Singapore facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of Singapore
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
 |
|
| Capital | Singapore (city-state) 1°17′N 103°50′E / 1.283°N 103.833°E |
| Largest planning area by population | Tampines |
| Official languages | |
| National language | Malay |
| Ethnic groups
(2023)
|
|
| Religion
(2020)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Singaporean |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic |
| Tharman Shanmugaratnam | |
| Lawrence Wong | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Independence
from the United Kingdom and Malaysia
|
|
|
• Self-governance
|
3 June 1959 |
| 16 September 1963 | |
| 9 August 1965 | |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
735.6 km2 (284.0 sq mi) (176th) |
| Population | |
|
• 2024 estimate
|
|
|
• Density
|
7,804/km2 (20,212.3/sq mi) (3rd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2023) | medium |
| HDI (2022) | very high · 9th |
| Currency | Singapore dollar (S$) (SGD) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (Singapore Standard Time) |
| Calling code | +65 |
| ISO 3166 code | SG |
| Internet TLD | .sg |
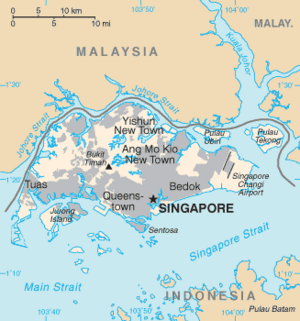
Singapore, also known as the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. It is made up of one main island, called Singapore Island, and 63 smaller islands. Singapore is located just north of the equator. It is near the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula.
Singapore has a long and interesting history that goes back over 800 years. It was once a busy trading port known as Temasek. Modern Singapore began in 1819 when Stamford Raffles set up a trading post for the British Empire. Singapore became a Crown colony under Britain in 1867.
During World War II, Japan took control of Singapore in 1942. After the war, it returned to British rule. Singapore gained its own government in 1959. In 1963, it joined the new country of Malaysia. However, Singapore left Malaysia in 1965 and became an independent country. Even without many natural resources, Singapore quickly grew into one of the richest countries in Asia.
Today, Singapore is a very developed country. It has one of the highest incomes per person in the world. It is a major hub for air travel, banking, and shipping. Singapore is known for its high quality of life. It ranks well in education, healthcare, and housing. Singaporeans also have long lives and fast internet. It is a very safe country with low levels of corruption.
Singapore has a diverse population. It has four official languages: English, Malay, Mandarin, and Tamil. English is the main language used for business and government. The country celebrates different cultures and races.
Singapore is a parliamentary republic. This means its government is chosen by the people. The People's Action Party (PAP) has been in power since 1959. Singapore is a founding member of ASEAN. It also hosts many international meetings.
Contents
- What's in a Name? Singapore's Story
- Singapore's Journey Through Time
- Singapore's Strong Economy
- Singapore's Geography and Nature
- Getting Around Singapore
- Key Industries in Singapore
- People and Culture of Singapore
- Education in Singapore
- Healthcare in Singapore
- Culture and Arts in Singapore
- Media and Communication
- Images for kids
- See also
What's in a Name? Singapore's Story
The name "Singapore" comes from the Malay word Singapura. This word means 'lion city' in an old language called Sanskrit. The main island was once called Pulau Ujong. This means 'island at the end of a peninsula' in Malay.
Another old name for Singapore was Temasek. This might mean Sea Town. It comes from the Malay word tasek, meaning 'sea' or 'lake'.
The story goes that a prince named Sang Nila Utama from Sumatra saw a strange animal he thought was a lion. He then named the city Singapura. Lions were seen as symbols of power.
During World War II, when Japan took over, Singapore was called Syonan-to. This means 'light of the south'. Today, Singapore is often called the "Garden City" because of its many parks. It is also sometimes called the "Little Red Dot" because of its small size on a map.
Singapore's Journey Through Time
Early Days: Ancient Singapore
The Kingdom of Singapura was founded in 1299. In the 14th century, Singapore, then called Temasek, was a busy trading port. It was influenced by the Majapahit Empire and the Siamese kingdoms. Around the late 1300s, its ruler was attacked. This forced him to move to Malacca. Singapore became less important for about 200 years. In 1613, Portuguese raiders burned down the settlement.
British Rule and Growth

In 1819, a British governor named Stamford Raffles arrived. He saw that Singapore was a great place for a new port. He made a deal with the local ruler, Sultan Hussein. This allowed the British to set up a trading post.

