Ontario, California facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Ontario, California
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Clockwise: Ovitt Family Community Library; Empire Towers; Ontario Convention Center; Chaffey High School
|
|||||
|
|||||
| Motto(s):
Southern California's Next Urban Center
|
|||||
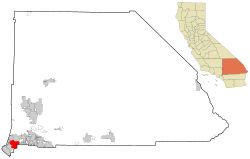
Location in San Bernardino County in California
|
|||||
| Country | United States | ||||
| State | California | ||||
| County | San Bernardino | ||||
| Incorporated | December 10, 1891 | ||||
| Named for | Ontario, Canada | ||||
| Government | |||||
| • Type | City Council / City Manager | ||||
| Area | |||||
| • Total | 50.00 sq mi (129.50 km2) | ||||
| • Land | 49.97 sq mi (129.43 km2) | ||||
| • Water | 0.03 sq mi (0.08 km2) 0.13% | ||||
| Elevation | 1,004 ft (306 m) | ||||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||||
| • Total | 175,265 | ||||
| • Rank | 3rd in San Bernardino County 25th in California 144th in the United States |
||||
| • Density | 3,507/sq mi (1,354.1/km2) | ||||
| Time zone | UTC−8 (Pacific) | ||||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−7 (PDT) | ||||
| ZIP codes |
91758, 91761, 91762, 91764
|
||||
| Area code | 909 | ||||
| FIPS code | 06-53896 | ||||
| GNIS feature IDs | 1652764, 2411323 | ||||
Ontario is a city in San Bernardino County, California. It is about 35 miles east of downtown Los Angeles. The city is part of the Greater Los Angeles Area. In 2020, about 175,265 people lived here.
Ontario is home to the Ontario International Airport. This airport is very busy, especially for cargo. It helps move a lot of goods from the ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach to other parts of the country.
The city got its name from the province of Ontario in Canada. Canadian engineer George Chaffey and his brothers started the "Ontario Model Colony" here in 1882.
Contents
Discovering Ontario's Past
Early History: The Tongva People
For over 1,000 years, the Tongva people lived in the area now known as Ontario. Their land was called Tovaangar. The Ontario area was connected to a village called Cucamonga.
In 1769, the Spanish Empire's Portolá expedition explored this region. They named the Santa Ana River.
Spanish and Mexican Rule (1771–1847)
In 1771, Spanish missionaries from New Spain built Mission San Gabriel Arcángel nearby. This mission is now in San Gabriel. The Tongva people were forced to work for the mission.

Explorer Juan Bautista de Anza traveled through this area in 1774. He created a land route between Sonora and San Gabriel. Today, an Ontario city park and a middle school are named after him. This route became known as the El Camino Real.
In 1822, Mexico won its independence from Spain. The lands in California, including Ontario, then became part of Mexico.
In 1826, American explorer Jedediah Smith passed through what is now Upland. This was part of the first known trip across North America from east to west. He used Native American trails that later became the California Trail. This route is now Foothill Boulevard.
In 1839, the Mexican government gave the Rancho Cucamonga land to Tiburcio Tapia. This act also freed the Tongva people who had been working there.
Becoming Part of the United States (1847 Onward)
The 1800s: A New Beginning
In 1847, the United States took control of California after the Mexican–American War. California became a state in 1850. San Bernardino County was created in 1853.
In 1881, the Chaffey brothers, George and William, bought land from Rancho Cucamonga. They also bought rights to water from Mount San Antonio. They named their new settlement "Ontario" after their home province in Canada.
The Chaffey brothers built a clever water system. It channeled water from the mountains to the farms below. This helped farmers water their crops and prevented floods. They also created Euclid Avenue, a wide street with a grassy middle section.
The San Antonio Water Company started in 1882. It still provides water to Ontario and nearby areas today.
In 1885, the Chaffey brothers opened a branch of the University of Southern California. This included a high school. The Ontario Record newspaper also began that year.
Ontario was planned as a "Model Colony." It aimed to balance farming with city comforts like schools and shops. It was also meant to be a "dry town," meaning no alcohol was allowed.
