Micronesia facts for kids
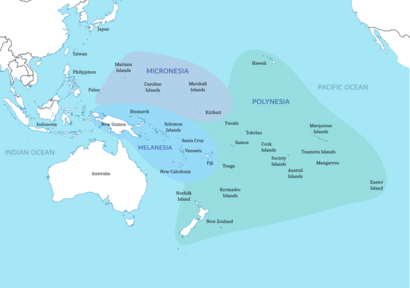
Micronesia is a group of islands in Oceania. It has about 2,000 small islands in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. Micronesia shares a similar history and culture with other island regions. These include Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Polynesia to the east, and Melanesia to the south. All these people are part of the larger group called Austronesian peoples.
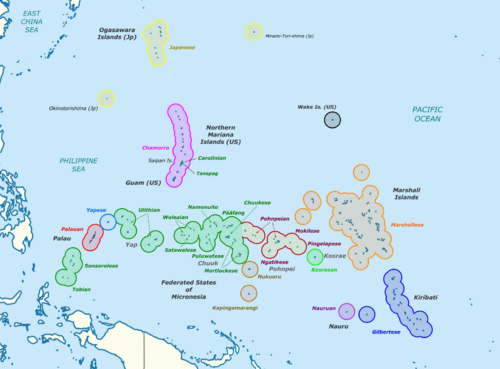
The region has a tropical marine climate, meaning it's warm and humid all year. It is part of the Oceanian realm. Micronesia includes four main groups of islands: the Caroline Islands, the Gilbert Islands, the Mariana Islands, and the Marshall Islands. There are also many other islands not part of these groups.
Different countries control parts of Micronesia. Some of the Caroline Islands are part of the Republic of Palau. Others are part of the Federated States of Micronesia (often called "FSM" or "Micronesia"). The Gilbert Islands are part of the Republic of Kiribati. The Mariana Islands are linked to the United States. Some are part of Guam, a U.S. territory. The rest are part of the Northern Mariana Islands, a U.S. Commonwealth. The island of Nauru is its own country. The Marshall Islands are all part of the Republic of the Marshall Islands. Wake Island is claimed by both the United States and the Marshall Islands, but the U.S. Air Force manages it.
The name "Micronesia" has been used since 1832. However, the islands do not all share the same geology, history, languages, or cultures. Instead, they are a mix of different groups.
People first settled in Micronesia thousands of years ago. Scientists believe the Austronesian peoples came from Taiwan by boat between 3000 and 1500 BCE. They were the first to invent ocean-going boats, like catamarans. These boats helped them spread quickly across the Indo-Pacific islands.
Europeans first arrived in Micronesia in 1521. This was when the Magellan expedition landed in the Mariana Islands. The term "Micronesia" was first used by Louis Domeny de Rienzi in 1831, and then by Jules Dumont d'Urville in 1832.
Contents
Geography
Micronesia is a region in Oceania with about 2,100 islands. Their total land area is about 2,700 square kilometers (1,042 sq mi). The biggest island is Guam, which is 582 square kilometers (225 sq mi). The total ocean area around the islands is very large, about 7.4 million square kilometers (2.86 million sq mi).
There are four main island groups in Micronesia:
- the Caroline Islands (part of the Federated States of Micronesia and Palau)
- the Gilbert Islands (part of Kiribati)
- the Mariana Islands (part of the Northern Mariana Islands and Guam, USA)
- the Marshall Islands
The country of Nauru is a separate island. There are also other smaller islands and groups of islands.
Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands are a group of about 500 small coral islands. They are north of New Guinea and east of the Philippines. The Carolines are split into two countries: the Federated States of Micronesia (about 600 islands on the eastern side) and Palau (250 islands on the western side).
Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands are a chain of sixteen atolls and coral islands. They are arranged in a line from north to south. The equator divides the northern and southern Gilbert Islands. The Republic of Kiribati includes all of the Gilberts, including Tarawa, where the country's capital is located.
Mariana Islands
The Mariana Islands are a chain of fifteen volcanic mountains. They formed when the Pacific Plate moved under the Mariana plate. This area is very active with volcanoes. The Marianas were divided in 1898. The United States took Guam after the Spanish–American War. Spain then sold the northern islands to Germany in 1899.
