Taiwan facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of China
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Flag anthem:
中華民國國旗歌 Zhōnghuá Míngúo Gúoqígē "National Flag Anthem of the Republic of China" |
|
| Capital | Taipei 25°04′N 121°31′E / 25.067°N 121.517°E |
| Largest city | New Taipei City |
| Official languages | Standard Chinese |
| Official script | Traditional Chinese |
| National languages |
|
| Ethnic groups
(2016)
|
|
| Religion
(2020)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Taiwanese |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic |
| Tsai Ing-wen | |
| Lai Ching-te | |
| Chen Chien-jen | |
| Legislature | Legislative Yuan |
| Establishment | |
| c. August 1624 | |
| 14 June 1661 | |
|
• Annexed by the Qing dynasty
|
5 September 1683 |
|
• Ceded to the Empire of Japan
|
17 April 1895 |
|
• Republic of China established
|
10 October 1911 |
|
• Taiwan and Penghu restored to ROC rule
|
25 October 1945 |
|
• Current ROC government established
|
20 May 1948 |
|
• ROC government moved to Taipei
|
7 December 1949 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
36,197 km2 (13,976 sq mi) |
| Population | |
|
• 1 July 2022 estimate
|
|
|
• 2010 census
|
23,123,866 |
|
• Density
|
650/km2 (1,683.5/sq mi) (10th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2017) | ▲ 34.1 medium |
| HDI (2021) | very high · 19th |
| Currency | New Taiwan dollar (NT$) (TWD) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (National Standard Time) |
| ISO 3166 code | TW |
| Internet TLD | |
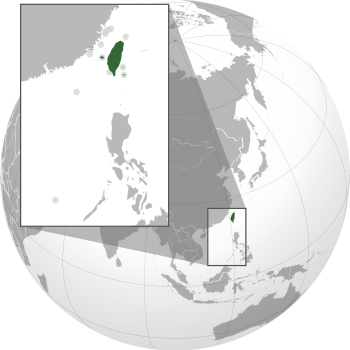
Taiwan, also known as the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. It is located where the East China Sea and South China Sea meet the Pacific Ocean. To its northwest is China, to the northeast is Japan, and to the south is the Philippines.
Taiwan controls 168 islands, covering about 36,193 square kilometers. The main island, also called Formosa, is 35,808 square kilometers. It has mountains in the east and flat areas in the west. Most of Taiwan's population lives in the western plains. The capital city, Taipei, is part of the largest metropolitan area. Taiwan has about 23.9 million people, making it one of the most crowded countries.
People have lived in Taiwan for at least 25,000 years. The ancestors of today's Taiwanese indigenous peoples arrived about 6,000 years ago. In the 1600s, many Han Chinese people started moving to Taiwan. This happened during Dutch rule and later under the Kingdom of Tungning, which was the first Chinese state in Taiwan.
In 1683, the Qing dynasty of China took control of the island. Then, in 1895, Taiwan was given to Japan. After Japan lost World War II in 1945, the Republic of China took over. The ROC government moved to Taiwan in 1949 after losing the Chinese Civil War to Communist forces. Since then, the ROC's control has been mainly over Taiwan and a few smaller islands.
In the 1960s, Taiwan's economy grew very fast, a period known as the "Taiwan Miracle". Taiwan became a democracy in the late 1980s and early 1990s. People have been able to vote for their president since 1996. Taiwan's economy is one of the largest in the world. It focuses on making steel, machinery, electronics, and chemicals. Taiwan is a developed country with high rankings for civil liberties, healthcare, and human development.
The political status of Taiwan is a complex issue. In 1971, the United Nations decided to recognize the People's Republic of China (PRC) instead of the ROC. The PRC claims Taiwan as its territory and does not have diplomatic ties with countries that recognize the ROC. Taiwan has official diplomatic relations with 12 countries and the Holy See. Many other countries have unofficial offices that act like embassies. Taiwan is a close ally of the United States.
Contents
Understanding Taiwan's Name
The Island's Names: Formosa and Taiwan
The island of Taiwan has had different names over time. In 1542, Portuguese sailors called it Ilha Formosa, which means "beautiful island." This name, Formosa, was used by many Europeans for a long time.