By 1824, the whole island became part of the British Empire. Singapore joined the Straits Settlements in 1826. It became the main city in the region in 1836. Before Raffles arrived, only about a thousand people lived there. By 1860, the population grew to over 80,000, mostly Chinese. Singapore became a major center for rubber trade in the 1890s.
Singapore was not much affected by First World War. After the war, the British built a large naval base in Singapore. It was called the "Gibraltar of the East." However, the British navy was busy defending Britain during World War II. This left Singapore open to attack.
Japanese Occupation During World War II

Japan invaded Singapore in 1942. The British forces surrendered on February 15, 1942. This was a huge defeat for Britain. The Japanese occupation was a turning point for Singapore. Many Chinese people were killed during this time.
After the War: Towards Self-Rule
After Japan surrendered in 1945, Singapore faced problems. There was violence and a lack of food. The British returned in September 1945. Singapore became a separate British colony in 1946.
In the 1950s, there were protests and riots. Singapore gained full self-government in 1959. This meant it could manage its own affairs, except for defense and foreign relations. The People's Action Party (PAP) won the election that year.
Joining and Leaving Malaysia
Leaders of the PAP believed Singapore's future was with Malaya. They thought joining Malaya would help Singapore's economy. In 1963, Singapore joined Malaya, North Borneo, and Sarawak to form Malaysia.
However, Singapore and the Malaysian government disagreed on many things. This led to tensions and even race riots in 1964. On August 9, 1965, the Malaysian Parliament voted to remove Singapore from Malaysia. Singapore then became a new, independent country.
The Republic of Singapore Today

After leaving Malaysia, Singapore became the Republic of Singapore on August 9, 1965. Lee Kuan Yew became its first prime minister. Singapore joined the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) in 1967.
Lee Kuan Yew focused on fast economic growth. Singapore quickly developed high-tech industries. The Singapore Changi Airport opened in 1981. The Port of Singapore became one of the busiest in the world. Tourism also grew a lot.
The PAP has stayed in power since independence. Singapore has made some political changes over the years. In 1990, Goh Chok Tong became the second prime minister. In 2004, Lee Hsien Loong, Lee Kuan Yew's son, became the third. On May 15, 2024, Lawrence Wong became Singapore's fourth Prime Minister. He is the first prime minister born after Singapore's independence.
Singapore's Strong Economy
Singapore has a very strong and developed market economy. It is known as one of the Four Asian Tigers. This means it is one of the fast-growing economies in Asia. Singapore's economy is seen as free and good for business.
Singapore attracts many foreign companies. This is because of its good location, skilled workers, and low taxes. It also has modern buildings and little corruption. Singapore is one of the most competitive economies in the world.

The money used in Singapore is the Singapore dollar (S$). Singapore has a lot of money saved up from trade. It is also known for its low tax rates. This attracts wealthy people and businesses.
The government helps people in need. It provides financial aid, free medical care, and help with school fees. Singapore has a high quality of life. It ranks well in the Human Development Index.
Singapore's Geography and Nature
Singapore is made up of 63 islands. The largest is Pulau Ujong, which is the main island. Two man-made bridges connect Singapore to Johor, Malaysia. These are the Johor–Singapore Causeway and the Tuas Second Link. Some other large islands are Jurong Island and Sentosa. The highest natural point is Bukit Timah Hill.
Singapore has grown its land area a lot by reclaiming land from the sea. This means adding sand and earth to create new land. The country plans to add even more land in the future.
Nature and Green Spaces

Because Singapore is so developed, it has lost many of its original forests. However, the government works hard to protect its remaining wildlife. In 1967, Singapore started a plan to become a "garden city." This means creating many parks and green spaces.
Nearly 10% of Singapore's land is now parks and nature reserves. The Singapore Botanic Gardens is a famous tropical garden. It is also a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Climate: Tropical Weather