After World War I, Germany lost its colonies. The Northern Mariana Islands were given to Japan to manage. After World War II, the islands became a United Nations Trust Territory managed by the United States. In 1976, the Northern Mariana Islands became a U.S. Commonwealth. Its residents became U.S. citizens.
Marshall Islands

The Marshall Islands are north of Nauru and Kiribati. They are east of the Federated States of Micronesia. The islands have 29 low-lying atolls and 5 separate islands. In total, there are 1,156 individual islands and islets. The islands form two groups: the Ratak Chain and the Ralik Chain. All these islands are part of the Republic of the Marshall Islands. This country is a republic that works closely with the United States. The islands have few natural resources. Their economy relies on services, some fishing, and agriculture. Twenty-four of the 29 atolls are inhabited.
Bikini Atoll is an atoll in the Marshall Islands with 23 islands. Some islands were damaged during nuclear tests. The islands are made of low coral limestone and sand. Their average height is only about 7 feet (2.1 m) above low tide.
Nauru
Nauru is an oval-shaped island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It is about 42 kilometers (26 mi) south of the Equator. Nauru is the world's smallest republic, covering only 21 square kilometers (8.1 sq mi). It has about 10,670 residents, making it the third least-populated country.
The island is surrounded by a coral reef. This reef is visible at low tide and has many sharp points. The reef makes it hard to build a seaport. However, channels in the reef let small boats reach the island. A fertile coastal strip, 150 to 300 meters (490 to 980 ft) wide, lies behind the beach.
Wake Island
Wake Island is a coral atoll with a coastline of about 12 miles (19 km). It is just north of the Marshall Islands. It is a U.S. territory. Only the United States Air Force can access and manage the island. Wake Island is geographically close to Micronesia. However, it is not culturally part of it because people did not live there historically. Micronesians might have visited Wake Island long ago to fish, but there is no sign they settled there.
Geology
Most islands in Micronesia are coral atolls. Coral atolls start as coral reefs growing on the sides of a central volcano. When the volcano sinks into the sea, the coral keeps growing. This keeps the reef at or above water level. One exception is Pohnpei in the Federated States of Micronesia. It still has its central volcano with coral reefs around it.
Fauna
The Yap Islands are home to several unique bird species. These include the Yap monarch and the Olive white-eye. The endangered Yap flying-fox also lives only on Yap.

Climate
Micronesia has a tropical marine climate. This means it is warm and humid all year. Seasonal northeast trade winds help to keep the weather mild. Temperatures do not change much throughout the year. The dry season is from December or January to June. The rainy season is from July to November or December. Some islands can experience typhoons during the rainy season.
History
Early History
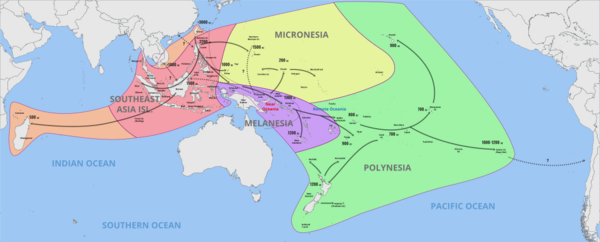
The Northern Mariana Islands were the first islands in Oceania settled by the Austronesian peoples. They arrived around 1500 BCE, sailing east from the Philippines. These people slowly moved south. They reached the Bismarck Archipelago and the Solomon Islands by 1300 BCE. There, they met other Austronesian groups moving through New Guinea and Island Melanesia. By 1200 BCE, they began sailing across open seas again. They reached Vanuatu, Fiji, and New Caledonia. Later, they became the ancestors of the Polynesian people.
Other Austronesian groups also arrived later, likely from Sulawesi. They settled Palau and Yap around 1000 BCE. Around 200 BCE, a group from Island Melanesia also moved north. They settled the islands of eastern Micronesia at about the same time.