The name "Taiwan" comes from "Tayouan." This was the name of a coastal area where the Dutch East India Company set up a trading post in the 1600s. It was named after a local Indigenous tribe. This area, now Tainan, became an important trading center. The name "Taiwan" became official in 1684 during the Qing dynasty.
The Country's Official Name
The official name of the country is the "Republic of China." When it was founded in 1912, it was often called "China." After the ROC government moved to Taiwan in 1949, it was sometimes called "Nationalist China" or "Free China." This helped tell it apart from "Communist China."
Over time, the country became known simply as "Taiwan." To make things clear, the government started using names like "Republic of China (Taiwan)" in 2005. In many international events, Taiwan uses the name "Chinese Taipei" as a way to participate without causing political issues with the People's Republic of China.
Taiwan's Journey Through History
Early Inhabitants of Taiwan
Taiwan was connected to mainland Asia thousands of years ago. Humans have lived here for at least 20,000 to 30,000 years. Around 6,000 years ago, farmers from what is now southeast China settled Taiwan. These people are the ancestors of today's Taiwanese indigenous peoples. They also started the Austronesian language family.
European and Chinese Rule (1600s-1895)
In 1624, the Dutch East India Company set up a base in Taiwan. They encouraged Chinese farmers to move to the island. By the 1660s, many Chinese people lived there, growing rice and sugar. In 1626, the Spanish Empire also set up a trading base in northern Taiwan, but the Dutch took it over in 1642.
In 1661, a Chinese general named Koxinga took over Taiwan from the Dutch. He was loyal to the old Ming dynasty. His rule, called the Kingdom of Tungning, was independent. But in 1683, the Qing dynasty from China took control of Taiwan.
Under Qing rule, more Chinese people moved to Taiwan. The island became a major producer of sugar and rice. By 1811, over two million Chinese settlers lived in Taiwan. The Qing government mostly left the mountain Indigenous peoples alone. Many rebellions happened during this time, mostly by Chinese settlers.
In 1874, Japan invaded southern Taiwan. This made the Qing government pay more attention to the island. Taiwan became a province of China in 1887, and Taipei became its capital.
Japanese Rule (1895–1945)
After losing a war with Japan in 1895, China gave Taiwan to Japan. Some people tried to resist, but Japanese forces took control. About 6,000 people died in the first year of Japanese rule.
Japan developed Taiwan's industries, railways, and education system. They used Taiwan's resources to help Japan's growth. For example, sugar production greatly increased. However, Chinese and Indigenous people were treated as second-class citizens. Japanese authorities also fought against Indigenous groups in the mountains. Around 1935, Japan tried to make Taiwanese people more like Japanese.
During World War II, Taiwan was an important naval and air base for Japan. Many factories and transport systems were destroyed by Allied bombings. Over 200,000 Taiwanese people served in the Japanese military. After Japan surrendered in 1945, most Japanese residents left Taiwan.
Republic of China in Taiwan (1945–Present)
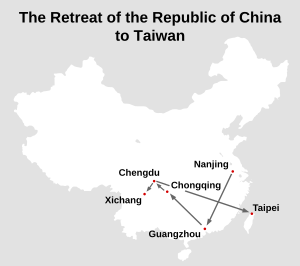
After World War II, Japan gave Taiwan back to the Republic of China (ROC). However, the Chinese Civil War started again on the mainland. In 1949, the Communist forces won and created the People's Republic of China. The ROC government, led by Chiang Kai-shek, moved to Taiwan. About 2 million people, including soldiers and leaders, came with them. They brought many national treasures and gold reserves.
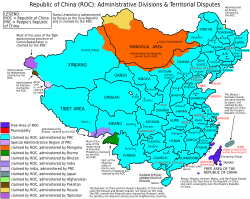
Since 1949, the ROC has controlled Taiwan, Penghu, and some smaller islands. The ROC government continued to claim all of China, but its actual control was limited to these islands. Over time, Taiwan became a strong, democratic country.