Singapore has a tropical rainforest climate. This means it has no clear seasons. It is always warm, humid, and rainy. Temperatures are usually between 23 and 32 degrees Celsius (73 to 90 degrees Fahrenheit). There is a wetter season from November to February.
Sometimes, from July to October, there is haze. This comes from bush fires in nearby Indonesia. Singapore is working to fight climate change. It plans to spend a lot of money to protect its low-lying coast from rising sea levels. Singapore also has a carbon tax to reduce pollution.
Water Supply: A National Priority
Singapore sees water as very important for its safety. The government wants to save water. Water is available to everyone and is of high quality. Singapore gets its water from Malaysia, collects rainwater, reclaims used water (called NEWater), and cleans seawater. Singapore aims to be self-sufficient in water by 2061.
Getting Around Singapore
Land Transport
Singapore has a good road system. To control traffic and pollution, the number of private cars is limited. Buying a car in Singapore is very expensive. People must pay high fees and get a special permit to own a car for 10 years. Cars drive on the left side of the road.
Singapore has an excellent public transport system. This includes trains (MRT and LRT) and buses. There are six MRT lines and three LRT lines. Taxis are also popular and affordable. The Johor–Singapore Causeway is one of the busiest border crossings in the world.
Air Travel
Singapore is a major international transport hub for air travel. Changi Airport is a very important airport in Southeast Asia. It connects Singapore to hundreds of cities worldwide. It has often been named one of the best airports in the world.
Singapore Airlines is Singapore's main airline. It is known as a top airline globally. It has won many awards.
Sea Transport
The Port of Singapore is one of the busiest ports in the world. It handles a huge amount of shipping. It is also the world's busiest port for moving goods from one ship to another. The port is a major center for ship repair and refueling.
Key Industries in Singapore
Singapore is a global leader in many industries. It is a major center for currency trading and finance. It is also a big hub for oil refining and trading. Singapore is a top producer of oil rigs and a leader in ship repair.
The economy is diverse. Its main areas are financial services, manufacturing, and oil refining. Singapore exports refined oil, computer chips, and computers. Other important industries include electronics and chemicals. Singapore is also very innovative, ranking high in global innovation indexes.
Many of Singapore's largest companies are in telecommunications, banking, and transport. Famous global companies include Singapore Airlines, Changi Airport, and the Port of Singapore. These companies have won many awards in their fields. Singapore has signed many free-trade agreements with other countries.
Tourism: A Welcoming City
Tourism is a big part of Singapore's economy. In 2018, over 18 million tourists visited Singapore. This is more than three times Singapore's population! Singapore is one of the most visited cities in the world.
Famous landmarks include the Merlion statue, Marina Bay Sands, and Gardens by the Bay. The Jewel Changi Airport and Orchard Road shopping area are also popular. The island of Sentosa has many resorts and attractions. The Singapore Botanic Gardens is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Other popular places are the Singapore Zoo, River Wonders, Bird Paradise, and Night Safari. Singapore also promotes itself as a place for medical tourism. Many foreigners come here for medical care.
People and Culture of Singapore