Around 800 CE, new settlers from Southeast Asia came to the Marianas. This began the Latte period. These new people built large structures with stone pillars called haligi. They also brought back rice. This made the Northern Marianas the only islands in Oceania where rice was grown before Europeans arrived. Rice was a special crop used in rituals. It became a main food only after Spanish colonization.
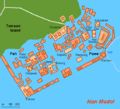
Building Nan Madol, a large stone city in Pohnpei, began around 1180 CE. The Leluh complex in Kosrae was built around 1200 CE.
European Contact and Control
The first known European contact happened in 1521. A Spanish expedition led by Ferdinand Magellan reached the Marianas. Records say the Chamorro people seemed friendly and curious.
More contact happened in the 1500s. In 1525, Diogo da Rocha may have been the first European to contact the Caroline Islands. He might have stayed on the Ulithi atoll and met people from Yap. Marshall Islanders met Spanish explorer Álvaro de Saavedra Cerón in 1529.
In the early 1600s, Spain took control of Guam, the Northern Marianas, and the Caroline Islands. These became part of the Spanish East Indies, ruled from the Spanish Philippines.
In the 1800s, Protestant missionaries came to Micronesia. They found it easier to convert people here than in other regions.
Changes in Control (1899-1945)
After the Spanish–American War, Spain lost many colonies. The United States took the Spanish Philippines and Guam. The U.S. also claimed Wake Island in 1899. Spain then sold its remaining small islands in Micronesia to the German Empire. This was part of the German–Spanish Treaty (1899). Under German rule, the islands became a protectorate. Nauru had already become a German colony in 1888.
In the early 1900s, three foreign powers controlled Micronesia:
- The United States controlled Guam and Wake Island.
- Germany controlled Nauru, the Marshall, Caroline, and Northern Mariana Islands.
- The British Empire controlled the Gilbert Islands (Kiribati).
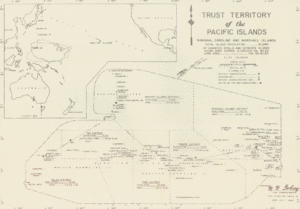
During World War I, Germany lost its Pacific islands. In 1923, Nauru became an Australian mandate. Japan was given control of Germany's other territories in Micronesia, called the South Seas Mandate. During World War II, Japanese troops occupied Nauru and some Gilbert Islands. After Japan's defeat, its mandate became a United Nations Trusteeship managed by the United States. This was called the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands. Nauru became independent in 1968.
Micronesia Today
Today, most of Micronesia's islands are independent countries. The exceptions are the Northern Mariana Islands, Guam, and Wake Island, which are U.S. territories.
Countries and Territories
| Country | Population (July 2018 estimate) | Area (km2) | Population density (/km2) | Urban population | Life expectancy | Literacy rate | Official language(s) | Main religion(s) | Ethnic groups |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 112,640 | 702 | 158 | 22% | 71.2 | 89% | English | Roman Catholic 50%, Protestant 47%, others 3% | Chuukese 48.8%, Pohnpeian 24.2%, Kosraean 6.2%, Yapese 5.2%, Yap outer islands 4.5%, Asian 1.8%, Polynesian 1.5%, other 7.8% | |
| 165,768 | 540 | 299 | 93% | 78.2 | 99% | English 38.3%, Chamorro 22.2% | Roman Catholic 85%, Buddhism 3.6, other religion 11.4% | Chamorro 37.1%, Filipino 26.3%, other Pacific islander 11.3%, white 6.9%, other 8.6%, mixed 9.8% | |
| 115,847 | 811 | 152 | 44% | 64.0 | 92% | English, Gilbertese (de facto) | Roman Catholic 55%, Protestant 36% | Micronesian 98.8% | |
| 58,413 | 181 | 293 | 71% | 71.5 | 93.7% | Marshallese 98.2%, English | Protestant 54.8%, other Christian 40.6% | Marshallese 92.1%, mixed Marshallese 5.9%, other 2% | |
| 10,670 | 21 | 480 | 100% | 65.0 | 99% | Nauruan, English (de facto) | Nauru Congregational Church 35.4%, Roman Catholic 33.2%, Nauru Independent Church (Protestant) 10.4%, Baha'i faith 10%, Buddhism 9% | Nauruan 58%, other Pacific Islander 26%, Chinese 8%, European 8% | |
| 56,882, | 464 | 113 | 91% | 76.9 | 97% | English, Chamorro and Carolinian | Roman Catholic, Buddhism 10.6% | Asian 56.3%, Pacific islander 36.3%, White 1.8%, other 0.8%, mixed 4.8% | |
| 17,907 | 459 | 47 | 81% | 71.5 | 92% | Palauan 64.7%, English | Roman Catholic 41.6%, Protestant 23.3% | Palauan 69.9%, Filipino 15.3%, Chinese 4.9%, other Asian 2.4%, white 1.9%, Carolinian 1.4%, other Micronesian 1.1%, other 3.2% | |
| Total | 538,127 | 3,178 |
Politics
The Pacific Community (SPC) is a group that helps countries and territories in the Pacific Ocean work together.