Taiwan's Geography and Climate
Island Features and Natural Beauty
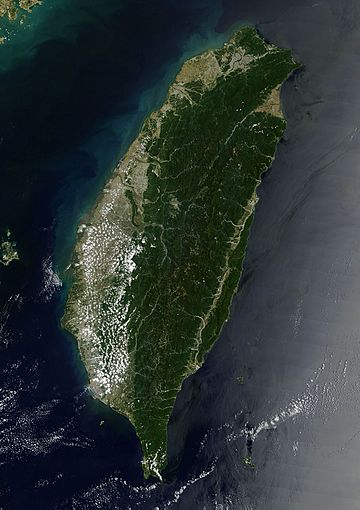
Taiwan's land area is about 36,193 square kilometers, made up of 168 islands. The main island, Formosa, is 99% of this area. It lies about 180 kilometers from mainland China across the Taiwan Strait. To its north is the East China Sea, and to its east is the Philippine Sea.
The island is mostly mountainous in the eastern two-thirds. There are five rugged mountain ranges. The highest peak is Yu Shan at 3,952 meters, making Taiwan the world's fourth-highest island. The western part of the island has flat plains where most people live. Taiwan is in an active earthquake zone, so it experiences many earthquakes. There are also active underwater volcanoes in the Taiwan Strait.
Taiwan has different natural environments, from subtropical forests to monsoon rainforests. The eastern mountains are covered in thick forests and have many kinds of wildlife.
Weather and Climate Patterns
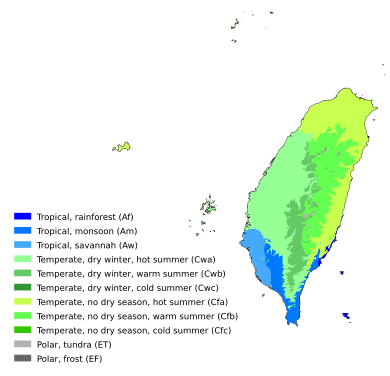
Taiwan is located on the Tropic of Cancer. This means it has a mostly tropical climate. The northern and central parts are subtropical, while the south is tropical. Mountainous areas have a temperate climate.
Taiwan gets a lot of rain, about 2,600 mm per year. The rainy season is in May and June. The whole island is hot and humid from June to September. Typhoons are most common in July, August, and September. In winter (November to March), the northeast has steady rain, but the central and southern parts are mostly sunny.
Due to climate change, Taiwan's average temperature has risen by 1.4°C in the last 100 years. This is twice the global average. Taiwan aims to cut carbon emissions by 20% by 2030 and 50% by 2050.
Geological Formation of Taiwan
Taiwan sits in a complex area where several tectonic plates meet. These plates are constantly moving and pushing against each other. This movement created Taiwan's mountain ranges. The island is still rising because of these plate collisions.
Major earthquake faults run through Taiwan. These faults have caused powerful earthquakes. For example, the "921 earthquake" in 1999 killed over 2,400 people. Most of Taiwan is at a high risk for earthquakes.
Government and Political Status
How Taiwan is Governed
Taiwan's government is based on its 1947 Constitution. It is a democratic republic. The government has five main branches, called Yuan:
- The Executive Yuan (cabinet)
- The Legislative Yuan (parliament)
- The Judicial Yuan (courts)
- The Control Yuan (audit agency)
- The Examination Yuan (civil service exams)
The president is the head of state and commander of the armed forces. The president is elected by popular vote for a four-year term. They can serve a maximum of two terms. The president chooses the members of the cabinet, including a premier.
The Legislative Yuan makes laws. It has 113 members who serve four-year terms. Most members are elected by popular vote. The Judicial Yuan is the highest court. It interprets laws and handles legal cases.

The Control Yuan checks on the actions of the government. It also includes the National Human Rights Commission. The Examination Yuan is in charge of exams for government jobs.
Taiwan's Political Status and Relations
Taiwan's political status is a debated topic. The People's Republic of China (PRC) claims Taiwan as its territory. The PRC says it is the only legal government of China. However, Taiwan has its own currency, passports, stamps, and military. It also has an independently elected president.
Taiwan is not an official member of the United Nations. This is because the UN recognized the PRC in 1971. The PRC tries to stop other countries from formally recognizing Taiwan as an independent country. Taiwan often participates in international events as "Chinese Taipei."
