the Pacific Coast, where it then increases again. The coastal areas of the Pacific Northwest get the most rainfall in the United States. Droughts are much more common in the West than in other parts of the U.S. Death Valley, California, is the driest place recorded in the U.S. Droughts in the West often lead to high fire risk, causing a lot of damage.
Farming in the West depends on rainfall, irrigation, soil, and temperature. Dry regions usually only support livestock grazing, like raising beef cattle. The "wheat belt" stretches from Texas through The Dakotas, producing most of the wheat and soybeans in the U.S. Irrigation in the Southwest allows for growing many fruits, nuts, vegetables, and flowers. Washington is known for apples, and Idaho for potatoes. California and Arizona are major producers of citrus fruits.
Since 1902, the U.S. government has built dams and irrigation projects to help farming grow in the West. After World War II, cities in the West grew rapidly. This growth, especially in states like New Mexico, Utah, Colorado, Arizona, and Nevada, has put a strain on water and power resources. Water is now often moved from farms to large cities.
Geology of the Western Landscape
The eastern part of the West is mostly plains, made of sedimentary rock. The Rocky Mountains show older igneous and metamorphic rock. The Inter-mountain States and Pacific Northwest have large areas of volcanic rock. Salt flats and salt lakes show that large inland seas once covered much of the West.
The Pacific states are the most geologically active areas in the United States. Earthquakes cause damage every few years in California. While the Pacific states have the most active volcanoes, extinct volcanoes and lava flows are found throughout most of the West.
History of the American West
Native Americans have lived in the Western United States for at least 11,000 years. Major settlement by Europeans began quickly in the 1840s. This was largely due to the Oregon Trail and the California Gold Rush of 1849. California grew so fast that it became a state in 1850.
One of the biggest migrations in American history happened in the 1840s. The Latter Day Saints (Mormons) moved from the Midwest to build a new community in Utah.
Cities like Omaha, Nebraska and St. Louis, Missouri were called "Gateway to the West." Omaha helped settlers get ready for their journey. St. Louis became rich from the fur trade in the West.
From 1863 to 1869, the first transcontinental railroad was built. It connected the eastern U.S. to the Pacific coast. This railroad changed how people settled and how the economy worked in the West. It made travel and shipping faster, safer, and cheaper.
The history of the American West in the late 1800s and early 1900s became a popular story in books and movies. The image of the cowboy, the homesteader, and westward expansion turned real events into a myth. This myth has shaped much of American popular culture since the late 19th century. Movies, especially western movies, often use the West to show ideas of self-reliance and American values.
The West in the 20th Century
The invention of the automobile allowed average Americans to travel the West. Businessmen promoted Route 66 to bring tourism and business to the West. In the 1950s, a museum called the Cowboy Hall of Fame was built. It showed off western culture to travelers from the East. Later, interstate highways crossed the West, bringing more trade and tourists.
The movies became a major source of entertainment. Hollywood in Los Angeles became the center for radio and television production.
California grew to be the most populated state and one of the world's top economies. Huge population growth in the late 1800s and 1900s created two large urban areas: Greater Los Angeles and the San Francisco Bay Area. These are among the largest metropolitan areas in the world. Other fast-growing cities include Denver, Phoenix, and Seattle.
Since the 1970s, historians have seen World War II as a major turning point for the West. The region saw huge social and economic changes. The population grew a lot, especially in cities. This was due to the expansion of airplane, ship, and weapons manufacturing. California also improved its universities and scientific research. After the war, millions more people moved to the West.
The West has always been more democratic and had more racial and gender equality. It continued to lead the country in modernization. New problems arose, especially environmental issues. Westerners took the lead in managing scarce water resources and dealing with smog.
Los Angeles has the largest Mexican population outside of Mexico. San Francisco has the largest Chinese community in North America. Oakland, California and Long Beach, California have large African-American populations. The state of Utah has a Mormon majority. Some cities like Albuquerque, New Mexico are near Indian reservations. In remote areas, there are settlements of Alaskan Natives and Native Hawaiians.
Culture of the West
Historically, the culture of the Western United States has been shaped by cowboys, pioneers, and Native Americans. The vast deserts and small, isolated towns, along with long highways and railroads, have created an image of the West as an open, endless space.
The West faces both the Pacific Ocean and the Mexican border. This has led to a mix of many ethnic groups. Hawaii is the only U.S. state where Asian Americans outnumber white residents. People from many Asian countries settled in California and other coastal states. They helped with the Gold rush, building the transcontinental railroad, farming, and more recently, high technology.
The border states—California, Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas—and other southwestern states like Colorado, Utah, and Nevada have large Hispanic populations. Many Spanish place names show their history as former Spanish and Mexican lands. Mexican-Americans have also grown in number in the Northwest and Southern states.
In the Pacific States, large port cities have become world centers for media and technology. Los Angeles is known for the Hollywood film industry. The area around Los Angeles was also a major center for the aerospace industry. Silicon Valley in the San Francisco Bay area is the heart of America's high-tech industry. This growth has made California the most populated state. Oregon and Washington have also grown quickly with companies like Boeing and Microsoft.
Alaska is a huge land with few people. Many are native Alaskans, and there are vast areas of wilderness protected in national parks. Hawaii's location makes it a key link between the United States and Asia, and a major tourism spot.
The Mountain States include Arizona, Colorado, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, and Wyoming. These states have fewer people per square mile. They developed as ranching and mining areas and only recently became more urban. They have unique cultures and try to balance city growth, recreation, and protecting the environment.
Special cultural points of the Mountain States include the large Mormon population in Utah and nearby areas. Also, there are the exciting casino resort towns of Las Vegas and Reno, Nevada. Many American Indian tribal reservations are also found here.
Major Cities in the West
These are the largest cities in the 13 Western states with populations over 500,000. These numbers are from the United States Census Bureau in April 2020:
Other Important Population Centers
- The city area of El Paso is in Texas, which is usually part of the Southern United States. However, it is sometimes also seen as part of the Western United States. Its population in April 2020 was 868,859.
- The largest city area in Alaska is Anchorage. Its population in April 2020 was 398,328.
- In the U.S. territories that are sometimes linked to the West, the largest population centers are Tafuna in American Samoa, Dededo in Guam, and Saipan in the Northern Mariana Islands.
Images for kids
-
The cowboy is a famous symbol of the American West.
-
The West is known for its wide-open spaces and long roads. This is a road in Utah leading to Monument Valley.
-
Zion National Park in southern Utah is one of many national parks in the state.
-
The beautiful coastline of Big Sur, California.
-
The Mojave Desert covers a large part of the Southwestern United States.
-
The amazing Grand Canyon in Arizona.
-
A red sunset in the High Desert region of California.
-
The High Desert region of Oregon.
-
Wild horses in the Pryor Mountains of Southeast Montana.
-
The first transcontinental railroad was very important for the history of the Western United States.
-
U.S. Route 66 helped the Western United States grow.
-
Newspaper Rock State Historic Monument in Utah has ancient carvings from the first people of the Southwest.
-
Pioneers were some of the first European Americans to settle in the West.
-
The Hollywood sign represents the American film industry.
See also
 In Spanish: Oeste de Estados Unidos para niños
In Spanish: Oeste de Estados Unidos para niños
 | Claudette Colvin |
 | Myrlie Evers-Williams |
 | Alberta Odell Jones |