Saipan, Northern Mariana Islands facts for kids
|
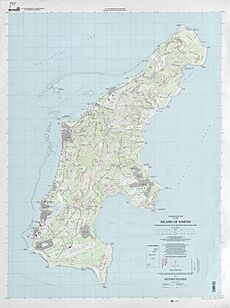
Top: Garapan Skyline; Bottom: Map of Saipan Island
|
|
 |
|
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Pacific Ocean |
| Coordinates | 15°11′N 145°45′E / 15.183°N 145.750°E |
| Archipelago | Marianas |
| Area | 118.98 km2 (45.94 sq mi) |
| Length | 12 mi (19 km) |
| Width | 5.6 mi (9 km) |
| Highest elevation | 1,560 ft (475 m) |
| Highest point | Mount Tapochau |
| Administration | |
|
United States
|
|
| Commonwealth | Northern Mariana Islands |
| Largest settlement | Garapan |
| Mayor | Ramon Camacho |
| Demographics | |
| Demonym | Chamorro; Carolinian (Refaluwasch) |
| Population | 43,385 |
| Ethnic groups |
|
| Additional information | |
| Time zone |
|
| ZIP code | 96950 |
| Area code(s) | 670 |
| ISO code | 580 |
| Official website | https://governor.gov.mp |
Saipan is the largest island and capital of the Northern Mariana Islands. This is a territory of the United States. It is located in the western Pacific Ocean. In 2020, about 43,385 people lived on Saipan. Its people have been United States citizens since the 1980s. Saipan is a main home for the Chamorro. They are the native people of the Mariana Islands.
People have lived on Saipan for over 4,000 years. From the 1600s, Spain ruled the island. After the Spanish–American War in 1898, the United States briefly took control. Then, Saipan was sold to Germany. After about 15 years, Japan took over for 30 years. This rule ended with the Battle of Saipan during World War II. The United States then gained control. After the war, Saipan became part of the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands. The United States managed it. In 1978, Saipan officially joined the United States. It became part of the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands.
Today, Saipan is home to about 90% of the Northern Mariana Islands' population. It has many resorts, golf courses, and beautiful beaches. There are also important nature sites and historical places from World War II. The main government offices are in Capitol Hill. The courts are in Susupe. Since the whole island is one municipality, Saipan is known as the capital. As of 2023, Ramon Camacho is the mayor of Saipan. Arnold Palacios is the governor of the Northern Mariana Islands.
In 2018, Typhoon Yutu hit Saipan. It caused a lot of damage across the island.
Contents
- What Does Saipan Mean?
- How Did Saipan's History Unfold?
- What is Saipan's Geography Like?
- What Kind of Music is Popular in Saipan?
- What Television Channels Are Available?
- How Do People Get Around Saipan?
- What Are Saipan's Villages and Towns?
- What Are the Best Places to Visit in Saipan?
- What is Saipan's Economy Like?
- Who Lives in Saipan?
- What Religions Are Practiced in Saipan?
- What Schools Are in Saipan?
- Who Are Some Famous People From Saipan?
- How Has Saipan Appeared in Books and Movies?
- Images for kids
- See also
What Does Saipan Mean?
In the Chamorro language, the island is called Saipan. Some Carolinian people say the name comes from their language. They say it means "a voyage empty." This refers to a story about how they found the island.
How Did Saipan's History Unfold?
Ancient Times
Archaeologists have found signs of human life on Saipan from over 4,000 years ago. These include cave drawings, old Latte Stones, and other items. These findings show links to cultures in Melanesia and Micronesia.
Spanish Rule
Europeans might have first seen Saipan in 1521. This was during the Spanish trip led by Ferdinand Magellan. The first clear record of Europeans arriving was in 1600. A Spanish ship, the Santa Margarita, crashed there. Its survivors stayed for two years.
Spain officially took over the island in 1668. A missionary named Diego Luis de San Vitores named it San José. After 1670, it became a stop for ships to get food and water. Many native Chamorro people died from diseases. They were also forced to move to Guam in 1720. Under Spanish rule, the island became a place for raising cattle and pigs. These animals fed Spanish ships traveling between the Philippines and Mexico.
Around 1815, many Carolinians from Satawal moved to Saipan. This happened when the Chamorros were kept on Guam. The Caroline Islands had been hit by a big typhoon. Their leader, Chief Aghurubw, asked the Spanish governor if they could settle on Saipan. The Spanish allowed them to move there.