The PRC wants to reunify with Taiwan peacefully. However, it has not ruled out using force. There is a large military presence on the Chinese coast facing Taiwan. The PRC also sends planes into Taiwan's air defense zone.
Taiwan's government has a special council to handle relations with the PRC. Both sides have private organizations that help with communication. In 1992, they had a meeting known as the 1992 Consensus. They agreed there was "one China" but disagreed on what "China" meant. In 2019, Taiwan's President Tsai Ing-wen rejected this consensus.
Taiwan's Military Strength
The Republic of China Army started in 1925. Its goal was to reunite China. After the Chinese Civil War, much of the army moved to Taiwan.
Taiwan's military used to focus on retaking mainland China. Now, its main goal is defense. The military has shifted its focus from the Army to the air force and navy. The military is now controlled by the civilian government.
Taiwan has reduced the size of its military since the 1990s. As of 2021, it has about 215,000 active members. All qualified males must serve in the military for a period. This was cut to four months in 2013 but will be extended to one year in 2024. Taiwan also has about 2.5 million reservists.

Taiwan buys a lot of military equipment from the United States. The Taiwan Relations Act guarantees this support. France and the Netherlands also sold weapons to Taiwan in the past.
The United States does not officially promise to defend Taiwan if it is invaded. However, US President Joe Biden has said several times that the US would intervene. White House officials say US policy has not changed. Other US allies, like Japan and Australia, might also get involved in a conflict.
Taiwan's Thriving Economy

Taiwan's economy grew very quickly in the late 20th century. This is known as the "Taiwan Miracle". Taiwan is one of the "Four Asian Tigers" along with Hong Kong, South Korea, and Singapore. As of 2022, Taiwan has the 21st largest economy in the world.
Agriculture now makes up less than 2% of Taiwan's economy. Instead, Taiwan's economy is driven by many small and medium-sized enterprises. These businesses focus on high-tech industries. Many traditional industries have moved overseas.
Taiwan has a strong, capitalist economy that relies on exports. The government is less involved in businesses now. Exports are the main reason for Taiwan's industrial growth. Taiwan has a large trade surplus and holds a lot of foreign currency reserves. In 2022, Taiwan's total trade was US$907 billion. Its biggest trading partners are China, the United States, and Japan.
Since the 1990s, Taiwan and China have had strong economic ties. China became Taiwan's largest export market in 2002. Taiwanese companies have invested over US$200 billion in China. Many Taiwanese people also work in China. Some worry that Taiwan is becoming too dependent on China's economy. Others believe that close economic ties make a military conflict less likely.

Taiwan is a major player in making advanced computer chips. Companies like Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. (TSMC) and United Microelectronic Corporation (UMC) are world leaders. TSMC is the world's biggest semiconductor manufacturing company. Other famous Taiwanese tech companies include Acer Inc., Asus, and Foxconn.
Getting Around Taiwan
Taiwan has a well-developed transportation system. Scooters are very popular for getting around. In 2019, there were twice as many scooters as cars.
Highways and railways are mostly found near the coasts, where most people live. Taiwan has 1,619 kilometers of motorways. Railways are mainly for passengers. The Taiwan Railways Administration (TRA) has a route around the island. The Taiwan High Speed Rail (THSR) runs fast trains on the west coast. Major cities like Taipei and Kaohsiung have their own metro systems.
Taiwan has several major airports, including Taiwan Taoyuan and Kaohsiung. The largest airlines are China Airlines and EVA Air.
There are seven international seaports. Kaohsiung is the busiest, handling most of Taiwan's cargo.
Education in Taiwan

Taiwan values education highly. This focus has helped the country achieve top rankings in global education. Taiwanese students do very well in math, science, and reading. In 2015, they scored among the best in the world on the PISA test.
Taiwan's education system has helped its economy grow. It has created a highly educated workforce. The university acceptance rate is very high, over 95% since 2008. This makes Taiwan one of the most educated countries. About 68.5% of high school students go on to university.
However, some people criticize the system for putting too much pressure on students. It is also said to produce too many university graduates for the available jobs. This can lead to unemployment or underemployment. Many students attend cram schools to prepare for exams.