Many farmers came to Ontario to grow citrus fruits. People seeking a drier climate for health reasons also moved here. To show off the water supply, a fountain was placed at the train station. It was turned on when trains arrived and turned off when they left! The original fountain was later replaced by the "Frankish Fountain," which is now at the Ontario Museum of History and Art.
The Chaffey brothers left in 1886. They sold their Ontario properties to the Ontario Land & Improvement Company. Central Ontario officially became a city in 1891.

The Graber Olive House was founded in 1894. It is the oldest operating olive packing business in the United States.
The 1900s: Growth and Change
Ontario's size grew a lot in 1900. Many European immigrants came to work in farming. Later, Filipinos and Japanese farm workers also arrived. Some even started their own plant nurseries.
In 1901, a new school, Chaffey College, opened. It offered both high school and college classes.
In 1906, the northern part of Ontario separated and became the city of Upland.
The city of Ontario opened the Ontario Municipal Airport in 1929. This is now the Ontario International Airport. It is the largest employer in the city.
From 1970 to 1980, the Ontario Motor Speedway hosted car races and music events like California Jam.
The Cardenas supermarket chain started in Ontario in 1981.
A Metrolink train station opened in Ontario in 1993. This connected Ontario to other parts of the Greater Los Angeles area.
The huge shopping mall Ontario Mills opened in 1996. It was built on the old Ontario Motor Speedway parking lot. In 1996, AMC Theatres opened a very large movie theater at Ontario Mills. Another big theater, Edwards Ontario Palace, opened nearby soon after.
The Ontario Convention Centre opened in 1997.
In 1999, a large farming area in southern Ontario was changed to allow homes and businesses. This area is now called Ontario Ranch.
The 2000s: Modern Ontario
The University of La Verne opened a law school campus in Ontario in 2001.
The Ontario Community Events Center opened in 2008. It hosts many professional sports teams.
In 2016, the headquarters of the Southern Baptist Convention's Gateway Seminary moved to Ontario.
Amazon opened its largest warehouse in the United States in Ontario in 2024.
Ontario's Geography and Climate
Ontario covers about 50 square miles. Most of this area is land, with a small amount of water.
Weather in Ontario
Ontario has a semi-arid climate. This means it has hot summers and mild winters. Strong Santa Ana Winds often blow through the area in autumn and winter. Temperatures can range from very hot (up to 118°F) to cool (down to 25°F).
| Climate data for Ontario, California (Ontario International Airport) (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1998–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 90 (32) |
90 (32) |
94 (34) |
101 (38) |
103 (39) |
112 (44) |
117 (47) |
112 (44) |
118 (48) |
107 (42) |
98 (37) |
87 (31) |
118 (48) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 82.2 (27.9) |
82.9 (28.3) |
88.5 (31.4) |
94.1 (34.5) |
96.2 (35.7) |
101.4 (38.6) |
104.9 (40.5) |
106.0 (41.1) |
106.9 (41.6) |
98.9 (37.2) |
92.0 (33.3) |
80.7 (27.1) |
110.5 (43.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 67.7 (19.8) |
68.1 (20.1) |
71.7 (22.1) |
75.7 (24.3) |
79.8 (26.6) |
86.4 (30.2) |
93.8 (34.3) |
94.9 (34.9) |
91.3 (32.9) |
82.6 (28.1) |
74.7 (23.7) |
66.9 (19.4) |
79.5 (26.4) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 56.1 (13.4) |
57.1 (13.9) |
60.2 (15.7) |
63.4 (17.4) |
67.7 (19.8) |
73.2 (22.9) |
79.2 (26.2) |
80.1 (26.7) |
77.6 (25.3) |
69.8 (21.0) |
61.9 (16.6) |
55.2 (12.9) |
66.8 (19.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 44.6 (7.0) |
46.2 (7.9) |
48.7 (9.3) |
51.1 (10.6) |
55.6 (13.1) |
60.0 (15.6) |
64.7 (18.2) |
65.2 (18.4) |
63.8 (17.7) |
57.1 (13.9) |
49.0 (9.4) |
43.6 (6.4) |
54.1 (12.3) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 33.9 (1.1) |
35.0 (1.7) |
39.2 (4.0) |
44.0 (6.7) |
48.5 (9.2) |
54.9 (12.7) |
59.3 (15.2) |
59.7 (15.4) |
55.9 (13.3) |
48.4 (9.1) |
39.3 (4.1) |
33.1 (0.6) |
31.3 (−0.4) |
| Record low °F (°C) | 25 (−4) |
29 (−2) |
33 (1) |
33 (1) |
42 (6) |
46 (8) |
56 (13) |
56 (13) |
51 (11) |
41 (5) |
32 (0) |
28 (−2) |
25 (−4) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 2.57 (65) |
3.07 (78) |
1.64 (42) |
0.76 (19) |
0.30 (7.6) |
0.02 (0.51) |
0.05 (1.3) |
0.03 (0.76) |
0.10 (2.5) |
0.41 (10) |
0.80 (20) |
1.89 (48) |
11.64 (296) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 5.1 | 6.4 | 5.3 | 3.6 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 2.2 | 3.7 | 5.6 | 35.5 |
| Source: NOAA (mean maxima/minima 2006–2020) | |||||||||||||
People of Ontario: Demographics
Ontario is a diverse city. Many people have roots in Mexico, making it the most common country of origin after the United States. Other common origins include the Philippines, El Salvador, Guatemala, and Vietnam.