German Rule
After the Spanish–American War in 1898, the United States briefly held Saipan. But then Spain sold it to Germany in 1899.
Germany managed the island as part of German New Guinea. However, Germany did not try to develop or settle the island much. It stayed under the control of its Spanish and mixed-race landowners.
Japanese Rule
In 1914, during World War I, Japan took the island. In 1919, the League of Nations gave Japan formal control. Saipan became a key island for Japan. Many Japanese, Koreans, Taiwanese, and Okinawans moved there. They started large sugar farms. The South Seas Development Company built sugar factories. Japan also built roads, ports, power stations, and schools. By 1943, Saipan had over 29,000 Japanese settlers. It also had nearly 4,000 Chamorro and Carolinian islanders.
World War II
Japan saw Saipan as a vital defense line for its homeland. So, they heavily guarded it from the late 1930s. They built many defenses, including underground forts and an airstrip. By mid-1944, nearly 30,000 soldiers were on the island.
The Battle of Saipan was a major part of World War II. It took place from June 15 to July 9, 1944. The United States Marine Corps and United States Army landed on the island's southwest beaches. After more than three weeks of hard fighting, they captured the island. The battle caused 3,426 American deaths and 10,364 injuries.
Out of about 30,000 Japanese defenders, only 921 were captured. The intense fighting also led to many civilian deaths. About 20,000 Japanese civilians died during the battle.
After Saipan was captured, American military was only about 1,300 miles from Japan. This put most Japanese cities within reach of American B-29 Superfortress bombers. Losing Saipan was a big defeat for Japan. It led to Prime Minister Hideki Tōjō resigning.
You can learn about the war history at American Memorial Park on Saipan. The Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands Museum also shares this history. After the war, most Japanese settlers returned to Japan.
Becoming a U.S. Territory
After World War II, Saipan became part of the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands. The United States managed this territory.
U.S. military bases on Saipan were closed or used for other things. For example, the Naval Advance Base Saipan was the headquarters for the U.N. Trusteeship from 1962 to 1986. The East Field airbase became an airport until the 1960s. Later, that area was turned into a golf course.
Joining the United States
The people of the Northern Mariana Islands voted to join the United States in 1975. Saipan became a part of the new Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands in 1978. On November 4, 1986, the islanders of the Northern Marianas, including Saipan, became United States citizens. This meant that U.S. citizens could visit or live in Saipan without a passport.
What is Saipan's Geography Like?
Saipan is the largest island in the Northern Mariana Islands. It is about 120 miles north of Guam. It is also about 5 miles northeast of Tinian. The Saipan Channel separates these two islands. Saipan is about 12 miles long and 5.6 miles wide. Its land area is about 115.38 square kilometers.
The western side of the island has sandy beaches. An offshore coral reef creates a large, calm lagoon. The eastern shore has rugged rocky cliffs and another reef. A narrow underwater bank called Marpi Reef is 28 miles north of Saipan. CK Reef is to the west.
The highest point on Saipan is Mount Tapochau. It is a limestone mountain about 1,560 feet high. Unlike many mountains in the Marianas, it is not an extinct volcano. It is a natural limestone formation.
North of Mount Tapochau, towards Banzai Cliff, there is a ridge of hills. Mount Achugao, about 2 miles north, might be what's left of an old volcanic cone.
Saipan also has smaller islands connected to it. Bird Island is a nature reserve for birds. It connects to Saipan only when the tide is low. Forbidden Island is similar but larger. It is on the southeast side of Saipan. Mañagaha is a small 100-acre island off the west coast. It is a popular place for tourists. You can get there by a ten-minute ferry ride.
An underwater limestone cave called the Grotto is up to 70 feet deep.
Plants and Animals of Saipan

Saipan's plant life is mostly limestone forest. Some developed areas have Leucaena leucocephala trees. These are also called "tangan-tangan" trees. They spread widely after World War II.
Tangan-Tangan trees were planted to stop soil from washing away. This was needed because the war damaged the land. Native forests remain in small areas. They are found on steep slopes and in highland conservation areas. Coconuts, papayas, and Thai hot peppers grow wild. Locals call these peppers "donni' såli" or "boonie peppers." Mangoes, taro root, breadfruit (called "Lemai"), and bananas are grown by families and farmers.