Taiwan's economy needs people with higher education, especially in science and engineering. Although only nine years of schooling are required, most students continue their education. As of 2020, Taiwan's literacy rate was 99.03%.
People and Culture of Taiwan
Taiwan's Population and Cities
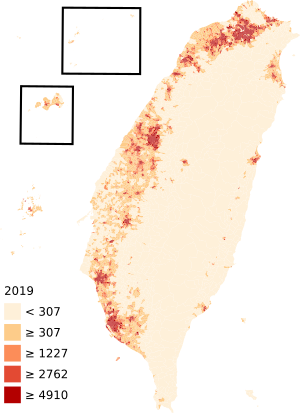
Taiwan has about 23.4 million people. Most live on the main island. Smaller populations live on islands like Penghu, Kinmen, and Matsu.
Taiwan has several large cities. New Taipei City is the most populated, followed by Taichung, Kaohsiung, and Taipei. These cities are important centers for living and working.
Diverse Ethnic Groups
Most of Taiwan's population (95%) is Han. These are mostly descendants of Hoklo and Hakka people who came from mainland China centuries ago. A smaller group, called waishengren, are descendants of Chinese nationalists who moved to Taiwan in 1949.
About 2.4% of the population are Taiwanese indigenous peoples. The government recognizes 16 different Indigenous groups. They mostly live in the eastern half of the island and on Orchid Island.
Languages Spoken in Taiwan
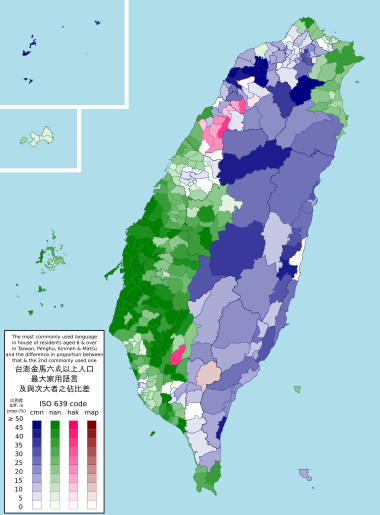
Taiwan does not have one single official language. Mandarin is the main language for business and education. Most people speak it. Traditional Chinese is used for writing.
About 70% of Taiwanese people speak Taiwanese Hokkien as their native language. The Hakka people, about 14-18% of the population, speak Hakka. While Mandarin is used in schools and media, other Chinese languages are becoming more popular again.
Formosan languages are spoken by the Indigenous peoples. These languages are part of the Austronesian language family, not Chinese. They are written using the Latin alphabet. However, their use has declined as Mandarin has become more common.
Taiwan is officially multilingual. Hakka and Indigenous languages are now recognized as national languages.
Religion and Beliefs
Estimated religious composition in 2020 Chinese folk religion (including Confucianism) (43.8%) Buddhists (21.2%) Others (including Taoists) (15.5%) Unaffiliated (13.7%) Christians (5.8%) Muslims (1%)
Taiwan's Constitution protects freedom of religion. The government respects people's right to practice their beliefs. Taiwan ranks highly for religious freedom.
The largest religions in Taiwan are Buddhism, Taoism, and Chinese folk religion. Many people also have no religion. There are smaller groups of Christians and Muslims. Confucianism is a major part of both Chinese and Taiwanese culture. Many Taiwanese people combine Confucian teachings with their religious beliefs.
Taiwan has many religious buildings. There are over 15,000 places of worship, including temples and churches. This is a very high number for its size. Taiwan is considered the most religious region in the Chinese-speaking world.
Healthcare in Taiwan
Taiwan has a healthcare system called National Health Insurance (NHI), started in 1995. It is a single-payer system, meaning the government manages healthcare funds. The system aims to give all citizens equal access to healthcare. By 2004, 99% of the population was covered.
NHI is funded by premiums and government money. Low-income families, veterans, and children under three do not have to pay co-payments. Most healthcare providers are private.
The system has improved healthcare for lower-income citizens. A survey showed that most patients are very satisfied with hospital services.
Taiwan's disease control authority is the Taiwan Centers for Disease Control (CDC). After the SARS outbreak in 2003, Taiwan set up the Central Epidemic Command Center (CECC). This center has been important in managing epidemics, including COVID-19.
