Malay Peninsula facts for kids
Location of the Malay Peninsula
|
|
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Southeast Asia |
| Coordinates | 7°00′N 100°00′E / 7.000°N 100.000°E |
| Adjacent bodies of water | Indian Ocean, Pacific Ocean |
| Area | 242,363.8 km2 (93,577.2 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 2,187 m (7,175 ft) |
| Highest point | Mount Tahan |
| Administration | |
| Peninsular Malaysia | |
| Largest settlement | Kuala Lumpur |
| Region | Tanintharyi |
| District | Kawthaung |
| Largest settlement | Kawthaung |
| Southern Thailand | |
| Largest settlement | Hat Yai |
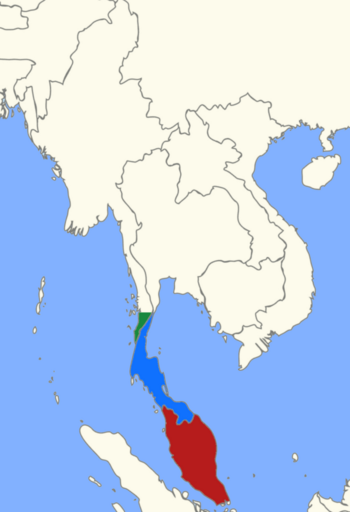
The Malay Peninsula is a long piece of land in Mainland Southeast Asia. It stretches from north to south and is the southernmost point of the Asian continent. This area includes Peninsular Malaysia, the southern part of Thailand, and the very tip of Myanmar (called Kawthaung). The island country of Singapore also has strong historical and cultural ties to this region.
The first people to live here were the Orang Asli and the Malays. The Titiwangsa Mountains run through the peninsula, forming its central backbone. These mountains are part of a larger system that starts in Tibet. The Strait of Malacca separates the Malay Peninsula from the island of Sumatra. To the south, the Straits of Johor separate it from Singapore.
Contents
What Does "Malay Peninsula" Mean?
The name "Malay Peninsula" comes from the Malay term Tanah Melayu. Tanah means "land" and Melayu refers to the Malays. So, it simply means "the Malay land." This term has been used for a long time, appearing in old Malay stories from the 1600s.
For example, in the famous story Hikayat Hang Tuah, Tanah Melayu often refers to the areas controlled by the Malacca Sultanate. In the early 1500s, a Portuguese explorer named Tomé Pires used a similar term, Terra de Tana Malaio. He used it to describe the southeastern part of Sumatra.
Ancient texts from India also mention a place called Malayadvipa, which means "mountain-insular continent." Some scholars believe this might have been the Malay Peninsula. Another Indian text mentions Malaiur, a kingdom with a strong mountain as its defense. The Greek geographer Ptolemy called a region here Golden Chersonese or Maleu-kolon. Chinese records from the Yuan dynasty also talked about Ma-li-yu-er, a nation in the Malay Peninsula. Even Marco Polo mentioned a kingdom called Malauir in his travel stories.
In the early 1900s, the term Tanah Melayu became important for Malay people who wanted to unite all the Malay states. This idea largely came true when the "Federation of Malaya" was formed in 1948.
Amazing Nature and Animals
The Malay Peninsula is covered in thick, green tropical forests. In the lowlands, you'll find tall dipterocarp trees. Higher up in the mountains, there are evergreen trees like those in the beech and laurel families. You can also find tropical conifer trees here.
These forests are home to thousands of different plants and animals. Many large, endangered mammals live here. These include the Asian elephant, gaur (a type of wild cattle), tiger, sun bear, Malayan tapir, clouded leopard, and siamang (a type of gibbon). Sadly, the Sumatran rhinoceros used to live here, but the last ones in Malaysia died in 2019. Now, only a few remain on the island of Sumatra.
The peninsula has different natural areas called ecoregions. The northern part, including the Tenasserim Hills, has semi-evergreen rainforests. A special plant boundary crosses the peninsula in southern Thailand. North of this line, trees often lose their leaves in dry seasons. South of it, in the Sundaland area, there's more rain all year, so trees stay green.
Peninsular Malaysia has three main ecoregions. The Peninsular Malaysian montane rain forests are found in the mountains above 1,000 meters. The lower lands and hills are part of the Peninsular Malaysian rain forests. There are also unique Peninsular Malaysian peat swamp forests in wet, low-lying areas on both sides of the peninsula. Both coasts are also lined with large areas of mangrove trees.
Countries and Regions in the Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula is shared by three countries: Malaysia, Myanmar, and Thailand.
Malaysia
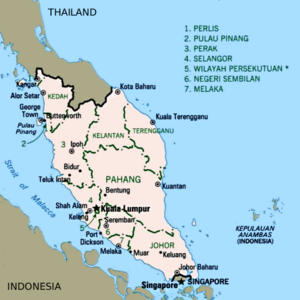
The Malaysian part of the peninsula is called Peninsular Malaysia. It includes many states and two special federal territories. Here's a look at the states:
| Flag | Emblem / Achievement |
State | Capital | Royal Capital | Area (km2) | Head of State | Head of Government |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Johor | Johor Bahru | Muar | 19,166 | Sultan | Menteri Besar | ||
| Kedah | Alor Setar | Anak Bukit | 9,492 | Sultan | Menteri Besar | ||
| Kelantan | Kota Bharu | Kubang Kerian | 15,040 | Sultan | Menteri Besar | ||
| Malacca | Malacca City | — | 1,712 | Yang di-Pertua Negeri (Governor) |
Chief Minister | ||
| Negeri Sembilan | Seremban | Seri Menanti | 6,658 | Yang di-Pertuan Besar (Grand Ruler) |
Menteri Besar | ||
| Pahang | Kuantan | Pekan | 35,965 | Sultan | Menteri Besar | ||
| Penang | George Town | — | 1,049 | Yang di-Pertua Negeri (Governor) |
Chief Minister | ||
| Perak | Ipoh | Kuala Kangsar | 21,146 | Sultan | Menteri Besar | ||
| Perlis | Kangar | Arau | 819 | Raja | Menteri Besar | ||
| Selangor* | Shah Alam | Klang | 7,951 | Sultan | Menteri Besar | ||
| Terengganu | Kuala Terengganu | Kuala Terengganu | 12,958 | Sultan | Menteri Besar |
* Two federal territories are located within Selangor. These are Kuala Lumpur and Putrajaya.
Myanmar
- Tanintharyi Region
Thailand
- Chumphon
- Krabi
- Nakhon Si Thammarat
- Narathiwat
- Pattani
- Phang Nga
- Phatthalung
- Phuket
- Ranong
- Satun
- Songkhla
- Surat Thani
- Trang
- Yala
See Also
 In Spanish: Península de Malaca para niños
In Spanish: Península de Malaca para niños
- Extreme points of Asia
- Geography of Malaysia
- Golden Chersonese
- Malay Archipelago
- Malaya (disambiguation)
- Malaysia–Thailand border
- Tenasserim Hills