The most spoken languages in Ontario, besides English, are Spanish, Vietnamese, and Chinese. The most common religion is Roman Catholicism.
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1890 | 683 | — | |
| 1900 | 722 | 5.7% | |
| 1910 | 4,274 | 492.0% | |
| 1920 | 7,280 | 70.3% | |
| 1930 | 13,583 | 86.6% | |
| 1940 | 14,197 | 4.5% | |
| 1950 | 22,872 | 61.1% | |
| 1960 | 46,617 | 103.8% | |
| 1970 | 64,118 | 37.5% | |
| 1980 | 88,820 | 38.5% | |
| 1990 | 133,179 | 49.9% | |
| 2000 | 158,007 | 18.6% | |
| 2010 | 163,924 | 3.7% | |
| 2020 | 175,265 | 6.9% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census | |||
In 2020, Ontario's population was 175,265. About 68% of the people identified as Hispanic or Latino.
Ontario's Economy
When Ontario was first founded, its economy was based on being a health resort. Soon after, farmers started growing lemons and oranges. Vintners (wine makers) and olive growers also came to the area. The Graber Olive House is a historic landmark that still produces olives today.
Dairy farming is also important, similar to nearby Chino. Parts of southern Ontario still have dairy and other farms. However, this area is being planned for new homes, businesses, and parks. This new development is called Ontario Ranch.
Before World War II, General Electric had a factory in Ontario that made clothing irons. After the war, many people moved to Ontario as the defense industry grew in Southern California. The Ontario International Airport was used for pilot training.
Today, Ontario still has some manufacturing, like Maglite flashlights. But the economy is now mostly about services and warehousing. Large companies like AutoZone and Nordstrom have major distribution centers here.
Other companies based in Ontario include Niagara Bottling, The Icee Company, and Phoenix Motorcars.
Top Employers in Ontario
Here are some of the biggest employers in Ontario:
| # | Employer | # of employees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ontario International Airport | 5,000–9,999 |
| 2 | United Parcel Service (UPS) | 5,000–9,999 |
| 3 | Workforce Personnel, Inc | 5,000–9,999 |
| 4 | Chaffey Union High School | 1,000-4,999 |
| 5 | City of Ontario | 1,000-4,999 |
| 6 | Ontario-Montclair School District | 1,000-4,999 |
| 7 | Primary Care Assoc Med Group | 1,000-4,999 |
| 8 | FedEx | 500-999 |
| 9 | The Home Depot | 500-999 |
| 10 | QVC, Inc | 500–999 |
Tourism in Ontario
The Greater Ontario Convention and Visitors Bureau works to bring visitors to the area. They promote Ontario as a great place to visit and help the local economy.
Arts and Culture in Ontario
Ontario has three museums: the Ontario Museum of History and Art, the Chaffey Community Museum of Art, and the Ontario Police Museum.
The Granada Theatre was built in 1925. It was once part of the Fox West Coast Theater chain.
Ontario also hosts "Road to California," one of the largest quilt shows in the United States. It attracts over 40,000 visitors.
The Ontario post office has two large paintings by Nellie Geraldine Best from 1942. One shows the city's founder, George Chaffey, and the other shows the completed Euclid Avenue.