Saipan is home to several unique bird species. These include the Mariana fruit dove and the white-throated ground dove. Other birds are the bridled white-eye, golden white-eye, and Micronesian myzomela. The Saipan reed warbler is an endangered bird found here.
The island used to have many giant African land snails. They were brought here as food or by accident. They became a farm pest. In recent years, a type of flatworm called Platydemus manokwari has helped control their numbers.
Saipan's Climate
Saipan has a tropical rainforest climate or tropical monsoon climate. Seasonal trade winds from the northeast (November to March) and easterly winds (May to October) affect it. The average high temperature all year is about 84°F (29°C). Temperatures do not change much throughout the year. The Guinness Book of World Records says Saipan has the world's least changing temperatures. However, temperatures can vary between the coast and mountains.
The drier season is from December to June. The rainier season is from July to November. Typhoon season is from July to December. Saipan often experiences at least one typhoon each year.
| Climate data for Saipan International Airport (1991–2020 normals, extremes 2000–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 89 (32) |
90 (32) |
91 (33) |
93 (34) |
96 (36) |
94 (34) |
99 (37) |
95 (35) |
94 (34) |
92 (33) |
92 (33) |
90 (32) |
99 (37) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 87.1 (30.6) |
86.7 (30.4) |
88.1 (31.2) |
89.3 (31.8) |
90.4 (32.4) |
91.1 (32.8) |
90.9 (32.7) |
90.9 (32.7) |
90.1 (32.3) |
89.2 (31.8) |
88.5 (31.4) |
88.0 (31.1) |
92.5 (33.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 84.1 (28.9) |
84.0 (28.9) |
84.9 (29.4) |
87.1 (30.6) |
88.2 (31.2) |
88.4 (31.3) |
87.8 (31.0) |
87.2 (30.7) |
87.2 (30.7) |
86.6 (30.3) |
86.5 (30.3) |
85.7 (29.8) |
86.5 (30.3) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 79.5 (26.4) |
79.1 (26.2) |
80.0 (26.7) |
82.0 (27.8) |
83.1 (28.4) |
83.4 (28.6) |
82.9 (28.3) |
82.4 (28.0) |
82.2 (27.9) |
81.8 (27.7) |
81.9 (27.7) |
81.0 (27.2) |
81.6 (27.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 74.8 (23.8) |
74.1 (23.4) |
75.2 (24.0) |
76.9 (24.9) |
78.0 (25.6) |
78.5 (25.8) |
78.1 (25.6) |
77.5 (25.3) |
77.2 (25.1) |
77.1 (25.1) |
77.3 (25.2) |
76.4 (24.7) |
76.8 (24.9) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 72.5 (22.5) |
71.5 (21.9) |
71.7 (22.1) |
73.4 (23.0) |
75.1 (23.9) |
75.7 (24.3) |
74.6 (23.7) |
73.5 (23.1) |
74.0 (23.3) |
73.9 (23.3) |
74.0 (23.3) |
73.9 (23.3) |
70.6 (21.4) |
| Record low °F (°C) | 70 (21) |
69 (21) |
69 (21) |
70 (21) |
73 (23) |
72 (22) |
71 (22) |
69 (21) |
72 (22) |
69 (21) |
69 (21) |
69 (21) |
69 (21) |
| Average rainfall inches (mm) | 3.65 (93) |
2.50 (64) |
1.96 (50) |
2.75 (70) |
3.12 (79) |
4.24 (108) |
7.43 (189) |
12.86 (327) |
11.42 (290) |
10.72 (272) |
5.21 (132) |
3.78 (96) |
69.64 (1,769) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.01 in) | 17.4 | 15.3 | 14.2 | 16.4 | 17.9 | 20.2 | 24.3 | 23.9 | 23.3 | 24.5 | 20.7 | 18.9 | 237.0 |
| Source: NOAA (mean maxima/minima 2006–2020) | |||||||||||||
What Kind of Music is Popular in Saipan?
Music on Saipan falls into three main types: local, American, and Asian. Local music includes Chamorro, Carolinian, Micronesian Hawaiian Reggae, and Palauan music. These often go with traditional dances. American music is like what you hear on U.S. radio. Asian music includes Japanese, Korean, Thai, and Philippine songs. Saipan has seven radio stations. They mostly play popular English songs, plus local and Philippine music.
In 2017, an album called Music Of The Marianas: Made In Saipan Vol.1 was released. It had 20 songs from different artists in the CNMI. The CD featured church choirs, calm acoustic songs, and island hip-hop.