Economy
The main way Micronesian countries earn money is by selling fishing rights to other countries. These countries use large boats to catch tuna. Some Japanese fishing boats still operate there. Money also comes from government grants, mostly from the United States. The U.S. also paid money into a fund for people from Bikini Atoll who had to move because of nuclear testing. There are few valuable minerals, except for some high-quality phosphate, especially on Nauru.
Most people from Micronesia can move and work freely in the United States. Money sent home by relatives working in the U.S. is a main source of income for families. Other income comes from government jobs and work in shops and restaurants.
The tourist industry mainly attracts scuba divers. They come to see the coral reefs, do wall dives, and visit sunken ships from World War II. Popular diving spots include Palau, Chuuk, Yap, and Pohnpei. Some private yacht owners visit, but they are not a major source of income.
Making copra (dried coconut meat) used to be a big source of money. However, world prices have fallen because of large palm plantations in places like Borneo.
People of Micronesia
The people of Micronesia today come from many different groups. However, they all share the Micronesian culture.
Because of this mix, many Micronesian groups feel connected to people in Melanesia or the Philippines. For example, the Yapese people are related to Austronesian tribes in the northern Philippines. Genetic studies also show that many Micronesian men have Japanese ancestors.
There are also many Asian communities across the region. They are especially large in the Northern Mariana Islands. Smaller groups of Europeans have also moved there or are descendants of earlier settlers.
Even though they are all in the same region, Micronesian islands have very different histories of being controlled by other countries. The areas managed by the U.S. have a unique experience. Micronesia relies a lot on its former or current ruling countries for economic support. This is similar to the French Pacific islands. Sometimes, people use the term American Micronesia to show this difference in cultural background.
A survey in 2011 found that 93.1% of Micronesians were Christians. A 2022 survey showed that 99% were Christian.
Indigenous Groups
Carolinian People
The ancestors of the Carolinian people may have come from Asia and Indonesia to Micronesia about 2,000 years ago. Their main language is Carolinian, also called Refaluwasch. About 5,700 people speak it. Carolinians have a matriarchal society. This means women, especially older women, are highly respected. Most Carolinians are Roman Catholic.
Carolinian people started moving to Saipan in the early 1800s. This was after the Spanish had greatly reduced the local Chamorro population. They mostly sailed in small canoes from other islands that a typhoon had damaged. Carolinians usually have darker skin than the native Chamorros.
Chamorro People
The Chamorro people are the native people of the Mariana Islands. These islands are divided between the U.S. territory of Guam and the U.S. Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands. Chamorro people are thought to have come from Southeast Asia around 2000 BCE. They are most closely related to other Austronesian natives in the Philippines and Taiwan. They are also related to people from the Carolines.
The Chamorro language is part of the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian family. Because Spain controlled Guam for over 300 years, many Chamorro words come from Spanish. The traditional Chamorro number system was replaced by Spanish numbers.
Chuukese People
The Chuukese people are an ethnic group in Oceania. They make up 48% of the population of the Federated States of Micronesia. Their language is Chuukese. Their home atoll, Chuuk, was also known as Truk.
Nauruan People
The Nauruan people are an ethnicity living on the Pacific island of Nauru. They are likely a mix of other Pacific peoples.