Since 1958, Ontario has displayed three-dimensional nativity scenes on Euclid Avenue during Christmas. These scenes are now supported by private organizations. To help fund them, the Ontario Chamber of Commerce started a craft fair called "Christmas on Euclid."
The All-States Picnic is an Independence Day celebration that began in 1939. It honored the many different places people in Ontario came from. Picnic tables were set up along Euclid Avenue, with signs for each state. The picnic was very popular, attracting 120,000 people in 1948. It stopped for a while but was brought back in 1991 to celebrate community pride.
Sports in Ontario
The Toyota Arena opened in 2008. It is a large arena with 11,000 seats. It hosts over 125 events each year, including sports games, concerts, and family shows.
The arena is home to the Ontario Reign, an ice hockey team in the American Hockey League. They are an affiliate of the Los Angeles Kings. The Reign have been very popular, leading their league in attendance for many years.
The Ontario Motor Speedway used to be in Ontario. It hosted many car races, including Formula One and NASCAR events. It was taken down in 1980.
| Club | League | Venue | Established | Championships |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Empire Strykers | MASL, Indoor soccer | Toyota Arena | 2013 | 0 |
| Ontario Reign | American Hockey League, Ice hockey | Toyota Arena | 2015 | 1 |
Education in Ontario
Ontario has several school districts, including Ontario/Montclair Elementary and Chaffey Joint Union. There are also private schools and two private military schools. The city has nine trade schools.
The University of La Verne College of Law is in downtown Ontario. Other universities like National University and Chapman University have campuses near the Ontario Mills mall. Gateway Seminary also has a campus in Ontario.
Ontario's Infrastructure
Transportation in Ontario
The Ontario International Airport offers flights for people and cargo. It is a major hub for companies like FedEx and UPS.
Several major freeways run through Ontario. Interstate 10 and State Route 60 go east-west. Interstate 15 runs north-south on the east side of the city. State Route 83, also known as Euclid Avenue, runs north-south on the west side.
The Amtrak station serves long-distance train lines. The Amtrak Thruway bus service also connects this station to other cities.
The Ontario-East Metrolink station connects Ontario to the Greater Los Angeles area and Orange County.
Omnitrans provides public bus transportation. A new bus rapid transit line, the sbX Purple Line, is also being built.
Cemeteries in Ontario
The Bellevue Memorial Park is located on West G Street. Notable people buried there include George Chaffey, one of the city's founders.
Shopping in Ontario
Ontario Mills is a very large shopping mall in Ontario. It is the biggest outlet mall in California. Cardenas, a supermarket chain focusing on Latin American cuisine, started and is based in Ontario.
Notable People from Ontario
Many interesting people have connections to Ontario:
- Hobie Alter – A pioneer in making surfboards and catamarans.
- Jeff Ayres – A basketball player who won an NBA championship.
- Rod Barajas – A Major League Baseball player.
- Beverly Cleary – A famous author who wrote many children's books.
- Landon Donovan – A well-known soccer player for the Los Angeles Galaxy and the US National Team.
- Prince Fielder – A baseball player for the Texas Rangers and Detroit Tigers.
- Anthony Muñoz – A football player in the Pro Football Hall of Fame.
- Mike Sweeney – A Major League Baseball player for the Kansas City Royals.
- Bobby Wagner – A football player who won a Super Bowl with the Seattle Seahawks.
- Frank Zappa – A famous musician.
Sister Cities
Ontario has five sister cities around the world:
 Brockville, Ontario, Canada (since 1977)
Brockville, Ontario, Canada (since 1977) Guamúchil, Sinaloa, Mexico (since 1982)
Guamúchil, Sinaloa, Mexico (since 1982) Mocorito, Sinaloa, Mexico (since 1982)
Mocorito, Sinaloa, Mexico (since 1982) Los Mochis, Sinaloa, Mexico (since 1988)
Los Mochis, Sinaloa, Mexico (since 1988) Winterthur, Canton of Zürich, Switzerland
Winterthur, Canton of Zürich, Switzerland Jieyang, China
Jieyang, China
See also
 In Spanish: Ontario (California) para niños
In Spanish: Ontario (California) para niños