What Television Channels Are Available?
Local TV stations on Saipan include:
- KPPI-LP (ABC7), which is an ABC channel. It shows programs from KTGM.
- KSPN 2, owned by the Flame Tree Network.
- The Visitors Channel 3, also owned by the Flame Tree Network.
- WSZE-TV 10, an NBC channel. It shows programs from KUAM-TV in Guam.
How Do People Get Around Saipan?
You can travel to and from Saipan using nine international airlines. They fly into Saipan International Airport. A small airline on Tinian flies small planes between the Northern Marianas islands and Guam. A ferry used to run between Saipan and Tinian. However, it stopped in 2010 and has not started again.
One of the island's main roads is Beach Road. It runs along the western coast of Saipan. In some places, the beach is just a few feet away. Flame trees and pine trees line the street. This road connects more than six villages on the western coast. Middle Road is the island's largest road. It goes through the center of the island. Like Beach Road, Middle Road connects several villages. Many offices, shops, hotels, and homes are on or near these roads. Middle Road is also called "Chalan Pale Arnold" on maps.
There is little public transportation on Saipan, except for school buses. Cars are the most common way to get around. Motorcycles are also used. Bicycles are only good in certain areas. Sidewalks are not common. Most are in Garapan and at some street corners.
What Are Saipan's Villages and Towns?
Saipan has 30 official villages. There are also many smaller areas and neighborhoods within these villages. For example, Afetnas is in San Antonio. Tapochau and I Denne are in Capitol Hill.
- As Lito
- As Matuis
- As Perdido
- Capitol Hill
- Chalan Kanoa
- Chalan Kiya
- Chalan Laulau
- Chalan Piao
- Chinatown
- Dandan
- Fina Sisu
- Garapan
- Gualo Rai
- Kagman
- Kannat Tabla
- Koblerville
- Lower Base
- Marpi
- Navy Hill
- Oleai
- Papago
- Sadog Tasi
- San Antonio
- San Jose
- San Roque
- San Vicente
- Susupe
- Tanapag
What Are the Best Places to Visit in Saipan?
Saipan has many popular places for tourists.
- Managaha Island is a 100-acre tropical beach island. You can visit it by ferry.
- American Memorial Park and Micro Beach are popular. Micro Beach is a 1-kilometer beach on the west side. It's a great spot to watch the sunset.
- Latte Stones are old stone structures from the island's past.
- Mount Tapochau is the highest point on the island. It offers amazing views of Saipan. On clear days, you can see other islands. There is a statue of Jesus Christ at the top.
- Last Command Post is a historical site from World War II. It was a Japanese command post during the Battle of Saipan.
- Bird Island Sanctuary beach is a beach near the Bird Island sanctuary. It faces east. There is also an observatory nearby to watch the birds.
- Forbidden Island is a small island connected to Saipan at low tide. You can hike to it. At high tide, the water separates it from Saipan. The island also has a lookout point.
- Japanese Lighthouse was built in 1934. It is now a cafe with island views.
- NMI Museum of History and Culture teaches about the island's past.
- The Grotto is a large underwater limestone cave.
What is Saipan's Economy Like?
Tourism has always been a key part of Saipan's economy. In the 1980s, making clothes became very important. The U.S. government allowed the CNMI to have different rules for minimum wage and immigration. This led to more hotels and tourism. But it also meant many clothing factories opened. These factories hired thousands of foreign workers, mostly young Chinese women, for low wages. The clothes made there could be labeled "Made in the U.S.A." and sent to the U.S. without extra taxes. By 1998, the island's clothing industry sent almost $1 billion worth of clothes to the mainland. There were concerns about the working conditions in these factories.
In 2005, rules about textile exports changed. Saipan's clothing factories started closing. By March 2007, 19 companies still made clothes on Saipan. Many well-known U.S. brands had factories there, like Gap, Levi Strauss, and Ralph Lauren. By January 2009, the last clothing factory closed. In November 2009, the U.S. government took control of immigration to the Northern Mariana Islands.
More recently, casino gaming has come to Saipan. At least five casinos now operate on the island. As of 2016, Imperial Pacific International Holdings was a major company there. They develop and run casinos, hotels, and restaurants. In 2014, they got a 25-year license to build and run casinos on Saipan. The Imperial Pacific Resort is still being built. It will have a luxury hotel, casino, restaurants, and shops.
