Chinese language facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Chinese |
|
|---|---|
| 汉语/漢語,华语/華語 or 中文 Hànyǔ, Huáyǔ or Zhōngwén |
|

Hànyǔ (Chinese) written in Hanzi
|
|
| Native to | People's Republic of China (PRC, commonly known as China), Republic of China (ROC, commonly known as Taiwan), Canada, Peru, Thailand, Vietnam, Malaysia, Brunei, Singapore, Indonesia, Mauritius, Australia, the United States, the Philippines and other places with Chinese communities |
| Native speakers | (1.2 billion cited 1984–2000) |
| Language family |
Sino-Tibetan
|
| Standard forms | |
| Dialects |
Jin
Huizhou
Wu (including Shanghainese)
Hunanese
Yue (including Cantonese-Taishanese)
Pinghua
Shaojiang
Northern Min
Eastern Min (including Fuchow)
Central Min
Pu Xian
Southern Min (including Amoy, Taiwanese)
Teochew (including Swatow, Chaozhou, Jieyang, parts of Shanwei/Meizhou)
|
| Writing system | Chinese characters, zhuyin fuhao, pinyin, Xiao'erjing |
| Official status | |
| Official language in |
|
| Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by | In the PRC: National Commission on Language and Script Work In the ROC: National Languages Committee In Singapore: Promote Mandarin Council/Speak Mandarin Campaign |
| Linguasphere | 79-AAA |
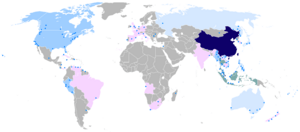
Map of the Sinophone world.
Information: Countries identified Chinese as a primary, administrative or native language Countries with more than 5,000,000 Chinese speakers Countries with more than 1,000,000 Chinese speakers Countries with more than 500,000 Chinese speakers Countries with more than 100,000 Chinese speakers Major Chinese speaking settlements |
|
| This article contains Chinese text. Without the correct software, you may see question marks, boxes, or other symbols instead of Chinese characters. |
| Chinese languages (Spoken) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 漢語 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 汉语 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | Han language | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese language (Written) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 中文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | Chinese text | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Chinese language is a group of languages spoken by Chinese people in China and many other parts of the world. It belongs to a language family called Sino-Tibetan. This family includes many languages spoken across Asia.
Chinese is not just one language. It includes many different regional varieties. The main ones are Mandarin, Wu, Yue, and Min. These varieties are so different that speakers often cannot understand each other. Because of this, many language experts consider them separate languages.
When we say 'Chinese', we might mean the spoken languages or the written system. Even though there are many spoken Chinese languages, they mostly use the same writing system. This means people who speak different Chinese languages can still read the same newspaper.
The official language in China is Standard Chinese. In English, we often call it Mandarin. In mainland China, it's known as "Pǔtōnghuà" (meaning "common speech"). In Taiwan, it's called "Guóyǔ" (meaning "national language"). Mandarin is taught all over China and used in official documents.
Chinese is mainly used by the Han people and other groups in China. It is almost always written using Chinese characters. These characters are symbols that represent words or ideas, called logograms. They also give some clues about how to say a word. However, the same character can be pronounced very differently in different Chinese languages. This is because Chinese characters have been around for at least 3,500 years.
Since Chinese does not have an alphabet, writing down pronunciations for dictionaries was a challenge. Today, Mandarin uses Hanyu Pinyin. This system uses Roman letters to show how Chinese words sound.
All Chinese languages use tones. This means that the meaning of a word can change depending on the pitch of your voice (whether it's high, low, or rising).
Contents
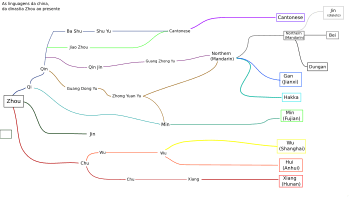
Chinese Language Families
The Chinese language is like a big tree with deep roots. This tree started growing thousands of years ago. Today, it has several main "limbs" or branches. Some people call these branches "dialects," while others call them separate "languages."
Just like Romance languages (like Spanish or French) all came from Latin, the Chinese languages also share a common origin. This is why they have many things in common, even though they sound different.
Here are the main groups of Chinese languages, listed by how many people speak them:
- Guan (also known as Mandarin): Spoken by about 850 million people.
- Wu: This group includes Shanghainese and is spoken by about 90 million people.
- Yue (also known as Cantonese): Spoken by about 80 million people.
- Min: This group includes Hokkien and Taiwanese, spoken by about 50 million people.
- Xiang: Spoken by about 35 million people.
- Hakka: Spoken by about 35 million people.
- Gan: Spoken by about 20 million people.
Traditional and Simplified Chinese Characters
In 1956, the government of the People's Republic of China introduced simplified Chinese characters. The goal was to make learning, reading, and writing Chinese easier for everyone.
Today, people in Mainland China and Singapore use these simpler characters. However, in Hong Kong, Taiwan, and other places where Chinese is spoken, people still use the more traditional characters.
Other languages also use Chinese characters. The Korean language uses them for some words, where they are called Hanja. The Japanese language uses them even more often, calling them Kanji.
A well-educated Chinese person today knows about 6,000 to 7,000 characters. To read a newspaper in Mainland China, you need to know around 3,000 characters. However, you can still understand a lot with just the 400 most common characters, even if you have to guess some less-used words.
Before 1956, all Chinese was written using only Traditional Characters. At that time, most Chinese people could not read or write. The government believed that making the characters simpler would help more people learn. This change has helped many people in China become able to read and write.
Common Chinese Phrases
Here are some examples of words and sentences in Mandarin Chinese. The table shows the Simplified Characters (used in Mainland China) on the left and Traditional Characters (used in Hong Kong and Taiwan) on the right. The pronunciation is given using the pinyin system.
| Word | Pinyin | Simplified | Traditional |
|---|---|---|---|
| How are you? | Nǐ hǎo ma? | 你好吗? | 你好嗎? |
| What is your name? | Nǐ jiào shénme míngzi? | 你叫什么名字? | 你叫什麽名字? |
| America | Měiguó | 美国 | 美國 |
| France | Fǎguó | 法国 | 法國 |
| Britain | Yīngguó | 英国 | 英國 |
| Germany | Déguó | 德国 | 德國 |
| Russia | Éguó | 俄国 | 俄國 |
| Thailand | Tàiguó | 泰国 | 泰國 |
| Poland | Bōlán | 波兰 | 波蘭 |
| Japan | Rìbĕn | 日本 | 日本 |
| Pakistan | Bājīsītǎn | 巴基斯坦 | 巴基斯坦 |
Related Pages
Images for kids
-
"Preface to the Poems Composed at the Orchid Pavilion" by Wang Xizhi, written in semi-cursive style
See also
 In Spanish: Idioma chino para niños
In Spanish: Idioma chino para niños