The exact origin of the Nauruan people is not fully known. It might be from the last Malayo-Pacific human migration around 1200 CE. It is possible that seafaring or shipwrecked Polynesians or Melanesians settled in Nauru.
Kaping People
About 3,000 people live in Kapingamarangi in the Federated States of Micronesia. They are nicknamed 'Kapings'. Their home atoll is one of the most remote places in Micronesia and the world. It is almost 200 miles (320 km) from the nearest land. There are no regular flights. The only reliable way to visit is by high-speed sailboat. Because it is so hard to reach, few sailors visit. The local language is Kapingamarangi. Since the 1970s, children have had to travel to Pohnpei for high school. Their parents often move with them, creating Kaping communities on Pohnpei.
Immigrant Groups
Asian People
There are large communities of people from East, South, and Southeast Asia in some Micronesian countries. These include immigrants, foreign workers, or their descendants. Most moved to the islands in the 1800s and 1900s.
In 2010, Guam's population was 26.3% Filipino, 2.2% Korean, 1.6% Chinese, and 2% other Asian. The Northern Mariana Islands were 50% Asian. Of these, 35.3% were Filipino, 6.8% Chinese, 4.2% Korean, and 3.7% other Asian (like Japanese, Bangladeshi, and Thai). In the Federated States of Micronesia, 1.4% were Asian. In Nauru, 8% were Chinese. In Palau, 16.3% were Filipino, 1.6% Chinese, 1.6% Vietnamese, and 3.4% other Asian.
Japanese rule in Micronesia also led to Japanese people settling and marrying local people. For example, Kessai Note, a former president of the Marshall Islands, has Japanese ancestors. Emanuel Mori, a former president of the Federated States of Micronesia, is a descendant of one of the first Japanese settlers.
European People
In 2010, 7.1% of Guam's population was white. In 2005, 8% of Nauru's population was European. Smaller numbers of "white" people were recorded in Palau (1.9%) and the Northern Mariana Islands (1.8%). Many Micronesians also have mixed ancestry, including European roots.
Languages
The largest group of languages in Micronesia are the Micronesian languages. They are part of the Oceanic languages family, which is part of the larger Austronesian language group.
Languages in the Micronesian family include Marshallese, Gilbertese, Kosraean, and Nauruan. There is also a large group called the Chuukic–Pohnpeic languages, which has 11 languages.
On the eastern side of the Federated States of Micronesia, the languages Nukuoro and Kapingamarangi are spoken. These are part of the Polynesian branch of Oceanic languages.
Finally, two Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken in Micronesia that are not part of the Oceanic languages. These are Chamorro in the Mariana Islands and Palauan in Palau.
Culture
Animals and Food
When Westerners first arrived, Palau had chickens and possibly pigs, but no dogs. Pigs are not native to Micronesia. Fruit bats are native to Palau, but other mammals are rare. Many reptiles live there. Shellfish and fish are important food sources. People in Palau, the Marianas, and Yap often chew betel nuts with lime and pepper leaf. The ceremonial drink called saka on Kosrae and sakau on Pohnpei was not known in Western Micronesia.
Architecture
The book Prehistoric Architecture in Micronesia says that the most impressive ancient buildings are "Palau's huge sculpted hills, large stone carvings, and decorated wooden structures on stone platforms." The building traditions of the Yapese people stayed mostly the same even after Europeans first arrived in the 1520s.
Art
Micronesia's art comes from the Lapita culture. One of the most famous artworks is the large stone city of Nan Madol. Building the city started in 1200 CE and continued when European explorers arrived around 1600. However, the city declined by 1800 and was completely abandoned by the 1820s.
In the 1800s, the region was divided by colonial powers, but art continued to grow. Men often carved wood, creating decorated ceremonial houses in Belau, special bowls, canoe decorations, and sometimes statues. Women made textiles and ornaments like bracelets and headbands. Traditional Micronesian art is usually simple and practical, but made with high quality. This was because they had few natural materials.