Who Lives in Saipan?
In 2010, Saipan's population was 48,220. This was a decrease from 2000. Many working immigrants and their families left. They either went back home or moved to places like Guam or the U.S. mainland for jobs. Saipan's population is about 90% of the Northern Mariana Islands' total population.
Many workers and professionals from the Philippines, China, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Myanmar moved to Saipan in the late 1900s. A large part of the island's population includes first-generation immigrants and their children. They come from Japan, China, Korea, the Philippines, Bangladesh, and other Micronesian islands.
In 2010, Saipan's population was:
- 50.9% Asian (including Filipino, Chinese, Korean, Japanese, Bangladeshi, Thai, Nepalese)
- 34.9% Pacific Islander (including Chamorro, Carolinian, Chuukese, Palauan, Pohnpeian, Yapese, Kosraean, Marshallese)
- 2.1% White
- 0.2% others
What Religions Are Practiced in Saipan?
Most native Chamorro and Carolinian people are Roman Catholic. About half of the island's general population are foreign workers. Many of them are Catholics from the Philippines.
Many Christian churches are active in Saipan. They offer services in different languages. These include English, Chamorro, Tagalog, Korean, and Chinese.
There are also Chinese and Filipino Protestant and Catholic churches. There is a Korean Protestant church, three mosques for the Bangladeshi community, and a Buddhist temple.
What Schools Are in Saipan?
The Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands Public School System serves Saipan. Public high schools are:
- Kagman High School (Kagman)
- Marianas High School (Susupe)
- Saipan Southern High School (Koblerville)
Many private schools are also on Saipan:
- Brilliant Star Montessori School - Navy Hill
- Saipan International School – As Lito
- Mount Carmel School – Chalan Kanoa
- Grace Christian Academy – Navy Hill
- Marianas Baptist Academy – Dandan
- Saipan Community School (grades K-8) – This Protestant school started in 1976.
- Saipan Seventh-day Adventist School (18 months-grade 8)
- Northern Marianas Academy (Fina Sisu).
Northern Marianas College is a two-year college for the Northern Mariana Islands. Eucon International College is a four-year college. It offers degrees in Bible and Education.
The Joeten-Kiyu Public Library (JKPL) is in Susupe, Saipan.
The Japanese Community School of Saipan is a special school for Japanese students. It is on the second floor of the USL Building in Gualo Rai. It opened on November 5, 1983.
Public middle schools:
- Tanapag Middle School
- Hopwood Middle School
- Chacha Ocean View Middle School
- Francisco Mendiola Sablan Middle School
- Dandan Middle School
Public elementary schools:
- Gregorio T. Camacho (GTC) Elementary School
- San Vicente Elementary School
- Koblerville Elementary School
- William S. Reyes Elementary School
- Kagman Elementary School
- Oleai Elementary School
- Garapan Elementary School
Who Are Some Famous People From Saipan?
- Theresa H. Arriola
- Tina Stege
- Jayatirtha Dasa
- Colin Sinclair
How Has Saipan Appeared in Books and Movies?
Saipan has been featured in many stories and films.
- The Tom Clancy novel Debt of Honor had Saipan as a major part of its plot.
- The 1960 movie Hell to Eternity tells the true story of GI Guy Gabaldon. He convinced 800 Japanese soldiers to surrender during the Battle of Saipan.
- Much of the 2002 film Windtalkers takes place during the invasion of Saipan in World War II.
- In 2011, a Japanese film called Oba: The Last Samurai was set in Saipan. It was about Captain Sakae Ōba holding out on Saipan until December 1, 1945.
- A big part of the novel Amrita by Japanese author Banana Yoshimoto happens in Saipan. It often talks about the island's landscape and spirit.
- Saipan is the setting for the P. F. Kluge novel The Master Blaster. This book tells a mysterious story about Saipan's past.
- In association football, Saipan is known for the "Saipan incident." This happened before the 2002 FIFA World Cup. The captain of the Republic of Ireland team, Roy Keane, had a heated argument with his manager, Mick McCarthy. This led to Keane leaving the team.
- In 2016, a horror film called Gehenna: Where Death Lives was released on Netflix. It's about American developers who find a supernatural being in a World War II bunker on Saipan.
- In 2024, Julian Assange briefly visited Saipan. He pleaded guilty in the federal courthouse there.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Saipán para niños
In Spanish: Saipán para niños