Singapore has a mix of different languages, religions, and cultures. In mid-2023, Singapore's population was about 5.9 million. About 74% of residents are of Chinese background. About 13.5% are Malay, and 9% are Indian.
Singapore's birth rate is very low. So, the government has programs to encourage families to have more children. Singapore also welcomes foreign workers and residents. Most households in Singapore own their homes. Many live in high-rise public housing apartments.
Religions in Singapore
| Religion in Singapore, 2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Religion | Percent | |||
| Buddhism | 31.1% | |||
| No religion | 20.0% | |||
| Christianity | 18.9% | |||
| Islam | 15.6% | |||
| Taoism and folk religion | 8.8% | |||
| Hinduism | 5.0% | |||
| Other religions | 0.6% | |||
Many different religions are practiced in Singapore. No single religion is followed by the majority of people. Buddhism is the most common religion. Christianity is second, followed by Islam, Taoism, and Hinduism. About one-fifth of the population has no religion.
Languages Spoken in Singapore
Singapore has four official languages: English, Malay, Mandarin, and Tamil.
| Language used most frequently at home | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language | Percent | |||
| English | 48.3% | |||
| Mandarin | 29.9% | |||
| Malay | 9.2% | |||
| Other Sinitic languages | 8.7% | |||
| Tamil | 2.5% | |||
| Others | 1.4% | |||
English is the common language for business, government, and education. The Constitution of Singapore is written in English. Malay is the national language. It is used in the national anthem, Majulah Singapura.
Most Singaporeans speak two languages. They learn English and their "mother tongue" (second language) in school. This helps keep their cultural identity. English is the most spoken language at home. Mandarin is the second most spoken.
Singaporean English is based on British English. There is also a local way of speaking English called Singlish. The government encourages people to use Standard English.
Education in Singapore

Education in Singapore is mostly supported by the government. English is the language used for teaching in all public schools. All subjects are taught in English, except for the "mother tongue" language.
Education has three main stages: primary, secondary, and pre-university. Primary school lasts for six years and is required. Secondary school lasts four to five years. After that, students can go to junior colleges or other schools for pre-university education. Singapore has six public universities. The National University of Singapore is one of the top universities in the world.
Students take national exams after each stage of education. Singaporean students do very well in international tests for math, science, and reading.
Healthcare in Singapore
Singapore has a very good healthcare system. It has one of the lowest infant death rates in the world. Singaporeans also have one of the longest life expectancies.
The government helps people pay for healthcare. It has a system called "3M." This includes Medifund for those who cannot afford care, Medisave for savings, and Medishield for insurance. Public hospitals are run by the government.
Culture and Arts in Singapore

Singapore has many different languages, religions, and customs. The government works to create a unique Singaporean identity. It also focuses on meritocracy. This means people are judged based on their abilities.
The national flower is the orchid, Vanda 'Miss Joaquim'. Singapore is known as the Lion City. The Merlion is a famous symbol. Major religious holidays are celebrated by everyone.
Arts and Creativity
The National Arts Council helps develop the arts. The National Gallery Singapore and Singapore Art Museum show many artworks. The ArtScience Museum combines art and science. The Esplanade is Singapore's largest performing arts center.
Singapore has literature in English, Malay, Mandarin, and Tamil. Many works have been translated. Singapore also has a diverse music scene. It includes pop, rock, folk, and classical music. The Singapore Symphony Orchestra is well-known.
Delicious Singaporean Food
Singapore is famous for its food. It mixes Chinese, Malay, and Indian flavors. Hainanese chicken rice is considered Singapore's national dish.
You can find food everywhere, from open-air hawker centers to fancy restaurants. Hawker centres are very popular. They have many food stalls with different dishes. The largest hawker center is in Chinatown Complex. It has the cheapest Michelin-starred meal in the world.
Sports and Fun

Sports clubs started in Singapore in the 1800s. Tan Howe Liang was Singapore's first Olympic medalist in 1960. Singapore hosted the first 2010 Summer Youth Olympics.
Indoor and water sports are very popular. Joseph Schooling won Singapore's first Olympic gold medal in swimming in 2016. Singapore's sailors are also among the best in the world. The women's table tennis team won a silver medal at the 2008 Beijing Olympics. In 2021, Loh Kean Yew became a badminton World Champion.
Singapore hosts the Singapore Grand Prix, a Formula One World Championship race. It was the first F1 night race.
Media and Communication
Companies linked to the government control most of Singapore's media. MediaCorp runs most TV and radio stations. There are six free TV channels.
Singapore's media is sometimes seen as very controlled. However, internet access is widely available. Singapore has one of the highest rates of smartphone use in the world.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Singapur para niños
In Spanish: Singapur para niños
 | Jessica Watkins |
 | Robert Henry Lawrence Jr. |
 | Mae Jemison |
 | Sian Proctor |
 | Guion Bluford |