Transport in Singapore facts for kids
Singapore is a small island country, and getting around is mostly done by land. You can reach many parts of Singapore, including islands like Sentosa and Jurong Island, by road. Another main way to travel is by train: the MRT covers most of Singapore, and the LRT runs within some neighborhoods. If you want to visit other islands from the main island, you can take a ferry.
Singapore is also a big connection point for the rest of the world. Two bridges link Singapore to Malaysia: the Causeway and the Second Link. The Singapore Changi Airport is a very important airport in Asia, and Singapore is a major port where goods are transferred between ships.
Contents
Public Transport in Singapore
Singapore has one of the best public transport systems in the world. This system includes buses, trains, and taxis.
How Public Transport Works
The Land Transport Authority (LTA) manages Singapore's public transport. They make sure buses, trains, and taxis run smoothly. An independent group, the Public Transport Council, sets the fares and bus service rules. Another group, TransitLink, helps make sure all parts of the system work together. This means you can use one payment method, like the EZ-Link card, for buses and trains.
The LTA wants people to use public transport more often. This helps reduce traffic and air pollution. Singapore has a big train system called the MRT and a smaller one called the LRT. Most buses have air conditioning because Singapore is hot and humid. You can pay for bus and MRT rides with cash or a special card called the EZ-Link card.
Travel Times
On a weekday, people in Singapore spend about 84 minutes using public transport to get to and from work. About 25% of riders travel for more than 2 hours every day. The average wait time at a bus stop or train station is 12 minutes. Some people wait for over 20 minutes daily. A single trip on public transport is usually about 7.3 kilometers long.
Tourist Pass for Easy Travel
If you're a tourist visiting Singapore, you can get a Singapore Tourist Pass. This pass lets you travel as much as you want on buses and trains. It costs S$10 for one day or S$20 for three days, plus a S$10 deposit. You can buy it at some MRT stations.
Train Transport
Mass Rapid Transit (MRT)
Singapore's public transport used to be mostly buses. But the first part of the MRT opened in 1987. Even though more people ride buses daily, the Land Transport Authority plans to make the train system even bigger. Eventually, buses will mainly help people get to and from train stations.
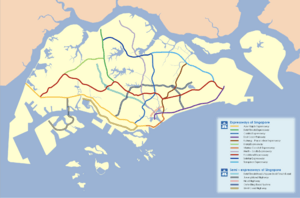
The MRT network has five main lines. It covers about 198.6 kilometers and has 119 stations. The North South Line, East West Line, and Circle Line are run by SMRT Trains. The North East Line and Downtown Line are run by SBS Transit.
Light Rail Transit (LRT)
Light rail trains, or LRTs, help connect people from their neighborhoods to the main MRT stations. The first LRT line opened in Bukit Panjang in 1999. It connects to the Choa Chu Kang MRT station. Later, similar LRT systems opened in Sengkang and Punggol. These are run by SBS Transit.
Other Train Systems
Singapore also has other special train systems. The Sentosa Express is a monorail that takes people around Sentosa island. It opened in 2006. The Changi Skytrain moves passengers between the different terminals at Singapore Changi Airport. It was updated in 2006.
Road Transport
Buses
Buses are a very common way to travel in Singapore. They cover routes all over the island.
Taxis and Ride-Hailing Services
Taxis are a popular way to get around Singapore. Their fares are usually lower than in many other developed countries. In December 2014, there were over 28,000 taxis in Singapore. You can flag down a taxi almost anywhere outside the city center. However, many people now use ride-hailing apps like Uber and Grab, which has changed how often taxis are used.
Air Transport
Singapore has six local airlines that fly from Singapore Changi Airport. They offer flights to over 70 cities on six continents. Singapore Airlines is the national airline. Its smaller airlines, SilkAir and Scoot, also fly from Changi Airport.