In 2019, the infant mortality rate was 4.2 deaths per 1,000 live births. Life expectancy in 2020 was 77.5 years for males and 83.9 years for females.
Taiwanese Culture and Arts
Taiwan's culture is a mix of different influences. It includes traditional Chinese culture, Indigenous cultures, Japanese influence, and Western values.
During a period of martial law, the Kuomintang government promoted traditional Chinese culture. This was to show that Taiwan represented true Chinese culture, unlike Communist China. This led to some aspects of Chinese culture, like Traditional Chinese, being better preserved in Taiwan.

After martial law ended, Taiwan became more democratic. This led to a flourishing of Taiwanese literature and media. Taiwan is ranked as one of the freest places in Asia for speech and expression. Many people from Hong Kong have moved to Taiwan seeking more freedom.
Taiwan's unique history has created distinct traditions. This includes food and music. The idea of Taiwanese multiculturalism helps include all groups in defining Taiwanese culture.
Arts and Entertainment
Taiwan has many famous classical musicians. Popular music artists include Teresa Teng and Jay Chou. Bands like Mayday and Chthonic are also well-known.
Taiwanese films have won international awards. Director Ang Lee has made famous movies like Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon and Life of Pi. Taiwan hosts the Golden Horse Film Festival and Awards.
The National Palace Museum has over 650,000 pieces of ancient Chinese art. It is one of the world's greatest collections.
Delicious Taiwanese Cuisine
Bubble tea, created in Taiwan in the 1980s, is now popular worldwide. Taiwanese food history is linked to migration and colonization. Famous dishes include Taiwanese beef noodle soup, Gua bao, Taiwanese fried chicken, and Aiyu jelly.
Taiwanese night markets are known for their amazing street food. The Guardian newspaper called them the "best street food markets in the world."
Sports in Taiwan
Baseball is considered Taiwan's national sport. It is very popular to watch. Taiwan's men's baseball team and women's softball team are ranked among the best in the world. The Chinese Professional Baseball League (CPBL) started in 1989. Many Taiwanese players have also played in Major League Baseball (MLB) in the US.
Basketball is another major sport in Taiwan. There are professional basketball leagues like the P. League+ and T1 League. Other team sports include volleyball and football.
Taiwan competes in international sports events as "Chinese Taipei." Taiwan has hosted major events like the 2009 World Games and the 2017 Summer Universiade.

Taekwondo is a very successful combat sport in Taiwan. Taiwanese athletes won the country's first two Olympic gold medals in taekwondo in 2004.
Taiwan also has many excellent players in individual sports. These include badminton, tennis, table tennis, and golf. Tai Tzu-ying is a top badminton player, and Yani Tseng is a famous golfer.
Taiwan's Calendar System
Taiwan uses the standard Gregorian calendar for most daily activities. The year is often shown using the Minguo era system. This system starts from 1912, the year the ROC was founded. So, 2023 is year 112 Minguo.

The Chinese calendar is a Lunisolar calendar. It is still used for traditional festivals like Chinese New Year and the Dragon Boat Festival.
Images for kids
-
Japanese colonial soldiers march Taiwanese captured after the Tapani Incident from the Tainan jail to court, 1915.
-
With President Chiang Kai-shek, the US President Dwight D. Eisenhower waved to crowds during his visit to Taipei in June 1960.
-
US Secretary of State Hillary Clinton and Taiwan's special envoy to the APEC summit, Lien Chan, November 2011.
-
The ruling DPP has traditionally leaned in favour of Taiwan independence and rejects the so-called "One-China policy".
-
The Presidential Southern Office in Fengshan District, Kaohsiung opened on 10 March 2017.
-
Tangwai (Independent) Taiwanese-born politician Wu San-lien (2L) celebrated his landslide victory (65.5%) in Taipei City's first mayoral election in January 1951 with supporters.
-
Taipei 101 held the world record for skyscraper height from 2004 to 2010.
-
Rice paddy fields in Yilan County.
See also
 In Spanish: República de China para niños
In Spanish: República de China para niños
- Index of Taiwan-related articles
- Outline of Taiwan