In the early 1900s, Micronesian culture faced strong influences from Western and Japanese powers. Some old art forms, especially sculpture, stopped being practiced. However, other arts like traditional architecture and weaving continued. After gaining independence in the second half of the century, there was new interest in traditional arts. New modern art also appeared in Micronesia towards the end of the 1900s.
Cuisine
The food in the Mariana Islands is tropical. It includes dishes like kelaguen and many others.
Marshallese cuisine includes local foods such as breadfruit, taro root, pandanus, and seafood.
Palauan cuisine includes local foods like cassava, taro, yam, potato, fish, and pork. Young Palauans often prefer Western food.
Education
Education systems in Micronesia vary by country. There are several colleges and universities.
The CariPac is a group of colleges and universities in Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, American Samoa, Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and Palau. The Agricultural Development in the American Pacific is a partnership of several colleges and universities in the region.
In the Federated States of Micronesia, education is required for children aged 6 to 13. Education is very important for their economy. The literacy rate for people aged 15 to 24 is 98.8%. The College of Micronesia-FSM has a campus in each of the four states. Its main campus is in Palikir, Pohnpei. The college also has a Fisheries and Maritime Institute (FMI) on the Yap islands.
Public education in Guam is managed by the Guam Department of Education. Guam also has several colleges, like the University of Guam and Guam Community College. There is also the Guam Public Library System.
Weriyeng is one of the last two schools that teach traditional navigation in the central Caroline Islands. The other is Fanur.
The Northern Marianas College is a two-year college in the Northern Mariana Islands.
The College of the Marshall Islands is a community college in the Marshall Islands.
Law
Understanding Law in Micronesia says that the laws in the Federated States of Micronesia are similar to those in Western countries. However, it also explains that law in Micronesia is a mix of different ideas.
The Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands, managed by the United States, used many U.S. laws. Many of these laws were adopted by the new Congress of the Federated States of Micronesia when it became self-governing in 1979.
Media
In September 2007, journalists in the region started the Micronesian Media Association.
Music and Dance
Micronesian music is important to the people living on the islands. Some music is based on mythology and old Micronesian rituals. It includes traditional songs passed down through generations, as well as modern music.
Traditional beliefs suggest that music can come to people in dreams and trances, rather than being created by composers. Micronesian folk music, like Polynesian music, mostly uses voices.
In the Marshall Islands, the roro is a traditional chant. It is usually about old legends. It is performed to help with navigation and to give strength to mothers during childbirth. Modern bands mix the unique songs of each island with modern music. While drums are not common in Micronesian music, one-sided hourglass-shaped drums are important in Marshallese music. There is a traditional Marshallese dance called beet. It is influenced by Spanish folk dances. In this dance, men and women move sideways in parallel lines. There is also a stick dance performed by the Jobwa, but only for very special events now.
Popular music from Micronesia and other parts of the world is played on radio stations in Micronesia.
Sports
The region hosts the Micronesian Games. This big sports event happens every four years. All of Micronesia's countries and territories take part, except Wake Island.
Nauru has two national sports: weightlifting and Australian rules football. In 2007, about 180 adults and 500 children played Australian rules football in Nauru. This means over 30% of the country's population played the sport.
Religion and Mythology
The main religion in Micronesia is Christianity (93%). In 2023, government numbers showed that 55% of the people were Catholic and 42% were Protestant. Another 2% belonged to other Christian groups. Other religions like Baha’i, Buddhism, Hinduism, Judaism, and Islam also exist.
Micronesian mythology includes the traditional beliefs of the people of Micronesia. There is no single belief system, as each island region has its own mythological beings. In 2014, 2.7% of the population followed folk religions.
There are important figures and myths in the traditions of the Federated States of Micronesia, Nauru, and Kiribati.
Shinto shrines from during or after World War II can be found in some Micronesian countries.
Images for kids
-
Image of the Castle Bravo nuclear test, on 1 March 1954, at Bikini Atoll.
-
Kili Island is one of the smallest islands in the Marshall Islands.
-
Wake Island as drawn by Alfred Thomas Agate during the United States Exploring Expedition.
-
A view of Nan Madol.
See also
 In Spanish: Micronesia para niños
In Spanish: Micronesia para niños