Some of Singapore's airlines are:
- Jetstar Asia Airways (started in 2004)
- Scoot (started in 2011)
- SilkAir (started in 1976)
- Singapore Airlines (started in 1937)
- Tigerair (started in 2003, later joined with Scoot)
Cable Car Transport
Singapore Cable Car

The Singapore Cable Car is another way to get to Sentosa island. It goes from Mount Faber on the main island to the resort island. The cable car system was updated in 2010.
Water Transport
On the main island, you can take a River Taxi along the Singapore River. This service started in 2013. There are also daily ferry services from Marina South Pier to the Southern Islands, like Kusu Island.
You can also take ferries from Singapore to the Indonesian Riau Islands, such as Batam and Bintan. These ferries leave from Tanah Merah and HarbourFront Ferry Terminals.
Transport Infrastructure
Airports
Singapore wants to be a major aviation hub in Asia. The Civil Aviation Authority of Singapore manages the aviation industry.
Singapore Changi Airport is one of the most important airports in the region. It has four terminals and connects to 185 cities in 58 countries. With its third terminal, Changi can handle 64 million passengers each year.
Seletar Airport is Singapore's first airport. Today, it is mainly used for private flights. It also has some flights to Malaysian islands like Tioman Island.
Ports and Harbours
You can find boats and ferry services to nearby islands in Malaysia and Indonesia. These services are available at various ferry terminals like Changi Ferry Terminal and Singapore Cruise Centre.
The Port of Singapore is one of the busiest ports in the world. It handles a huge amount of shipping. In 2004, it handled over 1 billion tons of shipping for the first time. Singapore is also the world's busiest place for transferring goods between ships. It is also the largest place for refueling ships. In 2007, the Port of Singapore was named the world's busiest port. It is also known as the Best Seaport in Asia.
Railways
Malaysian Railway
There is a train line that connects Singapore to the Malaysian rail network. Since 2011, the Woodlands Train Checkpoint has been the end point for these Malaysian trains in Singapore. Two new train links are being planned: a high-speed rail line to Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, and a shorter train system between Woodlands North and Johor Bahru, Malaysia.
MRT Lines
MRT trains travel through tunnels and on raised tracks along these lines:
- North South MRT Line (SMRT)
- East West MRT Line (SMRT)
- North East MRT Line (SBS Transit)
- Circle MRT Line (SMRT)
- Downtown MRT Line (SBS Transit)
LRT Lines
LRT trains run on raised tracks along these lines:
- Bukit Panjang LRT Line (SMRT)
- Sengkang LRT Line (SBS Transit)
- Punggol LRT Line (SBS Transit)
Causeway and Link Bridge
Singapore has two land connections to Malaysia. The Johor-Singapore Causeway was built in the 1920s. It connects Johor Bahru in Malaysia to Woodlands in Singapore and has both a road and a railway line. The Tuas Second Link is another bridge further west. It was finished in 1996 and connects Tuas in Singapore to Tanjung Kupang in Malaysia.
Roads and Expressways
Singapore was one of the first places to use tolls on roads to enter busy city areas. This system is now called Electronic Road Pricing.
Singapore has:
- 161 kilometers of expressways (main highways)
- 645 kilometers of major roads
- 557 kilometers of collector roads
- 2048 kilometers of local roads (as of 2011)
Traffic in Singapore drives on the left side of the road, which is common in Commonwealth countries.
Some of Singapore's expressways are:
- Ayer Rajah Expressway (AYE)
- Bukit Timah Expressway (BKE)
- Central Expressway (CTE)
- East Coast Parkway (ECP)
- Marina Coastal Expressway (MCE)
- Kallang–Paya Lebar Expressway (KPE)
- Kranji Expressway (KJE)
- Pan Island Expressway (PIE)
- Seletar Expressway (SLE)
- Tampines Expressway (TPE)
Expressways became important in Singapore after it gained independence. They helped reduce traffic congestion in the city center. They also made it easier for people living in new towns outside the city to travel to their workplaces in the city.
Images for kids
-
Singapore Airlines was the first airline to use the Airbus A380.
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |